“Multi-directional geodesic neural networks via equivariant convolution”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Multi-directional geodesic neural networks via equivariant convolution
Session/Category Title: Learning geometry
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
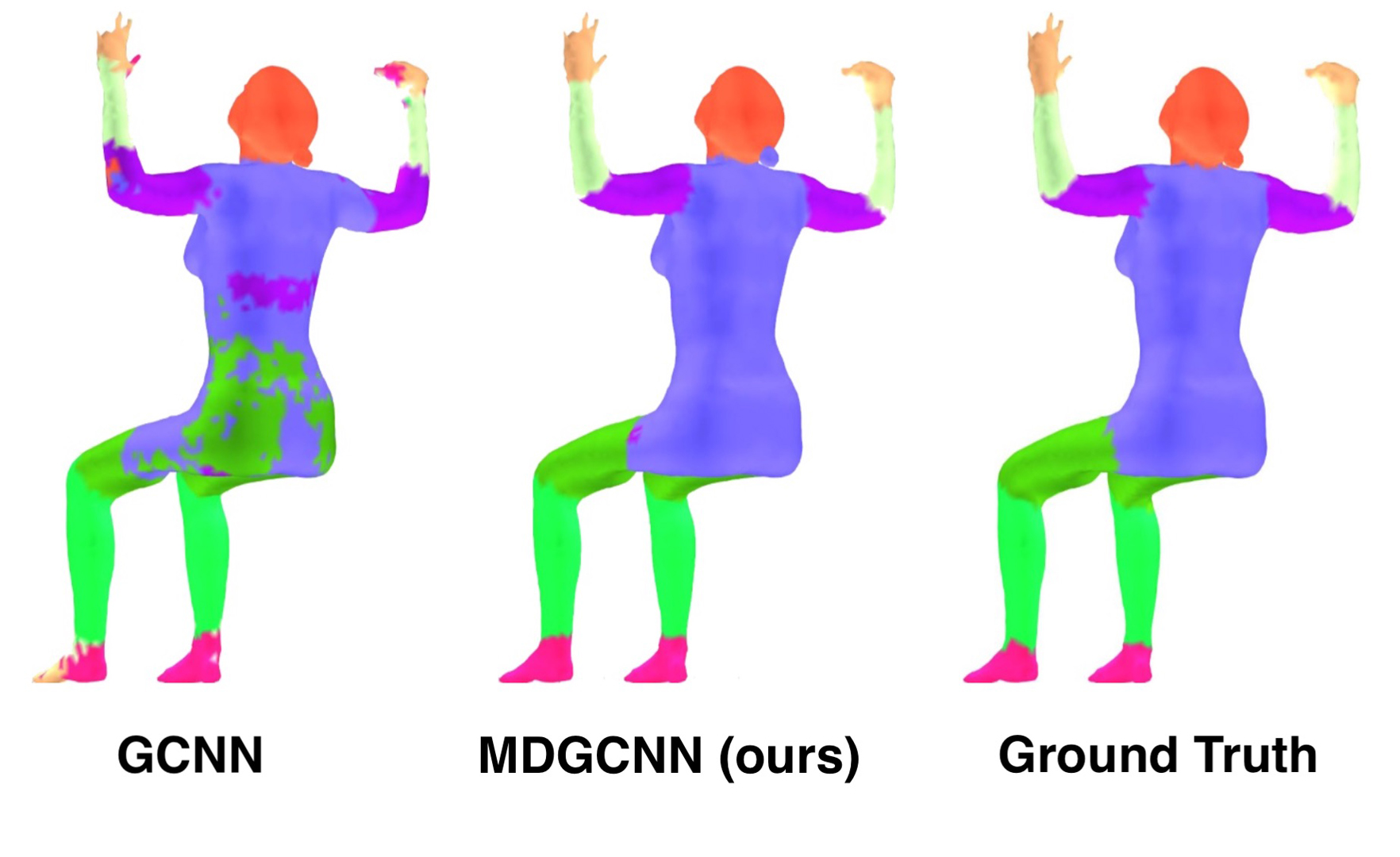
We propose a novel approach for performing convolution of signals on curved surfaces and show its utility in a variety of geometric deep learning applications. Key to our construction is the notion of directional functions defined on the surface, which extend the classic real-valued signals and which can be naturally convolved with with real-valued template functions. As a result, rather than trying to fix a canonical orientation or only keeping the maximal response across all alignments of a 2D template at every point of the surface, as done in previous works, we show how information across all rotations can be kept across different layers of the neural network. Our construction, which we call multi-directional geodesic convolution, or directional convolution for short, allows, in particular, to propagate and relate directional information across layers and thus different regions on the shape. We first define directional convolution in the continuous setting, prove its key properties and then show how it can be implemented in practice, for shapes represented as triangle meshes. We evaluate directional convolution in a wide variety of learning scenarios ranging from classification of signals on surfaces, to shape segmentation and shape matching, where we show a significant improvement over several baselines.
