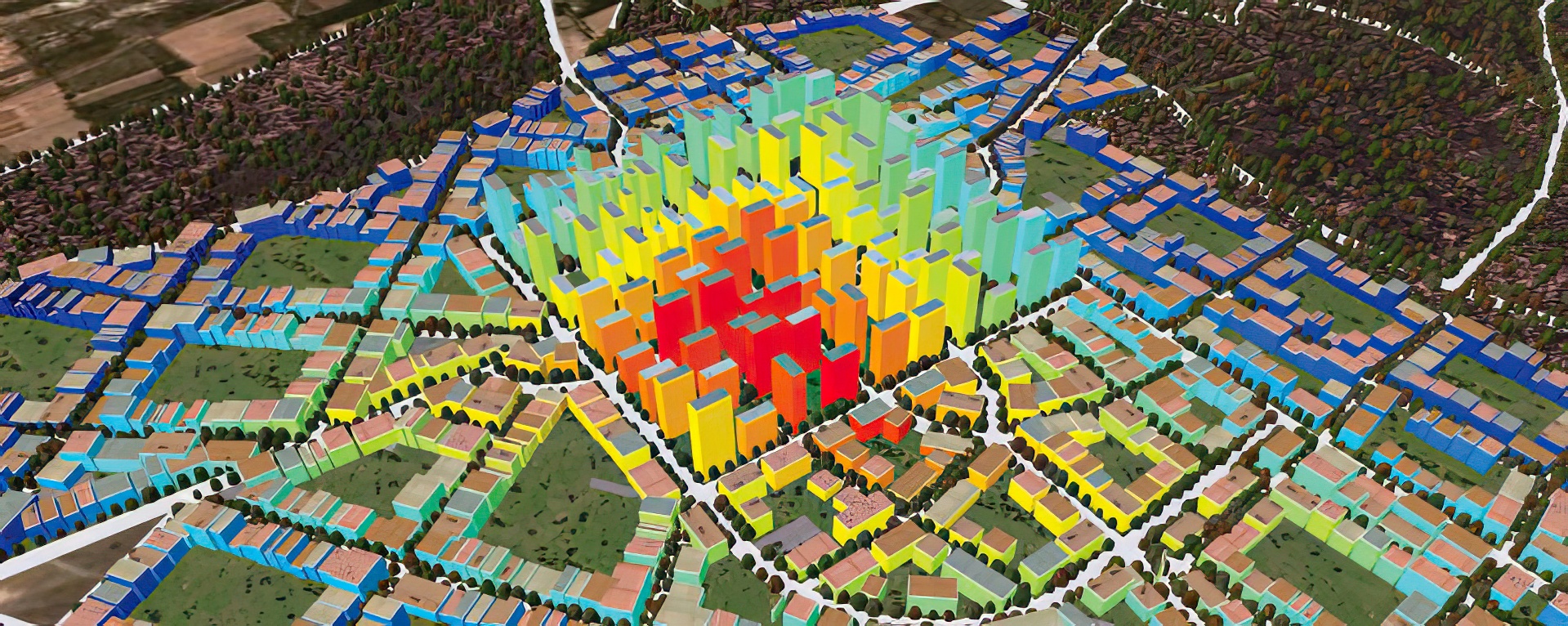
“Inverse design of urban procedural models” by Vanegas, Garcia-Dorado, Aliaga, Benes and Waddell
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Inverse design of urban procedural models
Session/Category Title:
- Shape Sets and Trees
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
We propose a framework that enables adding intuitive high level control to an existing urban procedural model. In particular, we provide a mechanism to interactively edit urban models, a task which is important to stakeholders in gaming, urban planning, mapping, and navigation services. Procedural modeling allows a quick creation of large complex 3D models, but controlling the output is a well-known open problem. Thus, while forward procedural modeling has thrived, in this paper we add to the arsenal an inverse modeling tool. Users, unaware of the rules of the underlying urban procedural model, can alternatively specify arbitrary target indicators to control the modeling process. The system itself will discover how to alter the parameters of the urban procedural model so as to produce the desired 3D output. We label this process inverse design.
References:
1. Alegre, F., and Dellaert, F. 2004. A probabilistic approach to the semantic interpretation of building facades. Workshop on Vision Techniques Applied to the Rehabilitation of City Centres.
2. Aliaga, D. G., Rosen, P. A., and Bekins, D. R. 2007. Style grammars for interactive visualization of architecture. IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Comp. Graph. 13, 4 (July), 786–797.
3. Aliaga, D. G., Vanegas, C. A., and Beneš, B. 2008. Interactive example-based urban layout synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 5 (Dec.), 160:1–160:10.
4. Batty, M. 2007. Cities and Complexity: Understanding Cities with Cellular Automata, Agent-Based Models, and Fractals. MIT Press.
5. Beneš, B., Štava, O., Měch, R., and Miller, G. 2011. Guided Procedural Modeling. Comp. Graph. Forum, 325–334.
6. Bertero, M., Poggio, T., and Torre, V. 1988. Ill-posed problems in early vision. Proceedings of the IEEE 76, 8 (Aug.), 869–889.
7. Bokeloh, M., Wand, M., and Seidel, H.-P. 2010. A connection between partial symmetry and inverse procedural modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 29 (July), 104:1–104:10.
8. Bourque, E., and Dudek, G. 2004. Procedural texture matching and transformation. Comp. Graph. Forum 23, 3, 461–468.
9. Calthorpe, P. 2010. Urbanism in the Age of Climate Change. Island Press.
10. Chenney, S., and Forsyth, D. A. 2000. Sampling plausible solutions to multi-body constraint problems. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’00, ACM, 219–228.
