“Towards multifocal displays with dense focal stacks”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Towards multifocal displays with dense focal stacks
Session/Category Title: Acquisition, rendering and display for virtual reality
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
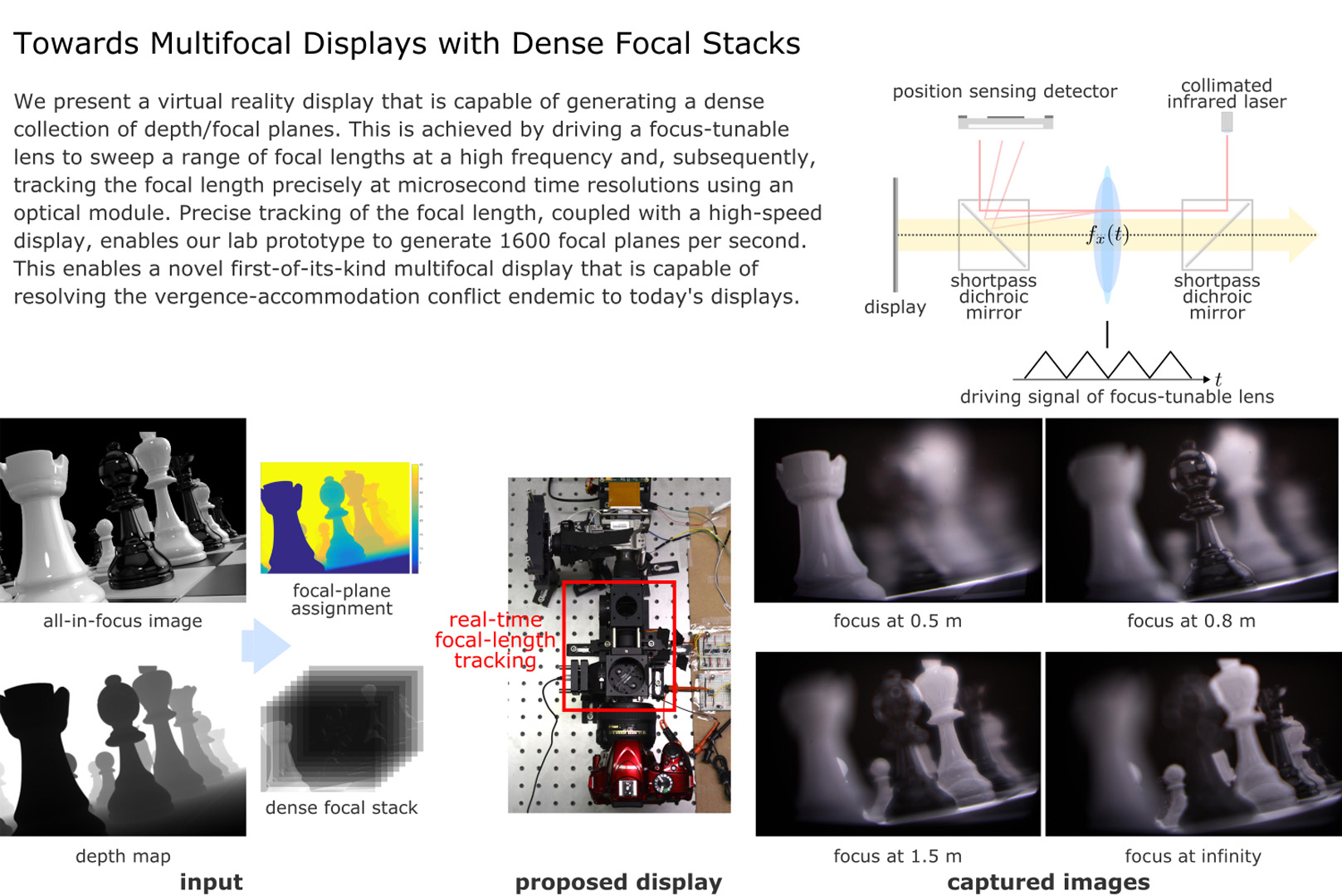
We present a virtual reality display that is capable of generating a dense collection of depth/focal planes. This is achieved by driving a focus-tunable lens to sweep a range of focal lengths at a high frequency and, subsequently, tracking the focal length precisely at microsecond time resolutions using an optical module. Precise tracking of the focal length, coupled with a high-speed display, enables our lab prototype to generate 1600 focal planes per second. This enables a novel first-of-its-kind virtual reality multifocal display that is capable of resolving the vergence-accommodation conflict endemic to today’s displays.
