“Functionality preserving shape style transfer” by Lun, Kalogerakis, Wang and Sheffer
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Functionality preserving shape style transfer
Session/Category Title:
- Shape Semantics
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
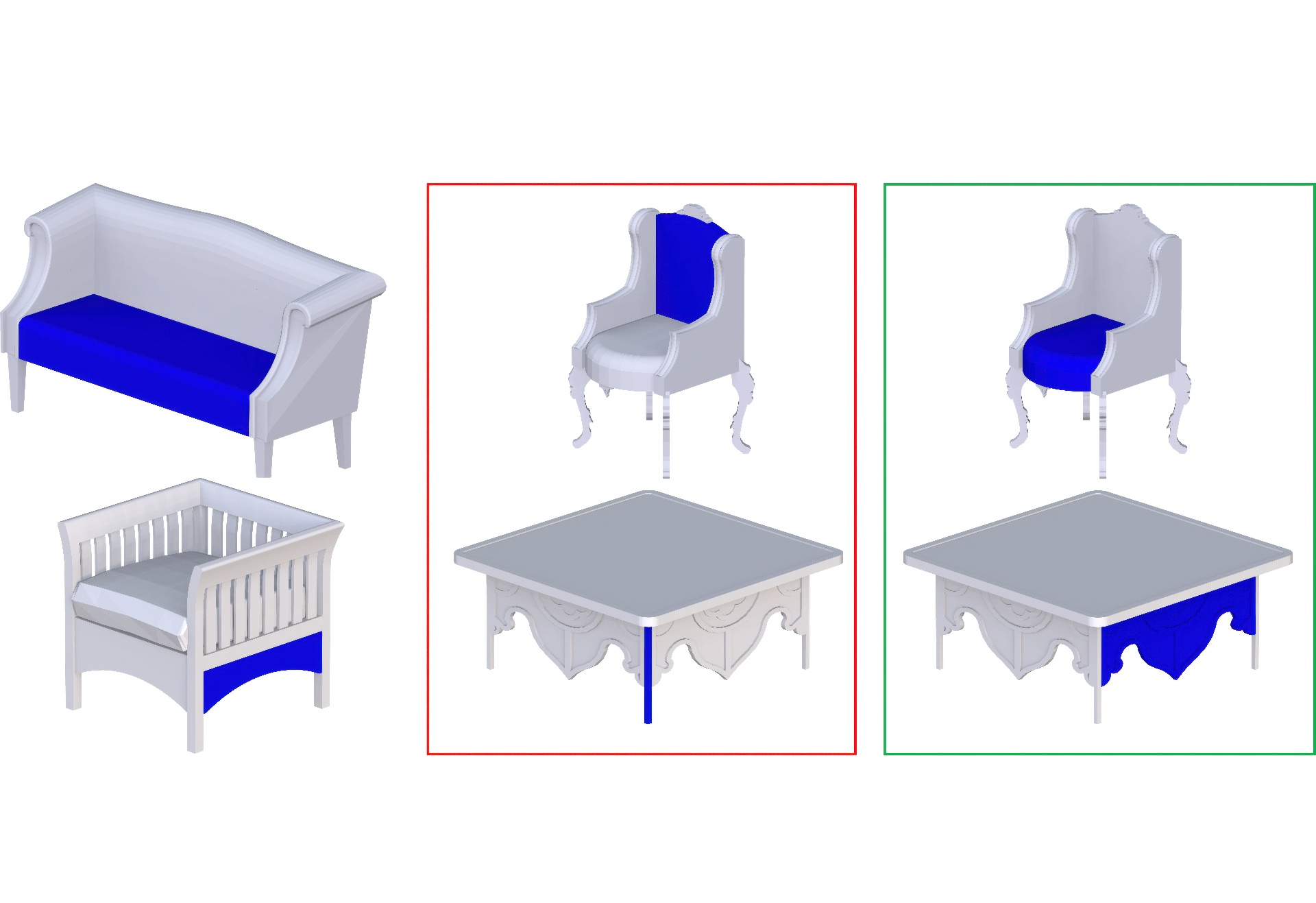
When geometric models with a desired combination of style and functionality are not available, they currently need to be created manually. We facilitate algorithmic synthesis of 3D models of man-made shapes which combines user-specified style, described via an exemplar shape, and functionality, encoded by a functionally different target shape. Our method automatically transfers the style of the exemplar to the target, creating the desired combination. The main challenge in performing cross-functional style transfer is to implicitly separate an object’s style from its function: while stylistically the output shapes should be as close as possible to the exemplar, their original functionality and structure, as encoded by the target, should be strictly preserved. Recent literature point to the presence of similarly shaped, salient geometric elements as a main indicator of stylistic similarity between 3D shapes. We therefore transfer the exemplar style to the target via a sequence of element-level operations. We allow only compatible operations, ones that do not affect the target functionality. To this end, we introduce a cross-structural element compatibility metric that estimates the impact of each operation on the edited shape. Our metric is based on the global context and coarse geometry of evaluated elements, and is trained on databases of 3D objects. We use this metric to cast style transfer as a tabu search, which incrementally updates the target shape using compatible operations, progressively increasing its style similarity to the exemplar while strictly maintaining its functionality at each step. We evaluate our framework across a range of man-made objects including furniture, light fixtures, and tableware, and perform a number of user studies confirming that it produces convincing outputs combining the desired style and function.