11. CNU, 2012. Congress for the new urbanism. www.cnu.org.
12. CTOD, 2012. Center for transit-oriented development. www.ctod.org.
13. Dellaert, F. 2003. A sample of monte carlo methods in robotics and vision. Proceedings of the ISM Int. Symposium on the Science of Modeling, 12.
14. Department of Transportation, C., 2010. Smart mobility 2010: A call to action for the new decade.
15. Gilks, W., Richardson, S., and Spiegelhalter, D. 1995. Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice. Chapman and Hall/CRC.
16. Hart, J. C., Baker, B., and Michaelraj, J. 2003. Structural simulation of tree growth and response. The Visual Computer 19, 151–163.
17. Hastings, W. 1970. Monte carlo samping methods using markov chains and their applications. Biometrika, 97–109.
18. Honda, M., Mizuno, K., Fukui, Y., and Nishihara, S. 2004. Generating autonomous time-varying virtual cities. In Proceedings of the Int. Conference on Cyberworlds, IEEE Computer Society, 45–52.
19. Kwatra, V., Essa, I., Bobick, A., and Kwatra, N. 2005. Texture optimization for example-based synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3 (July), 795–802.
20. Lefebvre, L., and Poulin, P. 2000. Analysis and synthesis of structural textures. Graphics Interface, 77–86.
21. Lipp, M., Scherzer, D., Wonka, P., and Wimmer, M. 2011. Interactive modeling of city layouts using layers of procedural content. Comp. Graph. Forum 30, 2, 345–354.
22. Merrell, P., and Manocha, D. 2008. Continuous model synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 5 (Dec.), 158:1–158:7.
23. Merrell, P., Schkufza, E., Li, Z., Agrawala, M., and Koltun, V. 2011. Interactive furniture layout using interior design guidelines. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (Jul.), 87:1–87:10.
24. Metropolis, N., Rosenbluth, A. W., Rosenbluth, M. N., Teller, A. H., and Teller, E. 1953. Equation of state calculations by fast computing machines. The Journal of Chemical Physics 21, 6, 1087–1092.
25. Müller, P., Zeng, G., Wonka, P., and Van Gool, L. 2007. Image-based procedural modeling of facades. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3 (July).
26. Murphy, T. P. 1980. Urban indicators: a guide to information sources. Gale Research Co.
27. Parish, Y. I. H., and Müller, P. 2001. Procedural modeling of cities. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’01, ACM, 301–308.
28. Park, J. P., Lee, K. H., and Lee, J. 2011. Finding syntactic structures from human motion data. Comp. Graph. Forum 30, 8, 2183–2193.
29. Riedmiller, M., and Braun, H. 1993. A direct adaptive method for faster backpropagation learning: the RPROP algorithm. In IEEE Int. Conf. on Neural Networks, vol. 1, 586–591.
30. Talton, J. O., Lou, Y., Lesser, S., Duke, J., Měch, R., and Koltun, V. 2011. Metropolis procedural modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 2 (Apr.), 11:1–11:14.
31. TRANSECT. 2012. Center for Applied Transect Studies. www.transect.org.
32. Turrin, M., von Buelow, P., and Stouffs, R. 2011. Design explorations of performance driven geometry in architectural design using parametric modeling and genetic algorithms. Adv. Eng. Inform. 25, 4 (Oct.), 656–675.
33. Vanegas, C. A., Aliaga, D. G., Beneš, B., and Waddell, P. A. 2009. Interactive design of urban spaces using geometrical and behavioral modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 5 (Dec.), 111:1–111:10.
34. Vanegas, C. A., Aliaga, D. G., Wonka, P., Müller, P., Waddell, P., and Watson, B. 2010. Modelling the appearance and behaviour of urban spaces. Comp. Graph. Forum 29, 1, 25–42.
35. Vanegas, C. A., Aliaga, D. G., and Beneš, B. 2010. Building reconstruction using manhattan-world grammars. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 358–365.
36. Veach, E., and Guibas, L. J. 1997. Metropolis light transport. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH ’97, ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., 65–76.
37. Stava, O., Benes, B., Mech, R., Aliaga, D. G., and Kristof, P. 2010. Inverse Procedural Modeling by Automatic Generation of L-systems. Comp. Graph. Forum 29, 2, 665–674.
38. Watson, B., Müller, P., Wonka, P., Sexton, C., Veryovka, O., and Fuller, A. 2008. Procedural urban modeling in practice. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 28, 3 (June), 18–26.
39. Weber, B., Müller, P., Wonka, P., and Gross, M. 2009. Interactive Geometric Simulation of 4D Cities. Comp. Graph. Forum 28, 2, 481–492.
40. Whiting, E., Ochsendorf, J., and Durand, F. 2009. Procedural modeling of structurally-sound masonry buildings. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 5 (Dec.), 112:1–112:9.
41. Wong, C. 2006. Indicators for Urban and Regional Planning: The Interplay of Policy and Methods. Routledge.
42. Xiao, J., Fang, T., Tan, P., Zhao, P., Ofek, E., and Quan, L. 2008. Image-based facade modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 5 (Dec.), 161:1–161:10.
43. Yu, L.-F., Yeung, S.-K., Tang, C.-K., Terzopoulos, D., Chan, T. F., and Osher, S. J. 2011. Make it home: automatic optimization of furniture arrangement. ACM Trans. Graph. 30, 4 (July), 86:1–86:12.