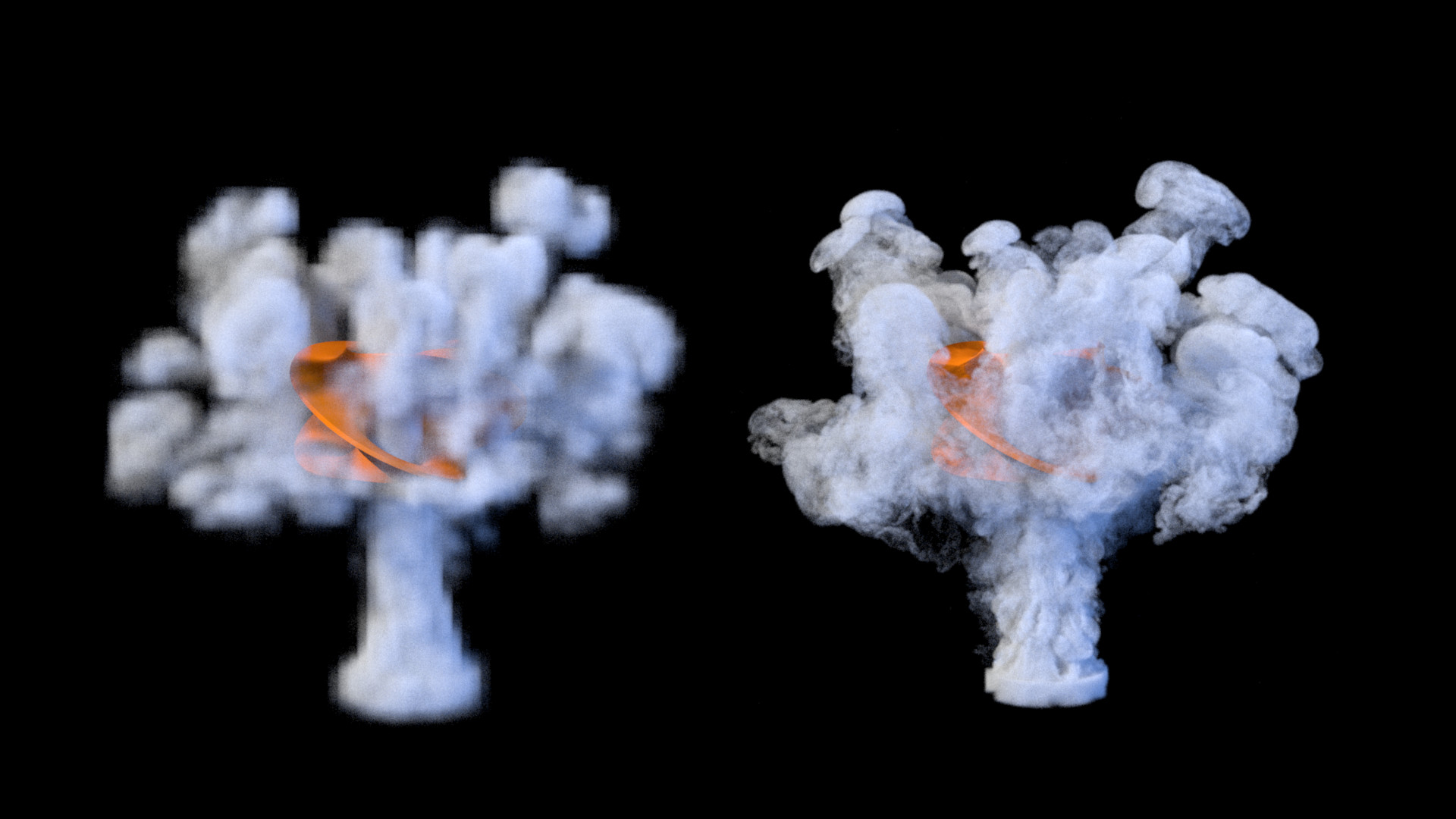
“Frequency-domain smoke guiding” by Forootaninia and Narain
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Frequency-domain smoke guiding
Session/Category Title: Animation: Fluid
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
We propose a simple and efficient method for guiding an Eulerian smoke simulation to match the behavior of a specified velocity field, such as a low-resolution animation of the same scene, while preserving the rich, turbulent details arising in the simulated fluid. Our method works by simply combining the high-frequency component of the simulated fluid velocity with the low-frequency component of the input guiding field. We show how to eliminate the grid-aligned artifacts that appear in naive guiding approaches, and provide a frequency-domain analysis that motivates the use of ideal low-pass and high-pass filters to prevent artificial dissipation of small-scale details. We demonstrate our method on many scenes including those with static and moving obstacles, and show that it produces high-quality results with very little computational overhead.
