“DeepFocus: learned image synthesis for computational displays” by Xiao, Kaplanyan, Fix, Chapman and Lanman
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- DeepFocus: learned image synthesis for computational displays
Session/Category Title: Acquisition, rendering and display for virtual reality
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
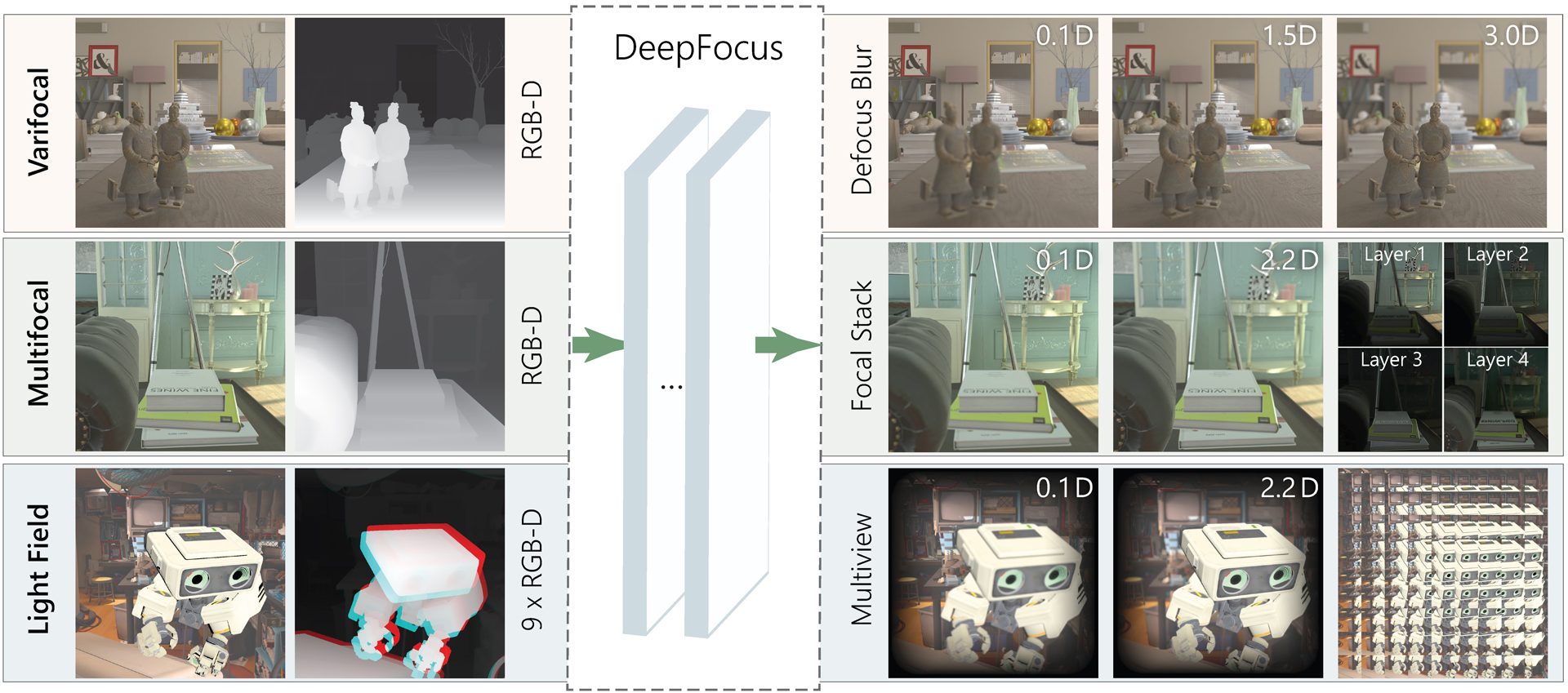
Addressing vergence-accommodation conflict in head-mounted displays (HMDs) requires resolving two interrelated problems. First, the hardware must support viewing sharp imagery over the full accommodation range of the user. Second, HMDs should accurately reproduce retinal defocus blur to correctly drive accommodation. A multitude of accommodation-supporting HMDs have been proposed, with three architectures receiving particular attention: varifocal, multifocal, and light field displays. These designs all extend depth of focus, but rely on computationally expensive rendering and optimization algorithms to reproduce accurate defocus blur (often limiting content complexity and interactive applications). To date, no unified framework has been proposed to support driving these emerging HMDs using commodity content. In this paper, we introduce DeepFocus, a generic, end-to-end convolutional neural network designed to efficiently solve the full range of computational tasks for accommodation-supporting HMDs. This network is demonstrated to accurately synthesize defocus blur, focal stacks, multilayer decompositions, and multiview imagery using only commonly available RGB-D images, enabling real-time, near-correct depictions of retinal blur with a broad set of accommodation-supporting HMDs.
