“Dynamic Split Body: Changing Body Perception and Self-Location by Manipulating Half-Body Position” by Kondo and Sugimoto
Conference:
Experience Type(s):
Title:
- Dynamic Split Body: Changing Body Perception and Self-Location by Manipulating Half-Body Position
Organizer(s)/Presenter(s):
Description:
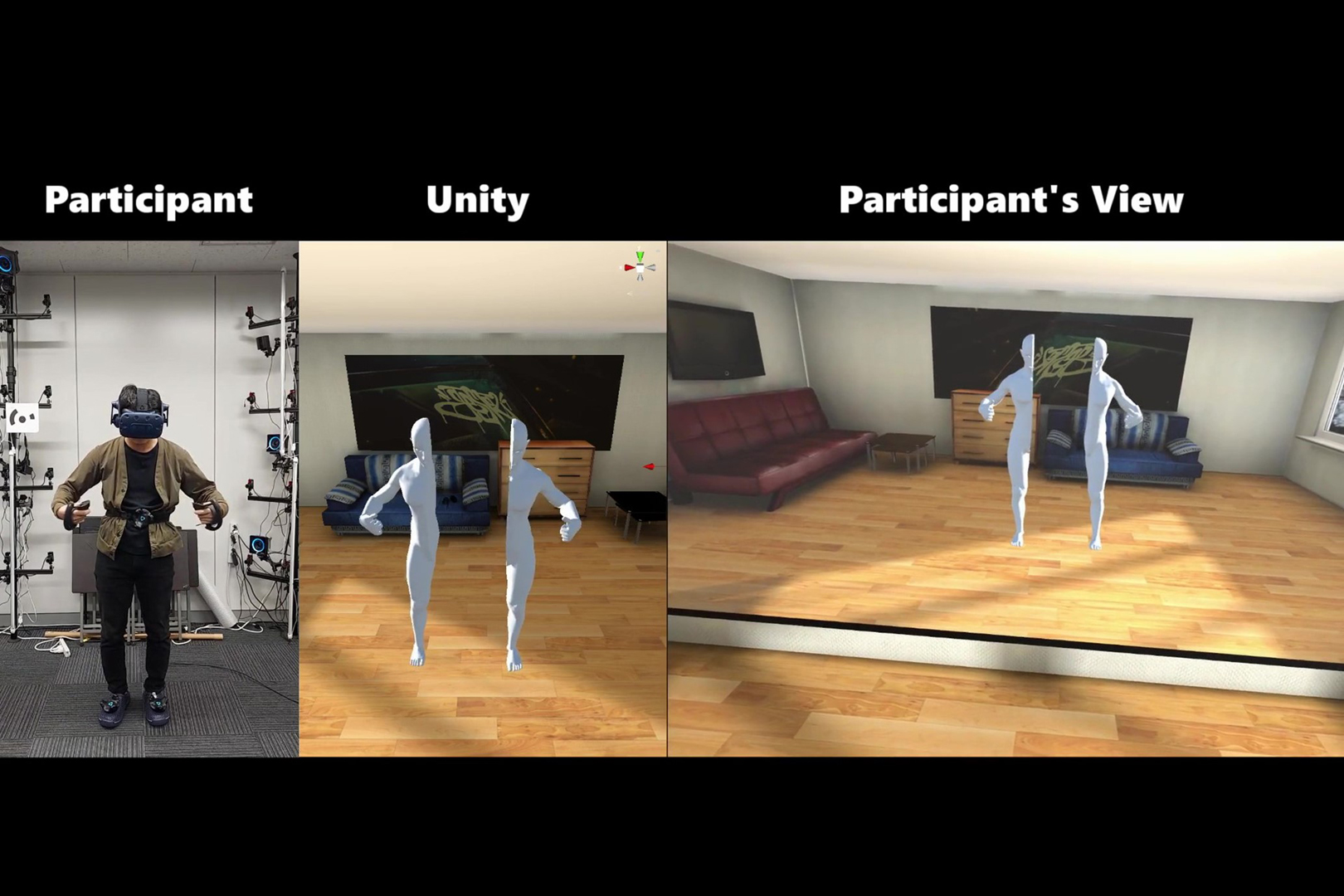
Some studies have been conducted to induce the sense of being in two locations by inducing body ownership in two bodies. However, the feeling of being in two locations was weak. In our previous study, we induced body ownership in a split avatar in advance to induce the sensation of being at two locations. As a result, although participants’ self-location extended to the right, the split avatar was perceived as a single body and they did not feel as if they were in two locations. Our demonstration expand our previous work by allowing participants to dynamically manipulate the position of the split body. We attempt to present an experience in which the split body is perceived as one body even though it is split, or the participants feel as if they are in two locations as two independent bodies. We also changed tracking system from OptiTrack to Lighthouse.
References:
[1] Laura Aymerich-Franch, Damien Petit, Gowrishankar Ganesh, and Abderrahmane Kheddar. 2016. The second me: Seeing the real body during humanoid robot embodiment produces an illusion of bi-location. Consciousness and cognition 46 (2016), 99–109.
[2] Mar Gonzalez-Franco, Daniel Perez-Marcos, Bernhard Spanlang, and Mel Slater. 2010. The contribution of real-time mirror reflections of motor actions on virtual body ownership in an immersive virtual environment. In 2010 IEEE virtual reality conference (VR). IEEE, 111–114.
[3] Arvid Guterstam, Dennis EO Larsson, Joanna Szczotka, and H Henrik Ehrsson. 2020. Duplication of the bodily self: a perceptual illusion of dual full-body ownership and dual self-location. Royal Society open science 7, 12 (2020), 201911.
[4] Ryota Kondo and Maki Sugimoto. 2022. Split body: Extending self-location by splitting a body left and right. Frontiers in Virtual Reality 3 (2022), 992803.
[5] Ryota Kondo, Yamato Tani, Maki Sugimoto, Masahiko Inami, and Michiteru Kitazaki. 2020. Scrambled body differentiates body part ownership from the full body illusion. Scientific reports 10, 1 (2020), 5274.
[6] Bigna Lenggenhager, Tej Tadi, Thomas Metzinger, and Olaf Blanke. 2007. Video ergo sum: manipulating bodily self-consciousness. Science 317, 5841 (2007), 1096–1099.
[7] Ivan Poupyrev, Mark Billinghurst, Suzanne Weghorst, and Tadao Ichikawa. 1996. The go-go interaction technique: non-linear mapping for direct manipulation in VR. In Proceedings of the 9th annual ACM symposium on User interface software and technology. 79–80.