“Robust flow-guided neural prediction for sketch-based freeform surface modeling”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Robust flow-guided neural prediction for sketch-based freeform surface modeling
Session/Category Title: Learning geometry
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
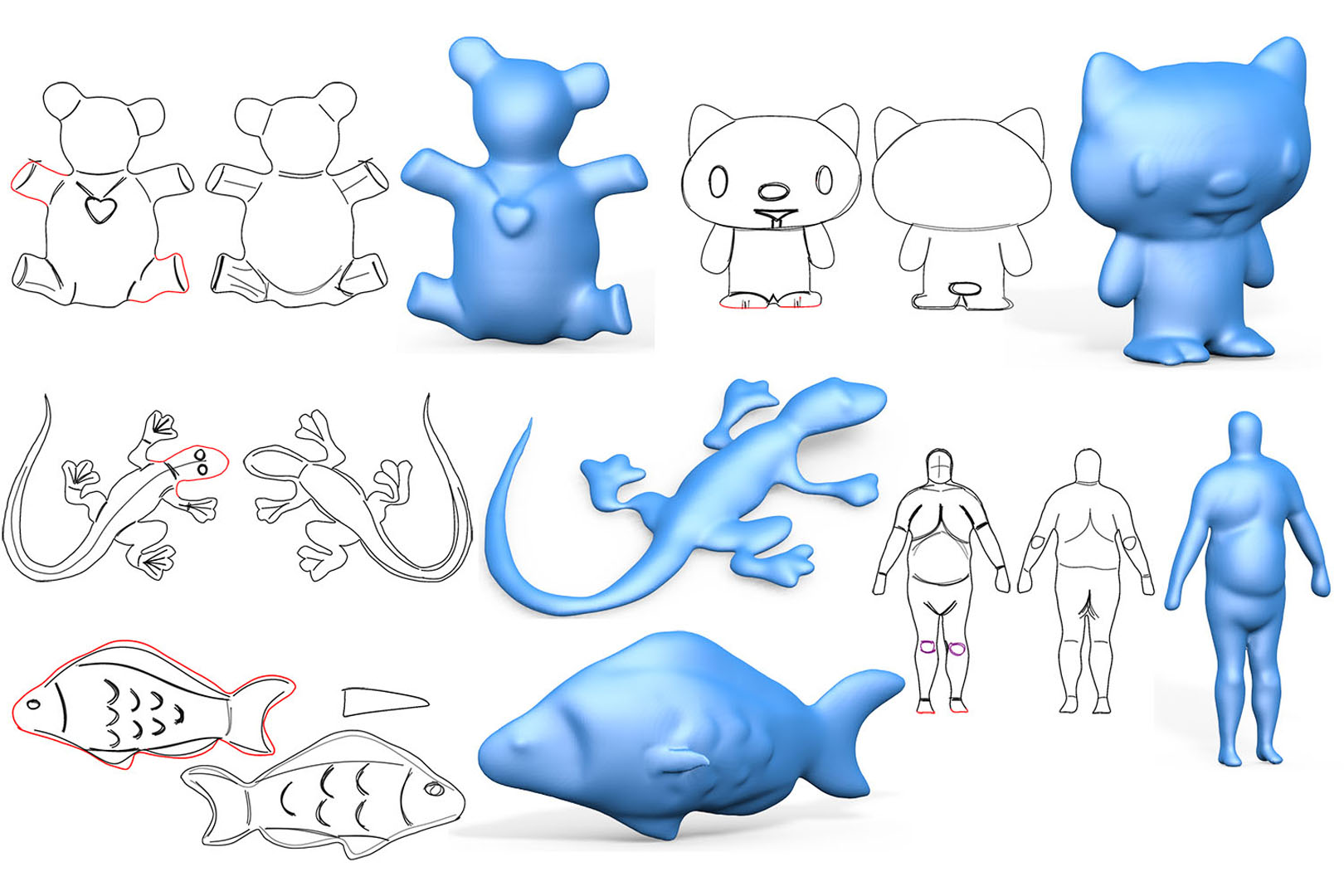
Sketching provides an intuitive user interface for communicating free form shapes. While human observers can easily envision the shapes they intend to communicate, replicating this process algorithmically requires resolving numerous ambiguities. Existing sketch-based modeling methods resolve these ambiguities by either relying on expensive user annotations or by restricting the modeled shapes to specific narrow categories. We present an approach for modeling generic freeform 3D surfaces from sparse, expressive 2D sketches that overcomes both limitations by incorporating convolution neural networks (CNN) into the sketch processing workflow.Given a 2D sketch of a 3D surface, we use CNNs to infer the depth and normal maps representing the surface. To combat ambiguity we introduce an intermediate CNN layer that models the dense curvature direction, or flow, field of the surface, and produce an additional output confidence map along with depth and normal. The flow field guides our subsequent surface reconstruction for improved regularity; the confidence map trained unsupervised measures ambiguity and provides a robust estimator for data fitting. To reduce ambiguities in input sketches users can refine their input by providing optional depth values at sparse points and curvature hints for strokes. Our CNN is trained on a large dataset generated by rendering sketches of various 3D shapes using non-photo-realistic line rendering (NPR) method that mimics human sketching of free-form shapes. We use the CNN model to process both single- and multi-view sketches. Using our multi-view framework users progressively complete the shape by sketching in different views, generating complete closed shapes. For each new view, the modeling is assisted by partial sketches and depth cues provided by surfaces generated in earlier views. The partial surfaces are fused into a complete shape using predicted confidence levels as weights.We validate our approach, compare it with previous methods and alternative structures, and evaluate its performance with various modeling tasks. The results demonstrate our method is a new approach for efficiently modeling freeform shapes with succinct but expressive 2D sketches.