References:
1. Martín Abadi, Ashish Agarwal, Paul Barham, and others. 2015. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. (2015). https://www.tensorflow.org/Software available from tensorflow.org.Google Scholar
2. Adobe. 2016. Adobe Fuse 3D Characters. (2016). https://www.mixamo.comGoogle Scholar
3. Mathieu Aubry, Ulrich Schlickewei, and Daniel Cremers. 2011. The wave kernel signature: A quantum mechanical approach to shape analysis. In ICCV Workshops. IEEE, 1626–1633.Google ScholarCross Ref
4. Davide Boscaini, Jonathan Masci, Simone Melzi, Michael M Bronstein, Umberto Castellani, and Pierre Vandergheynst. 2015. Learning class-specific descriptors for deformable shapes using localized spectral convolutional networks. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 34. Wiley Online Library, 13–23.Google Scholar
5. Davide Boscaini, Jonathan Masci, Emanuele Rodola, and Michael M. Bronstein. 2016. Learning shape correspondence with anisotropic convolutional neural networks. In arXiv:1605.06437.Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Michael M Bronstein, Joan Bruna, Yann LeCun, Arthur Szlam, and Pierre Vandergheynst. 2017. Geometric deep learning: going beyond euclidean data. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 34, 4 (2017), 18–42.Google ScholarCross Ref
7. François Chollet and others. 2015. Keras. https://github.com/fchollet/keras. (2015).Google Scholar
8. Michaël Deferrard, Xavier Bresson, and Pierre Vandergheynst. 2016. Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 3844–3852. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Danielle Ezuz, Justin Solomon, Vladimir G Kim, and Mirela Ben-Chen. 2017. GWCNN: A Metric Alignment Layer for Deep Shape Analysis. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 36. Wiley Online Library, 49–57. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Chamberlain Fong. 2015. Analytical methods for squaring the disc. arXiv preprint arXiv:1509.06344 (2015).Google Scholar
11. Michael Garland and Paul S. Heckbert. 1997. Surface Simplification Using Quadric Error Metrics. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’97). 209–216. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Paul Guerrero, Yanir Kleiman, Maks Ovsjanikov, and Niloy J Mitra. 2018. PCPNet Learning Local Shape Properties from Raw Point Clouds. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 37. Wiley Online Library, 75–85.Google Scholar
13. Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 770–778.Google ScholarCross Ref
14. Evangelos Kalogerakis, Melinos Averkiou, Subhransu Maji, and Siddhartha Chaudhuri. 2017. 3D Shape Segmentation with Projective Convolutional Networks. In Proc. CVPR.Google ScholarCross Ref
15. Diederik P Kingma and Jimmy Ba. 2014. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014).Google Scholar
16. Roman Klokov and Victor Lempitsky. 2017. Escape from cells: Deep kd-networks for the recognition of 3d point cloud models. In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, 863–872.Google ScholarCross Ref
17. I. Kostrikov, Z. Jiang, D. Panozzo, D. Zorin, and J. Bruna. 2017. Surface Networks. ArXiv e-prints (May 2017).Google Scholar
18. Alex Krizhevsky and Geoffrey Hinton. 2009. Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. (2009).Google Scholar
19. Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, and Geoffrey E Hinton. 2012. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems. 1097–1105. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Yangyan Li, Rui Bu, Mingchao Sun, and Baoquan Chen. 2018. PointCNN. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.07791 (2018).Google Scholar
21. Haggai Maron, Meirav Galun, Noam Aigerman, Miri Trope, Nadav Dym, Ersin Yumer, Vladimir G Kim, and Yaron Lipman. 2017. Convolutional Neural Networks on Surfaces via Seamless Toric Covers. SIGGRAPH. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Jonathan Masci, Davide Boscaini, Michael M. Bronstein, and Pierre Vandergheynst. 2015. Geodesic convolutional neural networks on Riemannian manifolds. In Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops. 37–45. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Daniel Maturana and Sebastian Scherer. 2015. Voxnet: A 3d convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition. In Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on. IEEE, 922–928.Google ScholarCross Ref
