“SPGrid: a sparse paged grid structure applied to adaptive smoke simulation” by Setaluri, Aanjaneya, Bauer and Sifakis
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- SPGrid: a sparse paged grid structure applied to adaptive smoke simulation
Session/Category Title:
- Newton's Garden
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
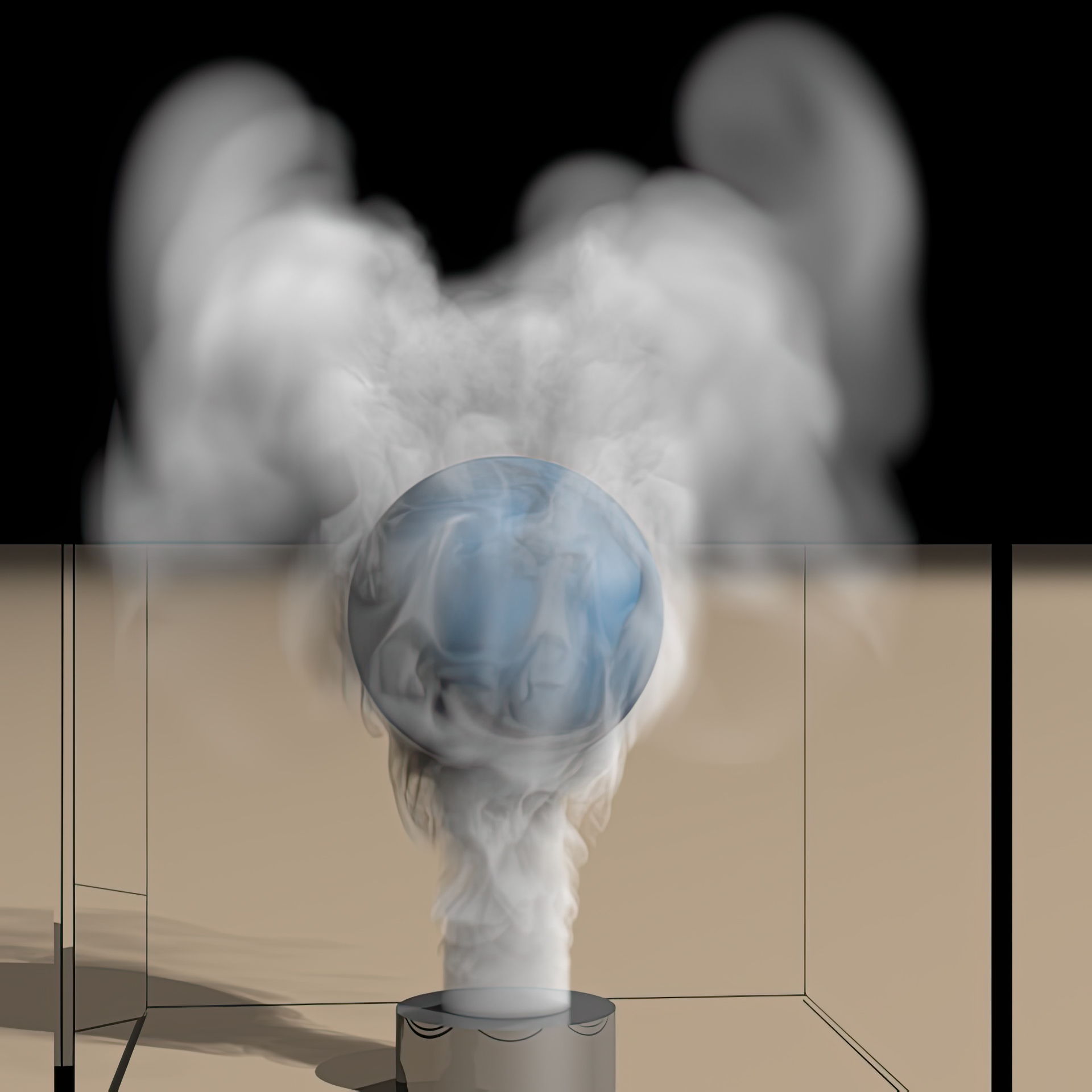
We introduce a new method for fluid simulation on high-resolution adaptive grids which rivals the throughput and parallelism potential of methods based on uniform grids. Our enabling contribution is SPGrid, a new data structure for compact storage and efficient stream processing of sparsely populated uniform Cartesian grids. SPGrid leverages the extensive hardware acceleration mechanisms inherent in the x86 Virtual Memory Management system to deliver sequential and stencil access bandwidth comparable to dense uniform grids. Second, we eschew tree-based adaptive data structures in favor of storing simulation variables in a pyramid of sparsely populated uniform grids, thus avoiding the cost of indirect memory access associated with pointer-based representations. We show how the costliest algorithmic kernels of fluid simulation can be implemented as a composition of two kernel types: (a) stencil operations on a single sparse uniform grid, and (b) structured data transfers between adjacent levels of resolution, even when modeling non-graded octrees. Finally, we demonstrate an adaptive multigrid-preconditioned Conjugate Gradient solver that achieves resolution-independent convergence rates while admitting a lightweight implementation with a modest memory footprint. Our method is complemented by a new interpolation scheme that reduces dissipative effects and simplifies dynamic grid adaptation. We demonstrate the efficacy of our method in end-to-end simulations of smoke flow.