References:
1. Asafi, S., Goren, A., and Cohen-Or, D. 2013. Weak convex decomposition by lines-of-sight. In Proc. SGP.
2. Bokeloh, M., Wand, M., and Seidel, H.-P. 2010. A connection between partial symmetry and inverse procedural modeling. ACM Trans. Graphics 29, 4.
3. Burges, C., Shaked, T., Renshaw, E., Lazier, A., Deeds, M., Hamilton, N., and Hullender, G. 2005. Learning to rank using gradient descent. In Proc. ICML.
4. Chaudhuri, S., Kalogerakis, E., Guibas, L., and Koltun, V. 2011. Probabilistic reasoning for assembly-based 3d modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4.
5. Frey, B. J., and Dueck, D. 2007. Clustering by passing messages between data points. Science 315.
6. Funkhouser, T., Kazhdan, M., Shilane, P., Min, P., Kiefer, W., Tal, A., Rusinkiewicz, S., and Dobkin, D. 2004. Modeling by example. ACM Trans. Graphics 23, 3.
7. Glover, F., and Laguna, M. 1997. Tabu Search. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell, MA, USA.
8. Hertzmann, A., Jacobs, C. E., Oliver, N., Curless, B., and Salesin, D. H. 2001. Image analogies. In Proc. SIGGRAPH.
9. Hertzmann, A., Oliver, N., Curless, B., and Seitz, S. M. 2002. Curve analogies. In Proc. Eurographics workshop on Rendering.
10. Hu, R., Zhu, C., van Kaick, O., Liu, L., Shamir, A., and Zhang, H. 2015. Interaction context (icon): Towards a geometric functionality descriptor. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4.
11. Hu, R., van Kaick, O., Wu, B., Huang, H., Shamir, A., and Zhang, H. 2016. Learning how objects function via co-analysis of interactions. ACM Trans. Graph., to appear.
12. Huang, Q.-X., Su, H., and Guibas, L. 2013. Fine-grained semi-supervised labeling of large shape collections. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6.
13. Huang, H., Kalogerakis, E., and Marlin, B. 2015. Analysis and synthesis of 3d shape families via deep-learned generative models of surfaces. Computer Graphics Forum 34, 5. Cross Ref
14. Huang, Q., Wang, H., and Koltun, V. 2015. Single-view reconstruction via joint analysis of image and shape collections. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4.
15. Jiang, Y., Koppula, H., and Saxena, A. 2013. Hallucinated humans as the hidden context for labeling 3d scenes. In Proc. CVPR.
16. Kalogerakis, E., Nowrouzezahrai, D., Simari, P., McCrae, J., Hertzmann, A., and Singh, K. 2009. Data-driven curvature for real-time line drawing of dynamic scene. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 1.
17. Kalogerakis, E., Chaudhuri, S., Koller, D., and Koltun, V. 2012. A probabilistic model for component-based shape synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4.
18. Kim, V. G., Chaudhuri, S., Guibas, L., and Funkhouser, T. 2014. Shape2pose: Human-centric shape analysis. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4.
19. Kleiman, Y., van Kaick, O., Sorkine-Hornung, O., and Cohen-Or, D. 2015. Shed: Shape edit distance for finegrained shape similarity. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 6.
20. Kraevoy, V., Sheffer, A., Shamir, A., and Cohen-Or, D. 2008. Non-homogeneous resizing of complex models. ACM Trans. Graphics 27, 5.
21. Kreavoy, V., Julius, D., and Sheffer, A. 2007. Model composition from interchangeable components. In Proc. Pacific Graphics, 129–138.
22. Laga, H., Mortara, M., and Spagnuolo, M. 2013. Geometry and context for semantic correspondences and functionality recognition in man-made 3d shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 5.