24. Eivind Lyche Melvær and Martin Reimers. 2012. Geodesic polar coordinates on polygonal meshes. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 31. Wiley Online Library, 2423–2435. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Federico Monti, Davide Boscaini, Jonathan Masci, Emanuele Rodolà, Jan Svoboda, and Michael M. Bronstein. 2017. Geometric Deep Learning on Graphs and Manifolds Using Mixture Model CNNs. In CVPR. IEEE Computer Society, 5425–5434.Google Scholar
26. Maks Ovsjanikov, Mirela Ben-Chen, Justin Solomon, Adrian Butscher, and Leonidas Guibas. 2012. Functional maps: a flexible representation of maps between shapes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 31, 4 (2012), 30. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Charles R Qi, Hao Su, Kaichun Mo, and Leonidas J Guibas. 2017. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. Proc. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE 1, 2 (2017), 4.Google Scholar
28. Charles R Qi, Hao Su, Matthias Nießner, Angela Dai, Mengyuan Yan, and Leonidas J Guibas. 2016. Volumetric and multi-view cnns for object classification on 3d data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 5648–5656.Google ScholarCross Ref
29. Charles Ruizhongtai Qi, Li Yi, Hao Su, and Leonidas J Guibas. 2017. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 5105–5114. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Olaf Ronneberger, Philipp Fischer, and Thomas Brox. 2015. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, 234–241.Google ScholarCross Ref
31. Samuele Salti, Federico Tombari, and Luigi Di Stefano. 2014. SHOT: Unique signatures of histograms for surface and texture description. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 125 (2014), 251–264.Google ScholarCross Ref
32. James Albert Sethian. 1999. Level set methods and fast marching methods: evolving interfaces in computational geometry, fluid mechanics, computer vision, and materials science. Vol. 3. Cambridge university press.Google Scholar
33. Konstantinos Sfikas, Theoharis Theoharis, and Ioannis Pratikakis. 2017. Exploiting the PANORAMA representation for convolutional neural network classification and retrieval. In Eurographics Workshop on 3D Object Retrieval.Google Scholar
34. Baoguang Shi, Song Bai, Zhichao Zhou, and Xiang Bai. 2015. Deeppano: Deep panoramic representation for 3-d shape recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 22, 12 (2015), 2339–2343.Google ScholarCross Ref
35. Ayan Sinha, Jing Bai, and Karthik Ramani. 2016. Deep learning 3d shape surfaces using geometry images. In European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 223–240.Google ScholarCross Ref
36. Justin Solomon, Gabriel Peyré, Vladimir G Kim, and Suvrit Sra. 2016. Entropic metric alignment for correspondence problems. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 4 (2016), 72. Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Hang Su, Subhransu Maji, Evangelos Kalogerakis, and Erik Learned-Miller. 2015. Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3d shape recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 945–953. Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Christian Szegedy, Wei Liu, Yangqing Jia, Pierre Sermanet, Scott Reed, Dragomir Anguelov, Dumitru Erhan, Vincent Vanhoucke, and Andrew Rabinovich. 2015. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proc. CVPR. 1–9.Google ScholarCross Ref
39. Peng-Shuai Wang, Yang Liu, Yu-Xiao Guo, Chun-Yu Sun, and Xin Tong. 2017. O-cnn: Octree-based convolutional neural networks for 3d shape analysis. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 72. Google ScholarDigital Library
40. Yue Wang, Yongbin Sun, Ziwei Liu, Sanjay E Sarma, Michael M Bronstein, and Justin M Solomon. 2018. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.07829 (2018).Google Scholar
41. Lingyu Wei, Qixing Huang, Duygu Ceylan, Etienne Vouga, and Hao Li. 2016. Dense human body correspondences using convolutional networks. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016 IEEE Conference on. IEEE, 1544–1553.Google ScholarCross Ref
42. Zhirong Wu, Shuran Song, Aditya Khosla, Fisher Yu, Linguang Zhang, Xiaoou Tang, and Jianxiong Xiao. 2015. 3d shapenets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 1912–1920.Google Scholar
43. Kai Xu, Vladimir G Kim, Qixing Huang, Niloy Mitra, and Evangelos Kalogerakis. 2016. Data-driven shape analysis and processing. In SIGGRAPH ASIA 2016 Courses. ACM, 4. Google ScholarDigital Library
44. Li Yi, Hao Su, Xingwen Guo, and Leonidas J. Guibas. 2017. SyncSpecCNN: Synchronized Spectral CNN for 3D Shape Segmentation. In CVPR. IEEE Computer Society, 6584–6592.Google Scholar