References:
1. Martín Abadi et al. 2015. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. https://www.tensorflow.org/Google Scholar
2. Kaan Akşit, Ward Lopes, Jonghyun Kim, Peter Shirley, and David Luebke. 2017. Near-eye Varifocal Augmented Reality Display Using See-through Screens. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 6 (2017), 189:1–189:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Kurt Akeley, Simon J. Watt, Ahna R. Girshick, and Martin S. Banks. 2004. A Stereo Display Prototype with Multiple Focal Distances. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3 (2004), 804–813. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Brian A. Barsky and Todd J. Kosloff. 2008. Algorithms for Rendering Depth of Field Effects in Computer Graphics. In Proc. ICCOMP. 999–1010. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Johannes Burge and Wilson S. Geisler. 2011. Optimal defocus estimation in individual natural images. PNAS 108 (2011), 16849–16854.Google ScholarCross Ref
6. Chakravarty R. Alla Chaitanya, Anton S. Kaplanyan, Christoph Schied, Marco Salvi, Aaron Lefohn, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Timo Aila. 2017. Interactive Reconstruction of Monte Carlo Image Sequences Using a Recurrent Denoising Autoencoder. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017), 98:1–98:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
7. Gaurav Chaurasia, Sylvain Duchene, Olga Sorkine-Hornung, and George Drettakis. 2013. Depth Synthesis and Local Warps for Plausible Image-based Navigation. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 3 (2013), 30:1–30:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Steven A. Cholewiak, Gordon S. Love, Pratul P. Srinivasan, Ren Ng, and Martin S. Banks. 2017. ChromaBlur: Rendering chromatic eye aberration improves accommodation and realism. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 6 (2017), 210:1–210:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Djork-Arné Clevert, Thomas Unterthiner, and Sepp Hochreiter. 2015. Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (elus). arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.07289 (2015).Google Scholar
10. Robert L. Cook, Thomas Porter, and Loren Carpenter. 1984. Distributed Ray Tracing. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 18, 3 (1984), 137–145. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Joe Demers. 2004. Depth of Field: A Survey of Techniques. In GPU Gems, Randima Fernando (Ed.). Addison-Wesley, 375–390.Google Scholar
12. Piotr Didyk, Pitchaya Sitthi-Amorn, William Freeman, Frédo Durand, and Wojciech Matusik. 2013. Joint View Expansion and Filtering for Automultiscopic 3D Displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6 (2013), 221:1–221:8. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. David Dunn, Cary Tippets, Kent Torell, Petr Kellnhofer, Kaan Akşit, Piotr Didyk, Karol Myszkowski, David Luebke, and Henry Fuchs. 2017. Wide Field Of View Varifocal Near-Eye Display Using See-Through Deformable Membrane Mirrors. IEEE TVCG 23, 4 (2017), 1322–1331. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. John Flynn, Ivan Neulander, James Philbin, and Noah Snavely. 2016. DeepStereo: Learning to Predict New Views From the World’s Imagery. In Proc. CVPR. 5515–5524.Google Scholar
15. Xavier Glorot and Yoshua Bengio. 2010. Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proc. Artificial Intelligence and Statistics. 249–256.Google Scholar
16. Paul Haeberli and Kurt Akeley. 1990. The Accumulation Buffer: Hardware Support for High-quality Rendering. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 24, 4 (1990), 309–318. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, and Jian Sun. 2016. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proc. CVPR. 770–778.Google ScholarCross Ref
18. Robert T. Held, Emily A. Cooper, and Martin S. Banks. 2012. Blur and Disparity Are Complementary Cues to Depth. Current Biology 22 (2012). Issue 5.Google Scholar