References:
1. Seok-Hyung Bae, Ravin Balakrishnan, and Karan Singh. 2008. ILoveSketch: As-natural-as-possible Sketching System for Creating 3D Curve Models. In UIST. 151–160. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Adrien Bernhardt, Adeline Pihuit, Marie-Paule Cani, and Loïc Barthe. 2008. Matisse: Painting 2D regions for Modeling Free-Form Shapes. In SBIM. 57–64. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Michael J. Black and Anand Rangarajan. 1996. On the unification of line processes, outlier rejection, and robust statistics with applications in early vision. IJCV 19, 1 (1996). Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Minh Tuan Bui, Junho Kim, and Yunjin Lee. 2015. 3D-look Shading from Contours and Hatching Strokes. Comput. Graph. 51 (2015), 167–176. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Tao Chen, Zhe Zhu, Ariel Shamir, Shi-Min Hu, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2013. 3-Sweep: Extracting Editable Objects from a Single Photo. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) 32, 6 (2013), 195:1–195:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Christopher B Choy, Danfei Xu, JunYoung Gwak, Kevin Chen, and Silvio Savarese. 2016. 3D-R2N2: A Unified Approach for Single and Multi-view 3D Object Reconstruction. In ECCV.Google Scholar
7. Forrester Cole, Aleksey Golovinskiy, Alex Limpaecher, Heather Stoddart Barros, Adam Finkelstein, Thomas Funkhouser, and Szymon Rusinkiewicz. 2008. Where Do People Draw Lines? ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 27, 3 (Aug. 2008). Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Forrester Cole, Kevin Sanik, Doug DeCarlo, Adam Finkelstein, Thomas Funkhouser, Szymon Rusinkiewicz, and Manish Singh. 2009. How Well Do Line Drawings Depict Shape?. In ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH), Vol. 28. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Doug DeCarlo, Adam Finkelstein, Szymon Rusinkiewicz, and Anthony Santella. 2003. Suggestive Contours for Conveying Shape. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 22, 3 (2003). Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Johanna Delanoy, Adrien Bousseau, Mathieu Aubry, Phillip Isola, and Alexei A. Efros. 2017. What You Sketch Is What You Get: 3D Sketching using Multi-View Deep Volumetric Prediction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.08390 (2017). Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Mathieu Desbrun, Mark Meyer, Peter Schröder, and Alan H. Barr. 1999. Implicit Fairing of Irregular Meshes Using Diffusion and Curvature Flow. In SIGGRAPH. 317–324. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Olga Diamanti, Amir Vaxman, Daniele Panozzo, and Olga Sorkine-Hornung. 2014. Designing N-PolyVector Fields with Complex Polynomials. SGP 33, 5 (2014), 1–11. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. D. Eigen and R. Fergus. 2015. Predicting Depth, Surface Normals and Semantic Labels with a Common Multi-scale Convolutional Architecture. In ICCV. 2650–2658. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Mathias Eitz, Ronald Richter, Tamy Boubekeur, Kristian Hildebrand, and Marc Alexa. 2012. Sketch-based Shape Retrieval. ACM Trans. Graph. 4 (July 2012). Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Haoqiang Fan, Hao Su, and Leonidas J. Guibas. 2017. A Point Set Generation Network for 3D Object Reconstruction from a Single Image. In CVPR.Google Scholar
16. Yotam Gingold, Takeo Igarashi, and Denis Zorin. 2009. Structured Annotations for 2D-to-3D Modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) 28, 5 (2009), 148:1–148:9. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Craig Gotsman, Xianfeng Gu, and Alla Sheffer. 2003. Fundamentals of Spherical Parameterization for 3D Meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 22, 3 (2003). Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Thibault Groueix, Matthew Fisher, Vladimir G. Kim, Bryan Russell, and Mathieu Aubry. 2018. AtlasNet: A Papier-Mâché Approach to Learning 3D Surface Generation. In CVPR.Google Scholar
