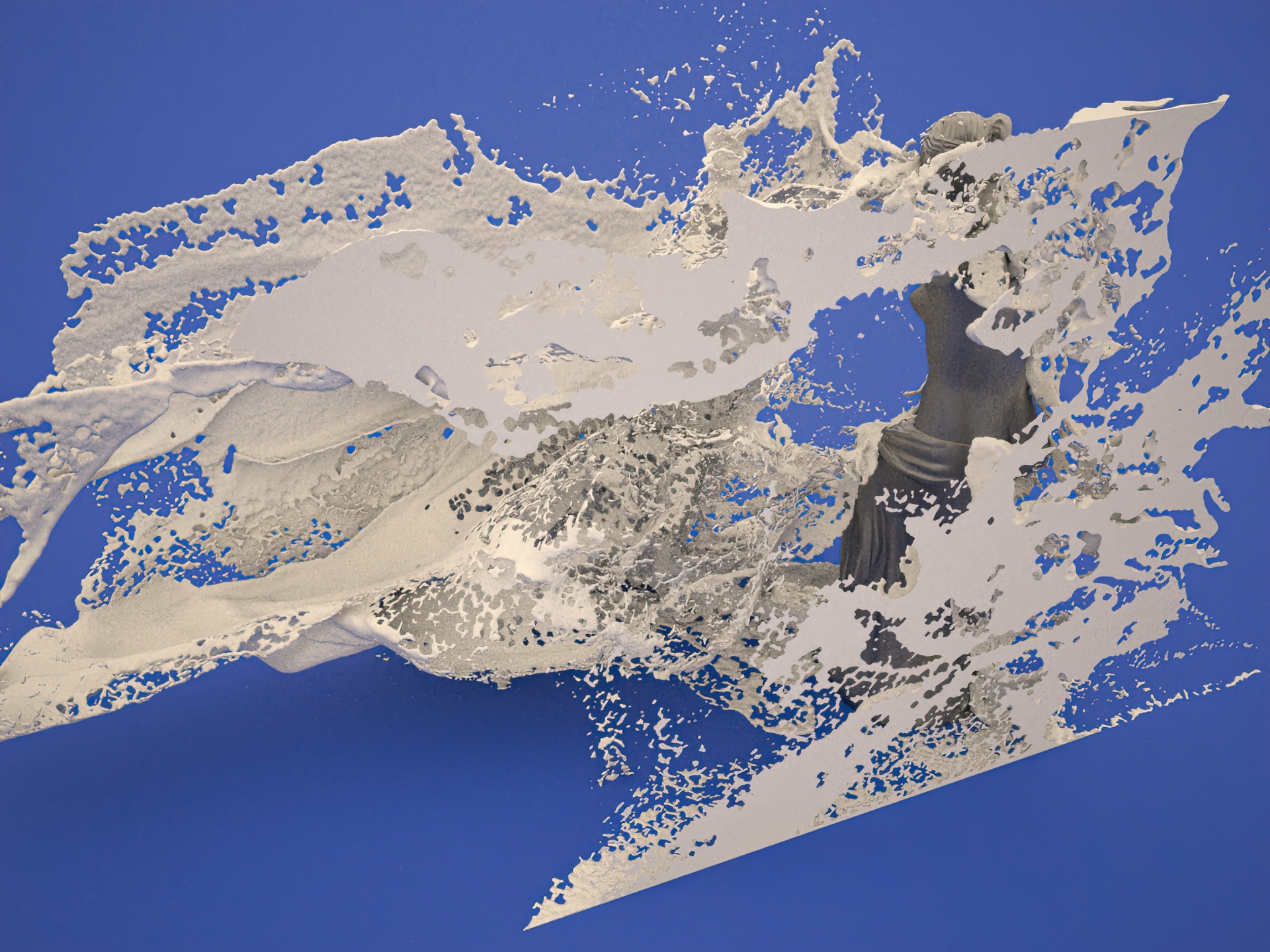
“Stretching and wiggling liquids”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Stretching and wiggling liquids
Session/Category Title:
- Physically based animation
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
This paper presents a novel framework for simulating the stretching and wiggling of liquids. We demonstrate that complex phase-interface dynamics can be effectively simulated by introducing the Eulerian vortex sheet method, which focuses on the vorticity at the interface (rather than the whole domain). We extend this model to provide user control for the production of visual effects. Then, the generated fluid flow creates complex surface details, such as thin and wiggling fluid sheets. To capture such high-frequency features efficiently, this work employs a denser grid for surface tracking in addition to the (coarser) simulation grid. In this context, the paper proposes a filter, called the liquid-biased filter, which is able to downsample the surface in the high-resolution grid into the coarse grid without unrealistic volume loss resulting from aliasing error. The proposed method, which runs on a single PC, realistically reproduces complex fluid scenes.