19. Robert T. Held, Emily A. Cooper, James F. O’Brien, and Martin S. Banks. 2010. Using Blur to Affect Perceived Distance and Size. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 2 (2010), 19:1–19:16. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. David M. Hoffman, Ahna R. Girshick, Kurt Akeley, and Martin S. Banks. 2008. Vergence-accommodation conflicts hinder visual performance and cause visual fatigue. Journal of Vision 8, 3 (2008), 33.Google ScholarCross Ref
21. Xinda Hu and Hong Hua. 2014. High-resolution optical see-through multi-focal-plane head-mounted display using freeform optics. Optics Express 22, 11 (2014).Google ScholarCross Ref
22. Hong Hua and Bahram Javidi. 2014. A 3D integral imaging optical see-through head-mounted display. Optics Express 22, 11 (2014).Google ScholarCross Ref
23. Fu-Chung Huang, Kevin Chen, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2015. The Light Field Stereoscope: Immersive Computer Graphics via Factored Near-eye Light Field Displays with Focus Cues. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (2015), 60:1–60:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Sergey Ioffe and Christian Szegedy. 2015. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proc. ICML. 448–456. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Nima Khademi Kalantari, Ting-Chun Wang, and Ravi Ramamoorthi. 2016. Learning-Based View Synthesis for Light Field Cameras. ACM Trans. Graph. 35, 6 (2016), 193:1–193:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Petr Kellnhofer, Piotr Didyk, Szu-Po Wang, Pitchaya Sitthi-Amorn, William Freeman, Fredo Durand, and Wojciech Matusik. 2017. 3DTV at Home: Eulerian-Lagrangian Stereo-to-Multiview Conversion. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017), 146:1–146:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Diederik P Kingma and Jimmy Ba. 2014. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980 (2014).Google Scholar
28. Robert Konrad, Emily A. Cooper, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2016. Novel Optical Configurations for Virtual Reality: Evaluating User Preference and Performance with Focus-tunable and Monovision Near-eye Displays. In Proc. SIGCHI. 1211–1220. Google ScholarDigital Library
29. Robert Konrad, Nitish Padmanaban, Keenan Molner, Emily A. Cooper, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2017. Accommodation-invariant Computational Near-eye Displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 4 (2017), 88:1–88:12. Issue 36. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. George-Alex Koulieris, Bee Bui, Martin S Banks, and George Drettakis. 2017. Accommodation and comfort in head-mounted displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017), 87. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Gregory Kramida. 2016. Resolving the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict in Head-Mounted Displays. IEEE TVCG 22, 7 (2016), 1912–1931.Google Scholar
32. Jaroslav Křivánek, Jiří Žára, and Kadi Bouatouch. 2003. Fast Depth of Field Rendering with Surface Splatting. In Proc. Computer Graphics International. 196–201.Google ScholarCross Ref
33. Douglas Lanman and David Luebke. 2013. Near-Eye Light Field Displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 32, 6 (2013), 220:1–220:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Sungkil Lee, Elmar Eisemann, and Hans-Peter Seidel. 2009. Depth-of-field rendering with multiview synthesis. In ACM Trans. Graph., Vol. 28. 134. Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Sungkil Lee, Gerard Jounghyun Kim, and Seungmoon Choi. 2008. Real-time depth-of-field rendering using point splatting on per-pixel layers. In Computer Graphics Forum, Vol. 27. Wiley Online Library, 1955–1962.Google Scholar
36. Sheng Liu and Hong Hua. 2010. A systematic method for designing depth-fused multi-focal plane three-dimensional displays. Optics express 18, 11 (2010), 11562–11573.Google Scholar
