“Learning an intrinsic garment space for interactive authoring of garment animation” by Wang, Shao, Fu and Mitra
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Learning an intrinsic garment space for interactive authoring of garment animation
Session/Category Title: Looking & Sounding Great
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
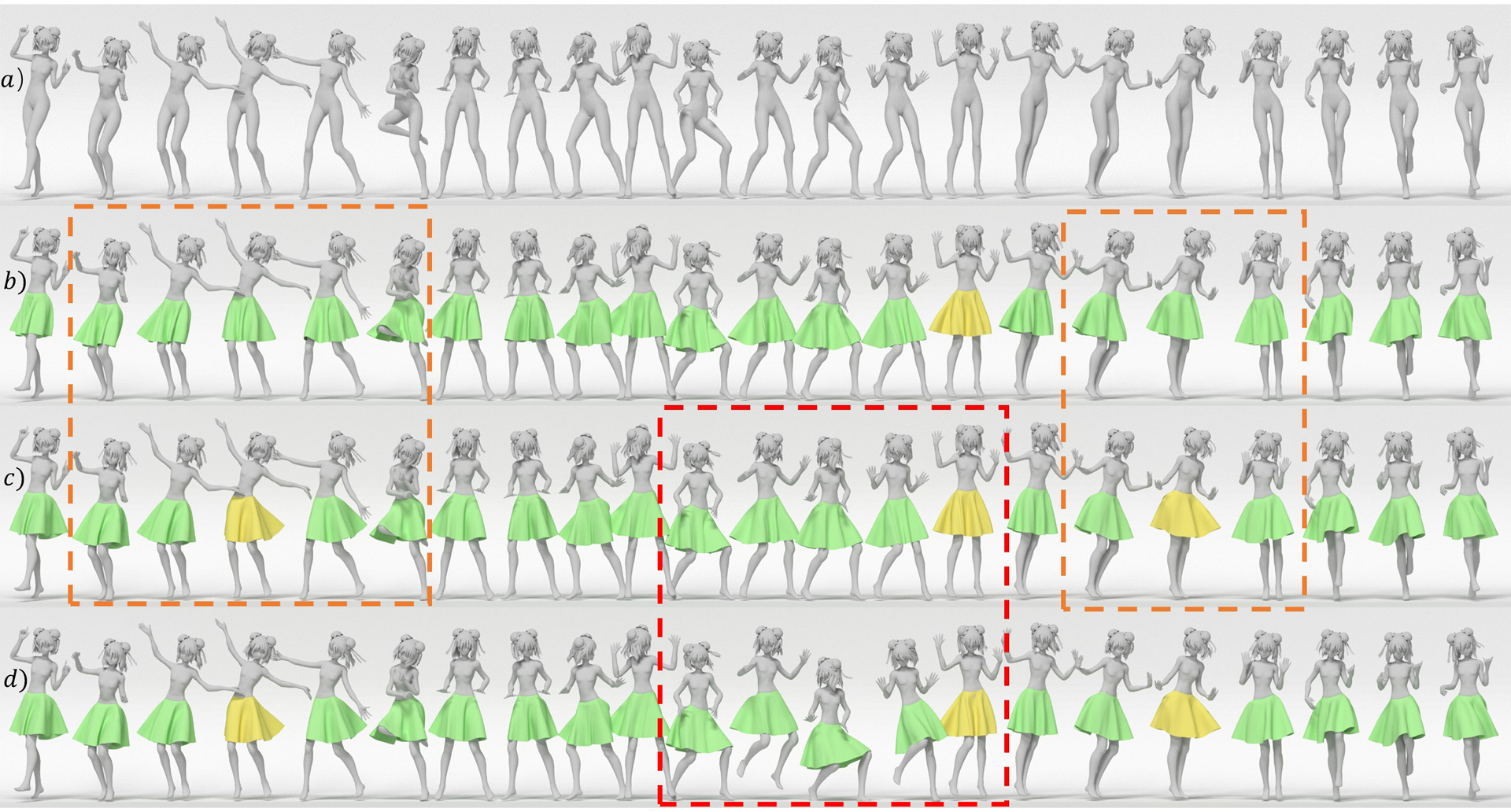
Authoring dynamic garment shapes for character animation on body motion is one of the fundamental steps in the CG industry. Established workflows are either time and labor consuming (i.e., manual editing on dense frames with controllers), or lack keyframe-level control (i.e., physically-based simulation). Not surprisingly, garment authoring remains a bottleneck in many production pipelines. Instead, we present a deep-learning-based approach for semi-automatic authoring of garment animation, wherein the user provides the desired garment shape in a selection of keyframes, while our system infers a latent representation for its motion-independent intrinsic parameters (e.g., gravity, cloth materials, etc.). Given new character motions, the latent representation allows to automatically generate a plausible garment animation at interactive rates. Having factored out character motion, the learned intrinsic garment space enables smooth transition between keyframes on a new motion sequence. Technically, we learn an intrinsic garment space with an motion-driven autoencoder network, where the encoder maps the garment shapes to the intrinsic space under the condition of body motions, while the decoder acts as a differentiable simulator to generate garment shapes according to changes in character body motion and intrinsic parameters. We evaluate our approach qualitatively and quantitatively on common garment types. Experiments demonstrate our system can significantly improve current garment authoring workflows via an interactive user interface. Compared with the standard CG pipeline, our system significantly reduces the ratio of required keyframes from 20% to 1 — 2%.