References:
1. Adams, B., Pauly, M., Keiser, R., and Guibas, L. J. 2007. Adaptively sampled particle fluids. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Papers, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH ’07.
2. Aftosmis, M. J., Berger, M. J., and Murman, S. M., 2004. Applications of space-filling curves to cartesian methods for CFD. 42nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit.
3. Ando, R., Thürey, N., and Wojtan, C. 2013. Highly adaptive liquid simulations on tetrahedral meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4 (July), 103:1–103:10.
4. Batty, C., Xenos, S., and Houston, B. 2010. Tetrahedral embedded boundary methods for accurate and flexible adaptive fluids. Computer Graphics Forum 29, 2, 695–704.Cross Ref
5. Brochu, T., Batty, C., and Bridson, R. 2010. Matching fluid simulation elements to surface geometry and topology. In SIGGRAPH ’10, 47:1–47:9.
6. Brun, E., Guittet, A., and Gibou, F. 2012. A local level-set method using a hash table data structure. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 6 (Mar.), 2528–2536.
7. Chentanez, N., and Müller, M. 2011. Real-time eulerian water simulation using a restricted tall cell grid. In SIGGRAPH ’11, 82:1–82:10.
8. Chentanez, N., Feldman, B. E., Labelle, F., O’Brien, J. F., and Shewchuk, J. R. 2007. Liquid simulation on lattice-based tetrahedral meshes. SCA ’07, 219–228.
9. Clausen, P., Wicke, M., Shewchuk, J. R., and O’Brien, J. 2013. Simulating liquids and solid-liquid interactions with lagrangian meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 2 (Apr.), 17:1–17:15.
10. Cohen, J., Tariq, S., and Green, S. 2010. Interactive fluid-particle simulation using translating Eulerian grids. In ACM SIGGRAPH Symp. on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games, 15–22.
11. Crassin, C., Neyret, F., Lefebvre, S., and Eisemann, E. 2009. Gigavoxels: Ray-guided streaming for efficient and detailed voxel rendering. I3D ’09, 15–22.
12. Desbrun, M., and Cani, M.-P. 1996. Smoothed particles: A new paradigm for animating highly deformable bodies. In Comput. Anim. and Sim. ’96, Springer-Verlag, 61–76.
13. Dobashi, Y., Matsuda, Y., Yamamoto, T., and Nishita, T. 2008. A fast simulation method using overlapping grids for interactions between smoke and rigid objects. Computer Graphics Forum 27, 2, 477–486.
14. English, R. E., Qiu, L., Yu, Y., and Fedkiw, R. 2013. Chimera grids for water simulation. SCA ’13, 85–94.
15. Fedkiw, R., Stam, J., and Jensen, H. W. 2001. Visual simulation of smoke. SIGGRAPH ’01, 15–22.
16. Feldman, B., O’Brien, J., Klingner, B., and Goktekin, T. 2005. Fluids in deforming meshes. SCA ’05, 255–259.
17. Ferstl, F., Westermann, R., and Dick, C. 2014. Large-scale liquid simulation on adaptive hexahedral grids. IEEE Trans. Visualization & Computer Graphics 20, 10 (Oct), 1405–1417.Cross Ref
18. Frisken, S., Perry, R., Rockwood, A., and Jones, T. 2000. Adaptively sampled distance fields: A general representation of shape for computer graphics. SIGGRAPH ’00, 249–254.
19. Golas, A., Narain, R., Sewall, J., Krajcevski, P., Dubey, P., and Lin, M. 2012. Large-scale fluid simulation using velocity-vorticity domain decomposition. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 6, 148:1–148:9.
