“Jump: virtual reality video”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Jump: virtual reality video
Session/Category Title:
- Video
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
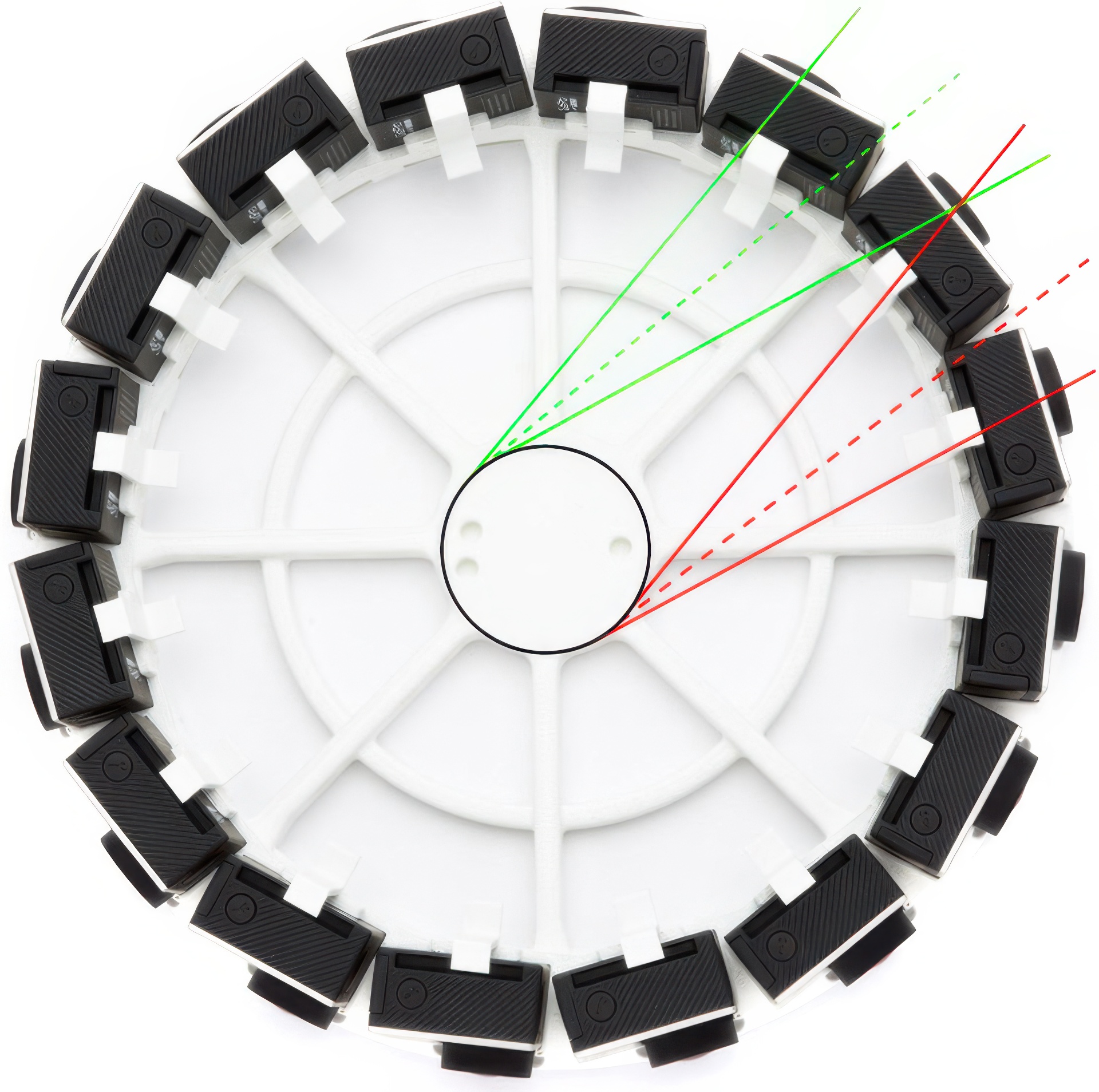
We present Jump, a practical system for capturing high resolution, omnidirectional stereo (ODS) video suitable for wide scale consumption in currently available virtual reality (VR) headsets. Our system consists of a video camera built using off-the-shelf components and a fully automatic stitching pipeline capable of capturing video content in the ODS format. We have discovered and analyzed the distortions inherent to ODS when used for VR display as well as those introduced by our capture method and show that they are small enough to make this approach suitable for capturing a wide variety of scenes. Our stitching algorithm produces robust results by reducing the problem to one of pairwise image interpolation followed by compositing. We introduce novel optical flow and compositing methods designed specifically for this task. Our algorithm is temporally coherent and efficient, is currently running at scale on a distributed computing platform, and is capable of processing hours of footage each day.