19. Xuekun Guo, Juncong Lin, Kai Xu, Siddhartha Chaudhuri, and Xiaogang Jin. 2016. CustomCut: On-demand Extraction of Customized 3D Parts with 2D Sketches. Computer Graphics Forum 35, 5 (2016), 89–100.Google ScholarCross Ref
20. Xiaoguang Han, Chang Gao, and Yizhou Yu. 2017. DeepSketch2Face: A Deep Learning Based Sketching System for 3D Face and Caricature Modeling. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4, Article 126 (July 2017), 12 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Aaron Hertzmann and Denis Zorin. 2000. Illustrating Smooth Surfaces. In SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Haibin Huang, Evangelos Kalogerakis, Ersin Yumer, and Radomir Mech. 2016. Shape Synthesis from Sketches via Procedural Models and Convolutional Networks. IEEE. T. Vis. Comput. Gr. 22, 10 (2016), 1.Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Emmanuel Iarussi, David Bommes, and Adrien Bousseau. 2015. BendFields: Regularized Curvature Fields from Rough Concept Sketches. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 34, 3 (2015), 24:1–24:16. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Takeo Igarashi, Satoshi Matsuoka, and Hidehiko Tanaka. 1999. Teddy: A Sketching Interface for 3D Freeform Design. In SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Pushkar Joshi and Nathan A. Carr. 2008. Repoussé: Automatic Inflation of 2D Artwork. In SBIM (SBM’08). Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Tilke Judd, Frédo Durand, and Edward H. Adelson. 2007. Apparent ridges for line drawing. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 26, 3 (2007), 19. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Amaury Jung, Stefanie Hahmann, Damien Rohmer, Antoine Begault, Laurence Boissieux, and Marie-Paule Cani. 2015. Sketching Folds: Developable Surfaces from Non-Planar Silhouettes. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 5, Article 155 (2015), 12 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
28. Michael Kazhdan and Hugues Hoppe. 2013. Screened Poisson Surface Reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 3, Article 29 (July 2013), 13 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Alex Kendall and Yarin Gal. 2017. What Uncertainties Do We Need in Bayesian Deep Learning for Computer Vision?. In NIPS. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Diederik P. Kingma and Jimmy Ba. 2014. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014).Google Scholar
31. Jeehyung Lee and Thomas Funkhouser. 2008. Sketch-based Search and Composition of 3D Models. In SBIM (SBM’08). 97–104. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Changjian Li, Hao Pan, Yang Liu, Xin Tong, Alla Sheffer, and Wenping Wang. 2017. BendSketch: Modeling Freeform Surfaces Through 2D Sketching. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 36, 4, Article 125 (July 2017), 14 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Zhaoliang Lun, Matheus Gadelha, Evangelos Kalogerakis, Subhransu Maji, and Rui Wang. 2017. 3D Shape Reconstruction from Sketches via Multi-view Convolutional Networks. In 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV).Google ScholarCross Ref
34. Andrew Nealen, Takeo Igarashi, Olga Sorkine, and Marc Alexa. 2007. FiberMesh: Designing Freeform Surfaces with 3D Curves. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 26, 3 (2007). Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Diego Nehab, Szymon Rusinkiewicz, James Davis, and Ravi Ramamoorthi. 2005. Efficiently Combining Positions and Normals for Precise 3D Geometry. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 24, 3 (July 2005), 536–543. Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Gen Nishida, Ignacio Garcia-Dorado, Daniel G. Aliaga, Bedrich Benes, and Adrien Bousseau. 2016. Interactive Sketching of Urban Procedural Models. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 35, 4 (2016), 130:1–130:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