References:
1. Autodesk Inc. 2015. Maya QUALOTH. http://www.qualoth.com/. (2015).Google Scholar
2. David Baraff and Andrew Witkin. 1998. Large Steps in Cloth Simulation. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’98). 43–54.Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Derek Bradley, Tiberiu Popa, Alla Sheffer, Wolfgang Heidrich, and Tamy Boubekeur. 2008. Markerless Garment Capture. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3 (Aug. 2008), 99:1–99:9.Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Edilson de Aguiar, Leonid Sigal, Adrien Treuille, and Jessica K. Hodgins. 2010. Stable Spaces for Real-time Clothing. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4 (July 2010), 106:1–106:9.Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Charles Dugas, Yoshua Bengio, François Bélisle, Claude Nadeau, and René Garcia. 2001. Incorporating second-order functional knowledge for better option pricing. In Advances in neural information processing systems. 472–478.Google Scholar
6. Katerina Fragkiadaki, Sergey Levine, Panna Felsen, and Jitendra Malik. 2015. Recurrent Network Models for Human Dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) (ICCV ’15). 4346–4354.Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Lawson Fulton, Vismay Modi, David Duvenaud, David I. W. Levin, and Alec Jacobson. 2019. Latent-space Dynamics for Reduced Deformable Simulation. Computer Graphics Forum (2019).Google Scholar
8. Rony Goldenthal, David Harmon, Raanan Fattal, Michel Bercovier, and Eitan Grinspun. 2007. Efficient Simulation of Inextensible Cloth. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3 (July 2007), 49:1–49:7.Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Peng Guan, Loretta Reiss, David A. Hirshberg, Alexander Weiss, and Michael J. Black. 2012. DRAPE: DRessing Any PErson. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4 (July 2012), 35:1–35:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Fabian Hahn, Bernhard Thomaszewski, Stelian Coros, Robert W. Sumner, Forrester Cole, Mark Meyer, Tony DeRose, and Markus Gross. 2014. Subspace Clothing Simulation Using Adaptive Bases. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July 2014), 105:1–105:9.Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. 2015. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 1026–1034.Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Daniel Holden, Taku Komura, and Jun Saito. 2017. Phase-functioned neural networks for character control. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 42.Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Daniel Holden, Jun Saito, and Taku Komura. 2016. A Deep Learning Framework for Character Motion Synthesis and Editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 4, Article 138 (July 2016), 138:1–138:11 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Ladislav Kavan, Steven Collins, Jiří Žára, and Carol O’Sullivan. 2007. Skinning with Dual Quaternions. In Proceedings of the 2007 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games (I3D ’07). 39–46.Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Ladislav Kavan, Dan Gerszewski, Adam W. Bargteil, and Peter-Pike Sloan. 2011. Physics-inspired Upsampling for Cloth Simulation in Games. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (July 2011), 93:1–93:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Ladislav Kavan and Jiří Žára. 2005. Spherical Blend Skinning: A Real-time Deformation of Articulated Models. In Proceedings of the 2005 Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games (I3D ’05). 9–16.Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Doyub Kim, Woojong Koh, Rahul Narain, Kayvon Fatahalian, Adrien Treuille, and James F. O’Brien. 2013. Near-exhaustive Precomputation of Secondary Cloth Effects. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (July 2013), 87:1–87:8.Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Alex Krizhevsky and Geoff Hinton. 2010. Convolutional deep belief networks on cifar-10. Unpublished manuscript 40, 7 (2010).Google Scholar
19. Zorah Lahner, Daniel Cremers, and Tony Tung. 2018. DeepWrinkles: Accurate and Realistic Clothing Modeling. In The European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV).Google Scholar