References:
1. Adams, B., Pauly, M., Keiser, R., and Guibas, L. J. 2007. Adaptively sampled particle fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3, 48. Google ScholarDigital Library
2. Bargteil, A. W., Goktekin, T. G., O’brien, J. F., and Strain, J. A. 2006. A semi-lagrangian contouring method for fluid simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 1, 19–38. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Bridson, R., Houriham, J., and Nordenstam, M. 2007. Curl-noise for procedural fluid flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3, 46. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Chentanez, N., Feldman, B. E., Labelle, F., O’Brien, J. F., and Shewchuk, J. R. 2007. Liquid simulation on lattice-based tetrahedral meshes. In SCA ’07: Proceedings of the 2007 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation, 219–228. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Enright, D., Marschner, S., and Fedkiw, R. 2002. Animation and rendering of complex water surfaces. ACM Trans. Graph. 21, 3, 736–744. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Enright, D., Nguyen, D., Gibou, F., and Fedkiw, R. 2003. Using the particle level set method and a second order accurate pressure boundary condition for free surface flows. In In Proc. 4th ASME-JSME Joint Fluids Eng. Conf., number FEDSM2003-45144. ASME, 1–6.Google Scholar
7. Fedkiw, R., Stam, J., and Jensen, H. W. 2001. Visual simulation of smoke. Computer Graphics (Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH 2001) 35, 15–22. Google ScholarDigital Library
8. Foster, N., and Fedkiw, R. 2001. Practical animation of liquids. Computer Graphics (Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH 2001) 35, 23–30. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. Gibou, F., Fedkiw, R. P., Cheng, L.-T., and Kang, M. 2002. A second-order-accurate symmetric discretization of the poisson equation on irregular domains. J. Comp. Phys. 176, 1, 205–227. Google ScholarDigital Library
10. Goktekin, T. G., Bargteil, A. W., and O’Brien, J. F. 2004. A method for animating viscoelastic fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3, 463–468. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Herrmann, M. 2003. Modeling primary breakup: A three-dimensional eulerian level set/vortex sheet method for two-phase interface dynamics. Annual Research Briefs, Center for Turbulence Research.Google Scholar
12. Herrmann, M. 2005. A eulerian level set/vortex sheet method for two-phase interface dynamics. J. Comp. Phys. 203, 2, 539–571. Google ScholarDigital Library
13. Hong, J.-M., and Kim, C.-H. 2005. Discontinuous fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3, 915–920. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Hong, J.-M., Lee, H.-Y., Yoon, J.-C., and Kim, C.-H. 2008. Bubbles alive. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3, 48. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Houston, B., Nielsen, M. B., Batty, C., Nilsson, O., and Museth, K. 2006. Hierarchical rle level set: A compact and versatile deformable surface representation. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 1, 151–175. Google ScholarDigital Library
16. Kim, B., Liu, Y., Llamas, I., and Rossignac, J. 2007. Advections with significantly reduced dissipation and diffusion. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 13, 1, 135–144. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Kim, D., Song, O.-Y., and Ko, H.-S. 2008. A semi-lagrangian cip fluid solver without dimensional splitting. Computer Graphics Forum 27, 2, 467–475.Google ScholarCross Ref
18. Kim, T., Thürey, N., James, D., and Gross, M. 2008. Wavelet turbulence for fluid simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3, 50. Google ScholarDigital Library