37. L. Olsen, F. Samavati, and J. Jorge. 2011. NaturaSketch: Modeling from Images and Natural Sketches. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. Mag. 31, 6 (2011), 24–34. Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Olaf Ronneberger, Philipp Fischer, and Thomas Brox. 2015. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015. Springer, 234–241.Google ScholarCross Ref
39. Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Doug DeCarlo. 2013. Real-time suggestive contours. (2013). http://www.cs.princeton.edu/gfx/proj/sugcon/Google Scholar
40. Ryan Schmidt, Azam Khan, Karan Singh, and Gord Kurtenbach. 2009. Analytic Drawing of 3D Scaffolds. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) 28, 5 (2009), 149:1–149:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Ryan Schmidt, Brian Wyvill, Mario Costa Sousa, and Joaquim A. Jorge. 2005. ShapeShop: Sketch-Based Solid Modeling with BlobTrees. In SBIM.Google Scholar
42. Cloud Shao, Adrien Bousseau, Alla Sheffer, and Karan Singh. 2012. CrossShade: Shading Concept Sketches Using Cross-section Curves. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 31, 4 (2012), 45:1–45:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
43. Alex Shtof, Alexander Agathos, Yotam Gingold, Ariel Shamir, and Daniel Cohen-Or. 2013. Geosemantic Snapping for Sketch-Based Modeling. Comput. Graph. Forum (EG) 32, 2 (2013), 245–253.Google ScholarCross Ref
44. H. Su, S. Maji, E. Kalogerakis, and E. Learned-Miller. 2015. Multi-view Convolutional Neural Networks for 3D Shape Recognition. In ICCV. 945–953. Google ScholarDigital Library
45. Wanchao Su, Dong Du, Xin Yang, Shizhe Zhou, and Hongbo Fu. 2018. Interactive Sketch-Based Normal Map Generation with Deep Neural Networks. In ACM i3D.Google Scholar
46. Maxim Tatarchenko, Alexey Dosovitskiy, and Thomas Brox. 2016. Multi-view 3D Models from Single Images with a Convolutional Network. In ECCV. 322–337.Google Scholar
47. Maxim Tatarchenko, Alexey Dosovitskiy, and Thomas Brox. 2017. Octree Generating Networks: Efficient Convolutional Architectures for High-resolution 3D Outputs. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.09438 (2017).Google Scholar
48. Fang Wang, Le Kang, and Yi Li. 2015c. Sketch-based 3D shape retrieval using Convolutional Neural Networks. CVPR (2015), 1875–1883.Google ScholarCross Ref
49. Peng-Shuai Wang, Xiao-Ming Fu, Yang Liu, Xin Tong, Shi-Lin Liu, and Baining Guo. 2015b. Rolling Guidance Normal Filter for Geometric Processing. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH ASIA) 34, 6, Article 173 (2015), 173:1–173:9 pages. Google ScholarDigital Library
50. X. Wang, D. F. Fouhey, and A. Gupta. 2015a. Designing deep networks for surface normal estimation. In CVPR. 539–547.Google Scholar
51. Jiajun Wu, Chengkai Zhang, Tianfan Xue, William T Freeman, and Joshua B Tenenbaum. 2016. Learning a probabilistic latent space of object shapes via 3d generative-adversarial modeling. In NIPS. 82–90. Google ScholarDigital Library
52. Xiaohua Xie, Kai Xu, Niloy J. Mitra, Daniel Cohen-Or, Wenyong Gong, Qi Su, and Baoquan Chen. 2013. Sketch-to-Design: Context-Based Part Assembly. Comput. Graph. Forum 32, 8 (2013), 233–245.Google ScholarCross Ref
53. Baoxuan Xu, William Chang, Alla Sheffer, Adrien Bousseau, James McCrae, and Karan Singh. 2014. True2Form: 3D Curve Networks from 2D Sketches via Selective Regularization. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 33, 4 (2014), 131:1–131:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
54. Kun Xu, Kang Chen, Hongbo Fu, Wei-Lun Sun, and Shi-Min Hu. 2013. Sketch2Scene: Sketch-based Co-retrieval and Co-placement of 3D Models. ACM Trans. Graph. (SIGGRAPH) 32, 4 (2013), 123:1–123:15. Google ScholarDigital Library
55. C. K. Yeh, S. Y. Huang, P. K. Jayaraman, C. W. Fu, and T. Y. Lee. 2016. Interactive High-Relief Reconstruction for Organic and Double-sided Objects from a Photo. IEEE. T. Vis. Comput. Gr. 99 (2016), 1–1.Google Scholar
56. Li Zhang, G. Dugas-Phocion, J. S. Samson, and S. M. Seitzt. 2001. Single view modeling of free-form scenes. In CVPR, Vol. 1. I-990–I-997.Google Scholar