37. Gordon D. Love, David M. Hoffman, Philip J.W. Hands, James Gao, Andrew K. Kirby, and Martin S. Banks. 2009. High-speed switchable lens enables the development of a volumetric stereoscopic display. Optics Express 17, 18 (2009).Google Scholar
38. Andrew Maimone, Andreas Georgiou, and Joel S Kollin. 2017. Holographic near-eye displays for virtual and augmented reality. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017), 85. Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Rafat Mantiuk, Kil Joong Kim, Allan G Rempel, and Wolfgang Heidrich. 2011. HDR-VDP-2: a calibrated visual metric for visibility and quality predictions in all luminance conditions. In ACM Trans. Graph., Vol. 30. 40. Google ScholarDigital Library
40. Belen Masia, Gordon Wetzstein, Piotr Didyk, and Diego Gutierrez. 2013. A survey on computational displays: Pushing the boundaries of optics, computation, and perception. Computers & Graphics 37, 8 (2013), 1012 — 1038. Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Nathan Matsuda, Alexander Fix, and Douglas Lanman. 2017. Focal Surface Displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 4 (2017), 86. Google ScholarDigital Library
42. Michael Mauderer, Simone Conte, Miguel A. Nacenta, and Dhanraj Vishwanath. 2014. Depth Perception with Gaze-contingent Depth of Field. In Proc. SIGCHI. 217–226. Google ScholarDigital Library
43. Olivier Mercier, Yusufu Sulai, Kevin Mackenzie, Marina Zannoli, James Hillis, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Douglas Lanman. 2017. Fast Gaze-Contingent Optimal Decompositions for Multifocal Displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 6 (2017), 237. Google ScholarDigital Library
44. O. Nalbach, E. Arabadzhiyska, D. Mehta, H.-P. Seidel, and T. Ritschel. 2017. Deep Shading: Convolutional Neural Networks for Screen Space Shading. Comput. Graph. Forum 36, 4 (2017), 65–78. Google ScholarDigital Library
45. Rahul Narain, Rachel A. Albert, Abdullah Bulbul, Gregory J. Ward, Martin S. Banks, and James F. O’Brien. 2015. Optimal Presentation of Imagery with Focus Cues on Multi-plane Displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4 (2015), 59:1–59:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
46. Mark A. A. Neil, Edward G. S. Paige, and Leon O. D. Sucharov. 1997. Spatial-light-modulator-based three-dimensional multiplanar display. SPIE 3012 (1997), 337–341.Google Scholar
47. Nvidia Corporation. 2017–2018. TensorRT. https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt.Google Scholar
48. Nitish Padmanaban, Robert Konrad, Tal Stramer, Emily A. Cooper, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2017. Optimizing virtual reality for all users through gaze-contingent and adaptive focus displays. PNAS 114, 9 (2017).Google Scholar
49. Deepak Pathak, Philipp Krahenbuhl, Jeff Donahue, Trevor Darrell, and Alexei A Efros. 2016. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2536–2544.Google ScholarCross Ref
50. Olaf Ronneberger, Philipp Fischer, and Thomas Brox. 2015. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, 234–241.Google ScholarCross Ref
51. Kai Selgrad, Christian Reintges, Dominik Penk, Pascal Wagner, and Marc Stamminger. 2015. Real-time depth of field using multi-layer filtering. In Proc. I3D. ACM, 121–127. Google ScholarDigital Library
52. Lixin Shi, Haitham Hassanieh, Abe Davis, Dina Katabi, and Fredo Durand. 2014. Light field reconstruction using sparsity in the continuous fourier domain. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 1 (2014), 12:1–12:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
53. Wenzhe Shi, Jose Caballero, Ferenc Huszár, Johannes Totz, Andrew P Aitken, Rob Bishop, Daniel Rueckert, and Zehan Wang. 2016. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In Proc. CVPR. 1874–1883.Google ScholarCross Ref
54. Takashi Shibata, Joohwan Kim, David M. Hoffman, and Martin S. Banks. 2011. The zone of comfort: Predicting visual discomfort with stereo displays. Journal of Vision 11, 8 (2011), 11.Google ScholarCross Ref