References:
1. Aydin, T. O., Stefanoski, N., Croci, S., Gross, M., and Smolic, A. 2014. Temporally coherent local tone mapping of hdr video. TOG.
2. Baker, S., Scharstein, D., Lewis, J. P., Roth, S., Black, M. J., and Szeliski, R. 2011. A database and evaluation methodology for optical flow. IJCV.
3. Baran, I., Schmid, J., Siegrist, T., Gross, M., and Sumner, R. W. 2011. Mixed-order compositing for 3d paintings. TOG.
4. Barron, J. T., and Poole, B. 2016. The fast bilateral solver. ECCV.
5. Brox, T., and Malik, J. 2011. Large displacement optical flow: Descriptor matching in variational motion estimation. TPAMI.
6. Carranza, J., Theobalt, C., Magnor, M. A., and Seidel, H.-P. 2003. Free-viewpoint video of human actors. TOG.
7. Collet, A., Chuang, M., Sweeney, P., Gillett, D., Evseev, D., Calabrese, D., Hoppe, H., Kirk, A., and Sullivan, S. 2015. High-quality streamable free-viewpoint video. TOG.
8. Couture, V., Langer, M. S., and Roy, S. 2010. Analysis of disparity distortions in omnistereoscopic displays. ACM Transactions on Applied Perception (TAP).
9. Couture, V., Langer, M. S., and Roy, S. 2011. Panoramic stereo video textures. ICCV.
10. Dodgson, N. A. 2004. Variation and extrema of human inter-pupillary distance. SPIE: Stereoscopic Displays and Applications, 3646.
11. Gluckman, J., Nayar, S. K., and Thoresz, K. J. 1998. Real-time omnidirectional and panoramic stereo. Proc. of Image Understanding Workshop.
12. Google, 2014. Google Cardboard. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Google Cardboard.
13. Gross, M., and Pfister, H. 2007. Point-Based Graphics. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
14. Hartley, R., and Zisserman, A. 2003. Multiple view geometry in computer vision. Cambridge university press.
15. Hasinoff, S. W., Sharlet, D., Geiss, R., Adams, A., Barron, J. T., Kainz, F., Chen, J., and Levoy, M. 2016. Burst photography for high dynamic range and low-light imaging on mobile cameras. SIGGRAPH Asia.
16. Horn, B. K. P., and Schunk, B. G. 1981. Determining optical flow. Artificial Intelligence.
17. Ishiguro, H., Yamamoto, M., and Tsuji, S. 1990. Omni-directional stereo for making global map. ICCV.
18. Jarabo, A., Masia, B., Bousseau, A., Pellacini, F., and Gutierrez, D. 2014. How do people edit light fields? SIGGRAPH.
19. Koppal, S. J., Zitnick, C. L., Cohen, M. F., Kang, S. B., Ressler, B., and Colburn, A. 2010. A viewer-centric editor for 3d movies. Computer Graphics and Applications.