References:
1. Kaan Akşit, Ward Lopes, Jonghyun Kim, Peter Shirley, and David Luebke. 2017. Near-eye Varifocal Augmented Reality Display Using See-through Screens. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 6 (2017), 189:1–189:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Kurt Akeley, Simon J Watt, Ahna Reza Girshick, and Martin S Banks. 2004. A Stereo Display Prototype with Multiple Focal Distances. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 23, 3 (2004), 804–813. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Ehsan Arbabi, Amir Arbabi, Seyedeh Mahsa Kamali, Yu Horie, MohammadSadegh Faraji-Dana, and Andrei Faraon. 2018. MEMS-tunable Dielectric Metasurface Lens. Nature Communications 9, 1 (2018), 812.Google ScholarCross Ref
4. Stefan Bernet and Monika Ritsch-Marte. 2008. Adjustable Refractive Power From Diffractive Moiré Elements. Applied Optics 47, 21 (2008), 3722–3730.Google ScholarCross Ref
5. Fergus W Campbell. 1957. The Depth of Field of the Human Eye. Optica Acta: International Journal of Optics 4, 4 (1957), 157–164.Google ScholarCross Ref
6. Jen-Hao Rick Chang, BVK Vijaya Kumar, and Aswin C Sankaranarayanan. 2016. 216 Shades of Gray: High Bit-depth Projection using Light Intensity Control. Optics Express 24, 24 (2016), 27937–27950.Google ScholarCross Ref
7. Gerwin Damberg, James Gregson, and Wolfgang Heidrich. 2016. High brightness HDR projection using dynamic freeform lensing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 35, 3 (2016), 24:1–24:11. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. eMirage. 2017. Barcelona Pavillion. https://download.blender.org/demo/test/pabellon_barcelona_v1.scene_.zip.Google Scholar
9. David M Hoffman, Ahna R Girshick, Kurt Akeley, and Martin S Banks. 2008. Vergence-accommodation Conflicts Hinder Visual Performance and Cause Visual Fatigue. Journal of Vision 8, 3 (2008), 33.Google ScholarCross Ref
10. Xinda Hu and Hong Hua. 2014. High-Resolution Optical See-Through Multi-focal-plane Head-mounted Display Using Freeform Optics. Optics Express 22, 11 (2014), 13896–13903.Google ScholarCross Ref
11. Hong Hua. 2017. Enabling Focus Cues in Head-mounted Displays. Proc. IEEE 105, 5 (2017), 805–824.Google ScholarCross Ref
12. Fu-Chung Huang, Kevin Chen, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2015. The Light Field Stereoscope: Immersive Computer Graphics via Factored Near-eye Light Field Displays with Focus Cues. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4 (2015), 60:1–60:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Afsoon Jamali, Douglas Bryant, Yanli Zhang, Anders Grunnet-Jepsen, Achintya Bhowmik, and Philip J Bos. 2018a. Design of a Large Aperture Tunable Refractive Fresnel Liquid Crystal Lens. Applied Optics 57, 7 (2018), B10–B19.Google ScholarCross Ref
14. Afsoon Jamali, Comrun Yousefzadeh, Colin McGinty, Douglas Bryant, and Philip Bos. 2018b. A Continuous Variable Lens System to Address the Accommodation Problem in VR and 3D Displays. In Imaging and Applied Optics. 3Tu2G.5.Google Scholar
15. Alexei A. Goon Jannick P. Rolland, Myron W. Krueger. 1999. Dynamic Focusing in Head-mounted Displays. Proceeding of SPIE 3639 (1999), 3639–3639-8.Google Scholar
16. Paul V Johnson, Jared AQ Parnell, Joohwan Kim, Christopher D Saunter, Gordon D Love, and Martin S Banks. 2016. Dynamic Lens and Monovision 3D Displays to Improve Viewer Comfort. Optics Express 24, 11 (2016), 11808–11827.Google ScholarCross Ref