References:
1. Kai Bai, Wei Li, Mathieu Desbrun, and Xiaopei Liu. 2019. Dynamic Upsampling of Smoke through Dictionary-based Learning. arXiv:cs.GR/1910.09166Google Scholar
2. Jernej Barbič and Jovan Popović. 2008. Real-time control of physically based simulations using gentle forces. ACM transactions on graphics (TOG) 27, 5 (2008), 1–10.Google Scholar
3. Miklós Bergou, Saurabh Mathur, Max Wardetzky, and Eitan Grinspun. 2007. TRACKS: Toward Directable Thin Shells. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Papers (SIGGRAPH ’07). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 50. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. J.U. Brackbill and H.M. Ruppel. 1986. FLIP: A method for adaptively zoned, particle-in-cell calculations of fluid flows in two dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 65, 2 (1986), 314 — 343. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Robert Bridson. 2015. Fluid simulation for computer graphics. AK Peters/CRC Press.Google Scholar
6. Qiaodong Cui, Pradeep Sen, and Theodore Kim. 2018. Scalable Laplacian Eigenfluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 87 (July 2018), 12 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Tyler De Witt, Christian Lessig, and Eugene Fiume. 2012. Fluid Simulation Using Laplacian Eigenfunctions. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 1, Article 10 (Feb. 2012), 11 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Raanan Fattal and Dani Lischinski. 2004. Target-driven Smoke Animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug. 2004), 441–448. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. R. Huang and J. Keyser. 2013. Automated sampling and control of gaseous simulations. 29 (2013), 751–760. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Ruoguan Huang, Zeki Melek, and John Keyser. 2011. Preview-Based Sampling for Controlling Gaseous Simulations. In Proceedings of the 2011 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA âĂŹ11). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 177–186. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Tiffany Inglis, M-L Eckert, James Gregson, and Nils Thuerey. 2017. Primal-Dual Optimization for Fluids. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 36. Wiley Online Library, 354–368.Google Scholar
12. Chenfanfu Jiang, Craig Schroeder, Andrew Selle, Joseph Teran, and Alexey Stomakhin. 2015. The Affine Particle-in-Cell Method. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, Article 51 (July 2015), 10 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Theodore Kim, Nils Thürey, Doug James, and Markus Gross. 2008. Wavelet turbulence for fluid simulation. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 27. ACM, 50.Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Dan Koschier, Jan Bender, Barbara Solenthaler, and Matthias Teschner. 2019. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Techniques for the Physics Based Simulation of Fluids and Solids. In Eurographics 2019 – Tutorials, Wenzel Jakob and Enrico Puppo (Eds.). The Eurographics Association. Google ScholarCross Ref
15. Benjamin Long and Erik Reinhard. 2009. Real-time fluid simulation using discrete sine/cosine transforms. In Proceedings of the 2009 symposium on Interactive 3D graphics and games. ACM, 99–106.Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Pierre-Luc Manteaux, Ulysse Vimont, Chris Wojtan, Damien Rohmer, and Marie-Paule Cani. 2016. Space-time Sculpting of Liquid Animation. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Motion in Games (MIG ’16). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 61–71. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Antoine McNamara, Adrien Treuille, Zoran Popović, and Jos Stam. 2004. Fluid Control Using the Adjoint Method. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (Aug. 2004), 449–456. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Rahul Narain, Jonas Zehnder, and Bernhard Thomaszewski. 2019. A Second-Order Advection-Reflection Solver. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 2, 2, Article Article 16 (July 2019), 14 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Michael B. Nielsen and Robert Bridson. 2011. Guide Shapes for High Resolution Naturalistic Liquid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4, Article 83 (July 2011), 8 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Michael B Nielsen and Brian B Christensen. 2010. Improved variational guiding of smoke animations. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 29. Wiley Online Library, 705–712.Google Scholar