20. Goswami, P., Schlegel, P., Solenthaler, B., and Pajarola, R. 2010. Interactive SPH simulation and rendering on the GPU. SCA ’10, 55–64.
21. Harlow, F. H., and Welch, J. E. 1965. Numerical calculation of time-dependent viscous incompressible flow of fluid with free surface. Physics of Fluids (1958-1988) 8, 12.
22. Houston, B., Nielsen, M. B., Batty, C., Nilsson, O., and Museth, K. 2006. Hierarchical RLE level set: A compact and versatile deformable surface representation. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 1, 151–175.
23. Irving, G., Guendelman, E., Losasso, F., and Fedkiw, R. 2006. Efficient simulation of large bodies of water by coupling two and three dimensional techniques. SIGGRAPH, 805–811.
24. Klingner, B., Feldman, B., Chentanez, N., and O’Brien, J. 2006. Fluid animation with dynamic meshes. SIGGRAPH ’06, 820–825.
25. Losasso, F., Gibou, F., and Fedkiw, R. 2004. Simulating water and smoke with an octree data structure. SIGGRAPH ’04, 457–462.
26. Losasso, F., Fedkiw, R., and Osher, S. 2005. Spatially adaptive techniques for level set methods and incompressible flow. Computers and Fluids 35, 2006.
27. McAdams, A., Sifakis, E., and Teran, J. 2010. A parallel multigrid poisson solver for fluids simulation on large grids. SCA ’10, 65–74.
28. Müller, M., Charypar, D., and Gross, M. 2003. Particle-based fluid simulation for interactive applications. SCA ’03, 154–159.
29. Museth, K. 2011. DB+Grid: A novel dynamic blocked grid for sparse high-resolution volumes and level sets. SIGGRAPH ’11.
30. Museth, K. 2013. VDB: High-resolution sparse volumes with dynamic topology. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 3 (July), 27:1–27:22.
31. Nielsen, M., and Bridson, R. 2011. Guide shapes for high resolution naturalistic liquid simulation. SIGGRAPH ’11, 1–8.
32. Nielsen, M. B., and Museth, K. 2006. Dynamic tubular grid: An efficient data structure and algorithms for high resolution level sets. J. Sci. Comput. 26, 3 (Mar.), 261–299.
33. Nielsen, M. B., Nilsson, O., Söderström, A., and Museth, K. 2007. Out-of-core and compressed level set methods. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 4 (Oct.).
34. Olshanskii, M. A., Terekhov, K. M., and Vassilevski, Y. V. 2013. An octree-based solver for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations with enhanced stability and low dissipation. Computers and Fluids 84, 0, 231–246.Cross Ref
35. Patel, S., Chu, A., Cohen, J., and Pighin, F. 2005. Fluid simulation via disjoint translating grids. SIGGRAPH ’05.
36. Premoze, S., Tasdizen, T., Bigler, J., Lefohn, A., and Whitaker, R. 2003. Particle–based simulation of fluids. In Comp. Graph. Forum (Eurographics Proc.), vol. 22, 401–410.Cross Ref
37. Selle, A., Rasmussen, N., and Fedkiw, R. 2005. A vortex particle method for smoke, water and explosions. SIGGRAPH ’05, 910–914.
38. Sin, F., Bargteil, A., and Hodgins, J. 2009. A point-based method for animating incompressible flow. SCA ’09, 247–255.
39. Solenthaler, B., and Gross, M. 2011. Two-scale particle simulation. SIGGRAPH ’11, 81:1–81:8.
40. Stam, J. 1999. Stable fluids. SIGGRAPH ’99, 121–128.
41. Sussman, M., Almgren, A. S., Bell, J. B., Colella, P., Howell, L. H., and Welcome, M. L. 1999. An adaptive level set approach for incompressible two-phase flows. J. Comput. Phys. 148, 1, 81–124.
42. Tan, J., Yang, X., Zhao, X., and Yang, Z. 2008. Fluid animation with multi-layer grids. In SCA ’08 Posters.
43. Teschner, M., Heidelberger, B., Müller, M., Pomerantes, D., and Gross, M. 2003. Optimized spatial hashing for collision detection of deformable objects. In VMV, 47–54.
44. Trottenberg, U., Oosterlee, C. W., and Schuller, A. 2001. Multigrid. Academic Press.
45. Zhu, Y., and Bridson, R. 2005. Animating sand as a fluid. SIGGRAPH ’05, 965–972.
46. Zhu, B., Lu, W., Cong, M., Kim, B., and Fedkiw, R. 2013. A new grid structure for domain extension. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 4, 63:1–63:12.