23. Lanckriet, G. R. G., Cristianini, N., Bartlett, P., Ghaoui, L. E., and Jordan, M. I. 2004. Learning the kernel matrix with semidefinite programming. J. Machine Learning Research 5.
24. Lewis, M. 2008. Architectura: elements of architectural style. Barrons Educational Series.
25. Li, H., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Cao, J., Shamir, A., and Cohen-Or, D. 2013. Curve style analysis in a set of shapes. Computer Graphics Forum 32, 6.
26. Liu, H., Vimont, U., Wand, M., Cani, M.-P., Hahmann, S., Rohmer, D., and Mitra, N. J. 2015. Replaceable substructures for efficient part-based modeling. Comp. Graph. Forum 34, 2.
27. Liu, T., Hertzmann, A., Li, W., and Funkhouser, T. 2015. Style compatibility for 3d furniture models. ACM Trans. Graphics 34, 4.
28. Lun, Z., Kalogerakis, E., and Sheffer, A. 2015. Elements of style: Learning perceptual shape style similarity. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4.
29. Ma, C., Huang, H., Sheffer, A., Kalogerakis, E., and Wang, R. 2014. Analogy-driven 3D style transfer. Computer Graphics Forum 33, 2.
30. Norman, D. 1988. The Design of Everyday Things. Basic Books.
31. Nutting, W. 1928. Furniture Treasury. Gr Macmillan Publishing.
32. Ohtake, Y., Belyaev, A., and Seidel, H.-P. 2004. Ridgevalley lines on meshes via implicit surface fitting. In Proc. Siggraph.
33. Savva, M., Chang, A. X., Hanrahan, P., Fisher, M., and Niessner, M. 2014. Scenegrok: Inferring action maps in 3d environments. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 6.
34. Savva, M., Chang, A. X., Hanrahan, P., Fisher, M., and Niessner, M. 2016. PiGraphs: Learning Interaction Snapshots from Observations. ACM Trans. Graph., to appear.
35. Schölkopf, B. 2001. The kernel trick for distances. In Proc. NIPS.
36. Sorkine, O., and Alexa, M. 2007. As-rigid-as-possible surface modeling. In Proc. SGP.
37. Talton, J., Yang, L., Kumar, R., Lim, M., Goodman, N. D., and MĚCH, R. 2012. Learning design patterns with bayesian grammar induction. In Proc. UIST, 63–74.
38. Tamuz, O., Liu, C., Belongie, S., Shamir, O., and Kalai, A. 2011. Adaptively learning the crowd kernel. In Proc. ICML.
39. Tibshirani, R. 1996. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society 58.
40. van Kaick, O., Zhang, H., Hamarneh, G., and Cohen-Or, D. 2011. A survey on shape correspondence. Computer Graphics Forum 30, 6, 1681–1707. Cross Ref
41. Xu, K., Li, H., Zhang, H., Cohen-Or, D., Xiong, Y., and Cheng, Z.-Q. 2010. Style-content separation by anisotropic part scales. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 6.
42. Xu, K., Zhang, H., Cohen-Or, D., and Chen, B. 2012. Fit and diverse: Set evolution for inspiring 3d shape galleries. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4.
43. Xu, K., Kim, V. G., Huang, Q., and Kalogerakis, E. 2016. Data-driven shape analysis and processing. Computer Graphics Forum, to appear.
44. Yumer, M., and Kara, L. 2012. Co-abstraction of shape collections. ACM Trans. Graphics 31, 6, 166:1–166:11.
45. Yumer, M., and Kara, L. 2014. Co-constrained handles for deformation in shape collections. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6.
46. Yumer, M. E., Chaudhuri, S., Hodgins, J. K., and Kara, L. B. 2015. Semantic shape editing using deformation handles. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4.
47. Zheng, Y., Cohen-Or, D., and Mitra, N. J. 2013. Smart variations: Functional substructures for part compatibility. Comp. Graph. Forum 32, 2. Cross Ref
48. Zhou, K., Huang, J., Snyder, J., Liu, X., Bao, H., Guo, B., and Shum, H.-Y. 2005. Large mesh deformation using the volumetric graph laplacian. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3.
49. Zhu, C., Byrd, R. H., Lu, P., and Nocedal, J. 1997. Algorithm 778: L-bfgs-b: Fortran subroutines for large-scale bound-constrained optimization. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 23, 4.
50. Zhu, Y., Fathi, A., and Fei-Fei, L. 2014. Reasoning about object affordances in a knowledge base representation. In Proc. ECCV.