19. Losasso, F., Gibou, F., and Fedkiw, R. 2004. Simulating water and smoke with an octree data structure. ACM Trans. Graph. 23, 3, 457–462. Google ScholarDigital Library
20. Losasso, F., Shinar, T., Selle, A., and Fedkiw, R. 2006. Multiple interacting liquids. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3, 812–819. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Losasso, F., Talton, J., Kwatra, N., and Fedkiw, R. 2008. Two-way coupled sph and particle level set fluid simulation. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 14, 4, 797–804. Google ScholarDigital Library
22. Marschner, S. R., and Lobb, R. J. 1994. An evaluation of reconstruction filters for volume rendering. In Proceedings of Visualization ’94, 100–107. Google ScholarDigital Library
23. Mihalef, V., Metaxas, D., and Sussman, M. 2007. Textured liquids based on the marker level set. Comput. Graph. Forum 26, 3, 457–466.Google ScholarCross Ref
24. Müller, M., Charypar, D., and Gross, M. 2003. Particle-based fluid simulation for interactive applications. In Proceedings of the 2003 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics symposium on Computer animation, 154–159. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Narain, R., Sewall, J., Carlson, M., and Lin, M. C. 2008. Fast animation of turbulence using energy transport and procedural synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 5, 166. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Perlin, K. 1985. An image synthesizer. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 19, 3, 287–296. Google ScholarDigital Library
27. Pozrikidis, C. 2000. Theoretical and computational aspects of the self-induced motion of three-dimensional vortex sheets. J. Fluid Mech. 425, 335–366.Google ScholarCross Ref
28. Premože, S., Tasdizen, T., Bigler, J., Lefohn, A., and Whitaker, R. T. 2003. Particle-based simulation of fluids. Computer Graphics Forum 22, 3, 401–410.Google ScholarCross Ref
29. Schechter, H., and Bridson, R. 2008. Evolving sub-grid turbulence for smoke animation. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation. Google ScholarDigital Library
30. Selle, A., Rasmussen, N., and Fedkiw, R. 2005. A vortex particle method for smoke, water and explosions. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3, 910–914. Google ScholarDigital Library
31. Selle, A., Fedkiw, R., Kim, B., Liu, Y., and Rossignac, J. 2008. An unconditionally stable maccormack method. J. Sci. Comput. 35, 2–3, 350–371. Google ScholarDigital Library
32. Sethian, J. 1999. Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods. Cambridge University Press.Google Scholar
33. Solenthaler, B., and Pajarola, R. 2009. Predictive-corrective incompressible sph. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, 40. Google ScholarDigital Library
34. Song, O.-Y., Shin, H., and Ko, H.-S. 2005. Stable but non-dissipative water. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 1, 81–97. Google ScholarDigital Library
35. Song, O.-Y., Kim, D., and Ko, H.-S. 2007. Derivative particles for simulating detailed movements of fluids. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 13, 4, 711–719. Google ScholarDigital Library
36. Stam, J. 1999. Stable fluids. Computer Graphics (Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH ’99) 33, Annual Conference Series, 121–128. Google ScholarDigital Library
37. Tryggvason, G. 1988. Numerical simulations of the rayleigh-taylor instability. J. Comp. Phys. 75, 2, 253–282. Google ScholarDigital Library
38. Wojtan, C., and Turk, G. 2008. Fast viscoelastic behavior with thin features. ACM Trans. Graph. 27, 3, 47. Google ScholarDigital Library
39. Zhu, Y., and Bridson, R. 2005. Animating sand as a fluid. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3, 965–972. Google ScholarDigital Library