55. M. Shinya. 1994. Post-filtering for Depth of Field Simulation with Ray Distribution Buffer. In Proc. Graphics Interface. 59–66.Google Scholar
56. Shinichi Shiwa, Katsuyuki Omura, and Fumio Kishino. 1996. Proposal for a 3-D display with accommodative compensation: 3DDAC. J. Soc. Information Display 4, 4 (1996).Google ScholarCross Ref
57. Side Effects. 1996–2018. Houdini. http://www.sidefx.com/.Google Scholar
58. Leonard M Smithline. 1974. Accommodative response to blur. JOSA 64, 11 (1974), 1512–1516.Google ScholarCross Ref
59. Pratul P. Srinivasan, Tongzhou Wang, Ashwin Sreelal, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Ren Ng. 2017. Learning to Synthesize a 4D RGBD Light Field from a Single Image. In Proc. ICCV. 2262–2270.Google ScholarCross Ref
60. Qi Sun, Fu-Chung Huang, Joohwan Kim, Li-Yi Wei, David Luebke, and Arie Kaufman. 2017. Perceptually-guided Foveation for Light Field Displays. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 6 (2017), 192:1–192:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
61. Unity Technologies. 2005–2018. Unity Engine. http://unity3d.com.Google Scholar
62. The Foundry. 1993–2018. NUKE. https://www.foundry.com/products/nuke.Google Scholar
63. Marc von Waldkirch. 2005. Retinal projection displays for accommodation-insensitive viewing. Ph.D. Dissertation. ETH Zurich.Google Scholar
64. Zhou Wang, Alan C Bovik, Hamid R Sheikh, and Eero P Simoncelli. 2004. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE TIP 13, 4 (2004), 600–612. Google ScholarDigital Library
65. Sven Wanner and Bastian Goldluecke. 2014. Variational light field analysis for disparity estimation and super-resolution. IEEE TPAMI 36, 3 (2014), 606–619. Google ScholarDigital Library
66. Simon J. Watt, Kevin J. MacKenzie, and Louise Ryan. 2012. Real-world stereoscopic performance in multiple-focal-plane displays: How far apart should the image planes be?. In SPIE Stereoscopic Displays And Applications, Vol. 8288.Google ScholarCross Ref
67. Gordon Wetzstein, Douglas Lanman, Matthew Hirsch, and Ramesh Raskar. 2012. Tensor displays: compressive light field synthesis using multilayer displays with directional backlighting. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4 (2012), 80:1–80:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
68. Sven Widmer, David Pajak, André Schulz, Kari Pulli, Jan Kautz, Michael Goesele, and David Luebke.Luebke. 2015. An Adaptive Acceleration Structure for Screen-space Ray Tracing. In Proc. High Performance Graphics. 67–76. Google ScholarDigital Library
69. Gaochang Wu, Mandan Zhao, Liangyong Wang, Qionghai Dai, Tianyou Chai, and Yebin Liu. 2017. Light field reconstruction using deep convolutional network on EPI. In Proc. CVPR.Google ScholarCross Ref
70. Wanmin Wu, Patrick Llull, Ivana Tošić, Noah Bedard, Kathrin Berkner, and Nikhil Balram. 2016. Content-adaptive focus configuration for near-eye multi-focal displays. In IEEE Multimedia and Expo.Google ScholarCross Ref
71. Yang Yang, Haiting Lin, Zhan Yu, Sylvain Paris, and Jingyi Yu. 2016. Virtual DSLR: High Quality Dynamic Depth-of-Field Synthesis on Mobile Platforms. Electronic Imaging 2016, 18 (2016), 1–9.Google ScholarDigital Library
72. Fisher Yu and Vladlen Koltun. 2015. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.07122 (2015).Google Scholar
73. Fisher Yu and Vladlen Koltun. 2016. Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions. In Proc. ICLR.Google Scholar
74. M Zannoli, GD Love, R Narain, and MS Banks. 2016a. Blur and the perception of depth at occlusions. Journal of vision 16, 6 (2016), 17.Google ScholarCross Ref
75. Marina Zannoli, Gordon D. Love, Rahul Narain, and Martin S. Banks. 2016b. Blur and the perception of depth at occlusions. Journal of Vision 16, 6 (2016), 17.Google ScholarCross Ref
76. Kai Zhang, Wangmeng Zuo, Shuhang Gu, and Lei Zhang. 2017. Learning deep CNN denoiser prior for image restoration. In Proc. CVPR, Vol. 2.Google ScholarCross Ref
77. Zhoutong Zhang, Yebin Liu, and Qionghai Dai. 2015. Light field from micro-baseline image pair. In Proc. CVPR. 3800–3809.Google ScholarCross Ref