20. Kyungho Lee, Seyoung Lee, and Jehee Lee. 2018. Interactive Character Animation by Learning Multi-objective Control. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 6, Article 180 (Dec. 2018), 10 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Tiantian Liu, Adam W. Bargteil, James F. O’Brien, and Ladislav Kavan. 2013. Fast Simulation of Mass-spring Systems. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6 (Nov. 2013), 214:1–214:7.Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Ian Mason, Sebastian Starke, He Zhang, Hakan Bilen, and Taku Komura. 2018. Few-shot Learning of Homogeneous Human Locomotion Styles. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37. Wiley Online Library, 143–153.Google Scholar
23. Rahul Narain, Armin Samii, and James F. O’Brien. 2012. Adaptive Anisotropic Remeshing for Cloth Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6 (Nov. 2012), 152:1–152:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Gerard Pons-Moll, Sergi Pujades, Sonny Hu, and Michael J. Black. 2017. ClothCap: Seamless 4D Clothing Capture and Retargeting. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (July 2017), 73:1–73:15.Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Tiberiu Popa, Q Zhou, Derek Bradley, V Kraevoy, Hongbo Fu, Alla Sheffer, and W Heidrich. 2009. Wrinkling Captured Garments Using Space-Time Data-Driven Deformation. Computer Graphics Forum 28 (03 2009), 427 — 435.Google Scholar
26. Igor Santesteban, Miguel A. Otaduy, and Dan Casas. 2019. Learning-Based Animation of Clothing for Virtual Try-On. Computer Graphics Forum 38, 2 (2019).Google Scholar
27. Leonid Sigal, Moshe Mahler, Spencer Diaz, Kyna McIntosh, Elizabeth Carter, Timothy Richards, and Jessica Hodgins. 2015. A perceptual control space for garment simulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4 (2015), 117.Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Rasmus Tamstorf, Toby Jones, and Stephen F. McCormick. 2015. Smoothed Aggregation Multigrid for Cloth Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6 (Oct. 2015), 245:1–245:13.Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Min Tang, Tongtong Wang, Zhongyuan Liu, Ruofeng Tong, and Dinesh Manocha. 2018. I-cloth: Incremental Collision Handling for GPU-based Interactive Cloth Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 6 (Dec. 2018), 204:1–204:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Gabriel Taubin. 1995. A signal processing approach to fair surface design. In Proceedings of the 22nd annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. ACM, 351–358.Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Nobuyuki Umetani. 2017. Exploring generative 3D shapes using autoencoder networks. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2017 Technical Briefs. ACM, 24.Google Scholar
32. Huamin Wang, Florian Hecht, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and James F. O’Brien. 2010. Example-based Wrinkle Synthesis for Clothing Animation. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2010 Papers (SIGGRAPH ’10). 107:1–107:8.Google Scholar
33. Huamin Wang and Yin Yang. 2016. Descent Methods for Elastic Body Simulation on the GPU. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 6 (Nov. 2016), 212:1–212:10.Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Tuanfeng Y. Wang, Duygu Ceylan, Jovan Popović, and Niloy J. Mitra. 2018. Learning a Shared Shape Space for Multimodal Garment Design. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 6, Article 203 (Dec. 2018), 13 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Nicholas J. Weidner, Kyle Piddington, David I. W. Levin, and Shinjiro Sueda. 2018. Eulerian-on-lagrangian Cloth Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4 (July 2018), 50:1–50:11.Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Ryan White, Keenan Crane, and D. A. Forsyth. 2007. Capturing and Animating Occluded Cloth. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3, Article 34 (July 2007).Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Wikipedia contributors. 2019. MikuMikuDance. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MikuMikuDance. (2019). [Online; accessed 7-May-2019].Google Scholar
38. Weiwei Xu, Nobuyuki Umentani, Qianwen Chao, Jie Mao, Xiaogang Jin, and Xin Tong.Google Scholar
39. 2014. Sensitivity-optimized Rigging for Example-based Real-time Clothing Synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July 2014), 107:1–107:11.Google Scholar
40. Jinlong Yang, Jean-Sébastien Franco, Franck Hétroy-Wheeler, and Stefanie Wuhrer. 2018. Analyzing clothing layer deformation statistics of 3d human motions. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). 237–253.Google ScholarDigital Library
41. He Zhang, Sebastian Starke, Taku Komura, and Jun Saito. 2018. Mode-adaptive Neural Networks for Quadruped Motion Control. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 145 (July 2018), 145:1–145:11 pages.Google ScholarDigital Library