17. Robert Konrad, Emily A Cooper, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2016. Novel Optical Configurations for Virtual Reality: Evaluating User Preference and Performance with Focus-tunable and Monovision Near-eye Displays. In Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI). 1211–1220. Google ScholarDigital Library
18. Robert Konrad, Nitish Padmanaban, Keenan Molner, Emily A Cooper, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2017. Accommodation-invariant Computational Near-eye Displays. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 88:1–88:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Gregory Kramida. 2016. Resolving the Vergence-accommodation Conflict in Head-mounted Displays. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 22, 7 (2016), 1912–1931.Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Douglas Lanman and David Luebke. 2013. Near-eye Light Field Displays. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 6 (2013), 220:1–220:10. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Seungjae Lee, Youngjin Jo, Dongheon Yoo, Jaebum Cho, Dukho Lee, and Byoungho Lee. 2018. TomoReal: Tomographic Displays. arXiv:1804.04619 (2018).Google Scholar
22. Peter Lincoln, Alex Blate, Montek Singh, Andrei State, Mary C. Whitton, Turner Whitted, and Henry Fuchs. 2017. Scene-adaptive High Dynamic Range Display for Low Latency Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the 21st ACM SIGGRAPH Symposium on Interactive 3D Graphics and Games. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Peter Lincoln, Alex Blate, Montek Singh, Turner Whitted, Andrei State, Anselmo Lastra, and Henry Fuchs. 2016. From Motion to Photons in 80 Microseconds: Towards Minimal Latency for Virtual and Augmented Reality. Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 22, 4 (2016), 1367–1376. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Sheng Liu, Dewen Cheng, and Hong Hua. 2008. An Optical See-through Head Mounted Display with Addressable Focal Planes. In IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality. 33–42. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Sheng Liu and Hong Hua. 2009. Time-multiplexed Dual-focal Plane Head-mounted Display with a Liquid Lens. Optics Letters 34, 11 (2009), 1642–1644.Google ScholarCross Ref
26. Patrick Llull, Noah Bedard, Wanmin Wu, Ivana Tosic, Kathrin Berkner, and Nikhil Balram. 2015. Design and Optimization of a Near-eye Multifocal Display System for Augmented Reality. In Imaging and Applied Optics. JTH3A.5.Google Scholar
27. Gordon D Love, David M Hoffman, Philip JW Hands, James Gao, Andrew K Kirby, and Martin S Banks. 2009. High-speed Switchable Lens Enables the Development of a Volumetric Stereoscopic Display. Optics Express 17, 18 (2009), 15716–15725.Google ScholarCross Ref
28. Kevin J MacKenzie, Ruth A Dickson, and Simon J Watt. 2012. Vergence and Accommodation to Multiple-image-plane Stereoscopic Displays: “Real World” Responses with Practical Image-plane Separations? Journal of Electronic Imaging 21 (2012), 21–21-9.Google ScholarCross Ref
29. Kevin J MacKenzie, David M Hoffman, and Simon J Watt. 2010. Accommodation to Multiple-focal-plane Displays: Implications for Improving Stereoscopic Displays and for Accommodation Control. Journal of Vision 10, 8 (2010), 22.Google ScholarCross Ref