20. Krähenbühl, P., and Koltun, V. 2012. Efficient nonlocal regularization for optical flow. ECCV.
21. Kroeger, T., Timofte, R., Dai, D., and Gool, L. J. V. 2016. Fast optical flow using dense inverse search. ECCV.
22. Lang, M., Wang, O., Aydin, T., Smolic, A., and Gross, M. 2012. Practical temporal consistency for image-based graphics applications. SIGGRAPH.
23. Levoy, M., and Hanrahan, P. 1996. Light field rendering. CGIT.
24. Lewis, J. 1995. Fast normalized cross-correlation. Vision interface.
25. Liu, C., Yuen, J., and Torralba, A. 2011. Sift flow: Dense correspondence across scenes and its applications. TPAMI.
26. Lucas, B. D., and Kanade, T. 1981. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. IJCAI.
27. Meka, A., Zollhoefer, M., Richardt, C., and Theobalt, C. 2016. Live intrinsic video. SIGGRAPH.
28. Menze, M., and Geiger, A. 2015. Object scene flow for autonomous vehicles. CVPR.
29. Peleg, S., Ben-Ezra, M., and Pritch, Y. 2001. Omnistereo: Panoramic stereo imaging. TPAMI.
30. Porter, T., and Duff, T. 1984. Compositing digital images. SIGGRAPH.
31. Pulli, K., Hoppe, H., Cohen, M., Shapiro, L., Duchamp, T., and Stuetzle, W. 1997. View-based rendering: Visualizing real objects from scanned range and color data. Proc. Eurographics Workshop on Rendering.
32. Qin, D., Takamatsu, M., and Nakashima, Y. 2004. Measurement for the panum’s fusional area in retinal fovea using a three-dimension display device. Journal of Light & Visual Environment. Cross Ref
33. Ragan-Kelley, J., Adams, A., Paris, S., Levoy, M., Ama-rasinghe, S., and Durand, F. 2012. Decoupling algorithms from schedules for easy optimization of image processing pipelines. SIGGRAPH.
34. Rav-Acha, A., Engel, G., and Peleg, S. 2008. Minimal aspect distortion (mad) mosaicing of long scenes. IJCV.
35. Revaud, J., Weinzaepfel, P., Harchaoui, Z., and Schmid, C. 2015. EpicFlow: Edge-Preserving Interpolation of Correspondences for Optical Flow. CVPR.
36. Richardt, C., Pritch, Y., Zimmer, H., and Sorkine-Hornung, A. 2013. Megastereo: Constructing high-resolution stereo panoramas. CVPR.
37. Samsung, 2015. Samsung Gear VR. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Samsung_Gear_VR.
38. Shimamura, J., Yokoya, N., Takemura, H., and Yamazawa, K. 2000. Construction of an immersive mixed environment using an omnidirectional stereo image sensor. Workshop on Omnidirectional Vision.
39. Shum, H.-Y., and He, L.-W. 1999. Rendering with concentric mosaics. CGIT.
40. Smolic, A. 2011. 3d video and free viewpoint videofrom capture to display. Pattern recognition.
41. Tanaka, K., and Tachi, S. 2005. Tornado: Omnistereo video imaging with rotating optics. TVCG.
42. Weissig, C., Schreer, O., Eisert, P., and Kauff, P. 2012. The ultimate immersive experience: panoramic 3D video acquisition. Springer.
43. Wilburn, B., Joshi, N., Vaish, V., Talvala, E.-V., Antunez, E., Barth, A., Adams, A., Horowitz, M., and Levoy, M. 2005. High performance imaging using large camera arrays. TOG.
44. Yang, J. C., Everett, M., Buehler, C., and McMillan, L. 2002. A real-time distributed light field camera. Rendering Techniques 2002.
45. Zitnick, C. L., Kang, S. B., Uyttendaele, M., Winder, S., and Szeliski, R. 2004. High-quality video view interpolation using a layered representation. TOG.
46. Zwicker, M., Pfister, H., van Baar, J., and Gross, M. 2001. Surface splatting. CGIT.