21. Michael B Nielsen, Brian B Christensen, Nafees Bin Zafar, Doug Roble, and Ken Museth. 2009. Guiding of smoke animations through variational coupling of simulations at different resolutions. In Proceedings of the 2009 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. ACM, 217–226.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Zherong Pan, Jin Huang, Yiying Tong, Changxi Zheng, and Hujun Bao. 2013. Interactive Localized Liquid Motion Editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6, Article 184 (Nov. 2013), 10 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Zherong Pan and Dinesh Manocha. 2017. Efficient Solver for Spacetime Control of Smoke. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 68a (July 2017). Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Nick Rasmussen, Douglas Enright, Duc Nguyen, Sebastian Marino, Nigel Sumner, Willi Geiger, Samir Hoon, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2004. Directable photorealistic liquids. In Proceedings of the 2004 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. 193–202.Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Karthik Raveendran, Nils Thuerey, Chris Wojtan, and Greg Turk. 2012. Controlling Liquids Using Meshes. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (SCA ’12). Eurographics Association, Goslar Germany, Germany, 255–264. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2422356.2422393Google Scholar
26. Syuhei Sato, Yoshinori Dobashi, Theodore Kim, and Tomoyuki Nishita. 2018. Example-based Turbulence Style Transfer. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 84 (July 2018), 9 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Andrew Selle, Ronald Fedkiw, Byungmoon Kim, Yingjie Liu, and Jarek Rossignac. 2008. An Unconditionally Stable MacCormack Method. J. Sci. Comput. 35, 2âĂŞ3 (June 2008), 350âĂŞ371. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Lin Shi and Yizhou Yu. 2005a. Controllable smoke animation with guiding objects. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 24, 1 (2005), 140–164.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Lin Shi and Yizhou Yu. 2005b. Taming liquids for rapidly changing targets. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. ACM, 229–236.Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Jos Stam. 2002. A Simple Fluid Solver Based on the FFT. J. Graph. Tools 6, 2 (Sept. 2002), 43âĂŞ52. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Alexey Stomakhin and Andrew Selle. 2017. Fluxed Animated Boundary Method. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article Article 68 (July 2017), 8 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Nils Thuerey, Theodore Kim, and Tobias Pfaff. 2013. Turbulent Fluids. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2013 Courses (SIGGRAPH ’13). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 6, 1 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Nils Thuerey and Tobias Pfaff. 2016. MantaFlow.(2016). URL http://mantaflow.com (2016).Google Scholar
34. Nils Thürey, Richard Keiser, Mark Pauly, and Ulrich Rüde. 2006. Detail-preserving fluid control. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation. Eurographics Association, 7–12.Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Adrien Treuille, Antoine McNamara, Zoran Popović, and Jos Stam. 2003. Keyframe control of smoke simulations. In ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 22. ACM, 716–723.Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Maximilian Werhahn, You Xie, Mengyu Chu, and Nils Thuerey. 2019. A Multi-Pass GAN for Fluid Flow Super-Resolution. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 2, 2, Article 10 (July 2019), 21 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
37. You Xie, Erik Franz, Mengyu Chu, and Nils Thuerey. 2018. tempoGAN: A Temporally Coherent, Volumetric GAN for Super-resolution Fluid Flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 95 (July 2018), 15 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Jonas Zehnder, Rahul Narain, and Bernhard Thomaszewski. 2018. An Advection-Reflection Solver for Detail-Preserving Fluid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 85 (July 2018), 8 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Yongning Zhu and Robert Bridson. 2005. Animating Sand as a Fluid. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3 (July 2005), 965âĂŞ972. Google ScholarDigital Library