30. Andrew Maimone, Andreas Georgiou, and Joel S Kollin. 2017. Holographic Near-eye Displays for Virtual and Augmented Reality. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 85:1–85:16. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Nathan Matsuda, Alexander Fix, and Douglas Lanman. 2017. Focal Surface Displays. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 4 (2017), 86:1–86:14. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Olivier Mercier, Yusufu Sulai, Kevin Mackenzie, Marina Zannoli, James Hillis, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Douglas Lanman. 2017. Fast Gaze-contingent Optimal Decompositions for Multifocal Displays. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 6 (2017), 237:1–237:15. Google ScholarDigital Library
33. Daniel Miau, Oliver Cossairt, and Shree K Nayar. 2013. Focal Sweep Videography with Deformable Optics. In IEEE Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP).Google Scholar
34. Rahul Narain, Rachel A Albert, Abdullah Bulbul, Gregory J Ward, Martin S Banks, and James F O’Brien. 2015. Optimal Presentation of Imagery with Focus Cues on Multi-plane Displays. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 34, 4 (2015), 59:1–59:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Optotune. 2017. Optotune Electrically Tunable Lens EL-10-30. http://www.optotune.com/images/products/Optotune.Google Scholar
36. Nitish Padmanaban, Robert Konrad, Tal Stramer, Emily A Cooper, and Gordon Wetzstein. 2017. Optimizing Virtual Reality for All Users Through Gaze-contingent and Adaptive Focus Displays. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 114, 9 (2017), 2183–2188.Google ScholarCross Ref
37. Sowmya Ravikumar, Kurt Akeley, and Martin S Banks. 2011. Creating Effective Focus Cues in Multi-plane 3D Displays. Optics Express 19, 21 (2011), 20940–20952.Google ScholarCross Ref
38. Shinichi Shiwa, Katsuyuki Omura, and Fumio Kishino. 1996. Proposal for a 3-D Display with Accommodative Compensation: 3DDAC. Journal of the Society for Information Display 4, 4 (1996), 255–261.Google ScholarCross Ref
39. Toshiaki Sugihara and Tsutomu Miyasato. 1998. System Development of Fatigue-less HMD System 3DDAC (3D Display with Accommodative Compensation: System implementation of Mk. 4 in Light-weight HMD. In ITE Technical Report 22.1. 33–36.Google Scholar
40. Qi Sun, Fu-Chung Huang, Joohwan Kim, Li-Yi Wei, David Luebke, and Arie Kaufman. 2017. Perceptually-guided Foveation for Light Field Displays. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 36, 6 (2017), 192:1–192:13. Google ScholarDigital Library
41. Nelson V Tabiryan, Svetlana V Serak, David E Roberts, Diane M Steeves, and Brian R Kimball. 2015. Thin Waveplate Lenses of Switchable Focal Length-New Generation in Optics. Optics express 23, 20 (2015), 25783–25794.Google Scholar
42. Varioptic. 2017. Varioptic Variable Focus Liquid Lens ARCTIC 25H. http://varioptic.com/media/cms_page_media/45/MADS_-_160429_-_Arctic_25H_family.pdf.Google Scholar
43. Dhanraj Vishwanath and Erik Blaser. 2010. Retinal Blur and the Perception of Egocentric Distance. Journal of Vision 10, 10 (2010), 26.Google ScholarCross Ref
44. Simon J Watt, Kurt Akeley, Marc O Ernst, and Martin S Banks. 2005. Focus Cues Affect Perceived Depth. Journal of Vision 5, 10 (2005), 7.Google ScholarCross Ref
45. Gordon Wetzstein, Douglas Lanman, Wolfgang Heidrich, and Ramesh Raskar. 2011. Layered 3D: Tomographic Image Synthesis for Attenuation-based Light Field and High Dynamic Range Displays. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 30, 4 (2011), 95:1–95:12. Google ScholarDigital Library
46. Marina Zannoli, Gordon D Love, Rahul Narain, and Martin S Banks. 2016. Blur and the Perception of Depth at Occlusions. Journal of Vision 16, 6 (2016), 17.Google ScholarCross Ref