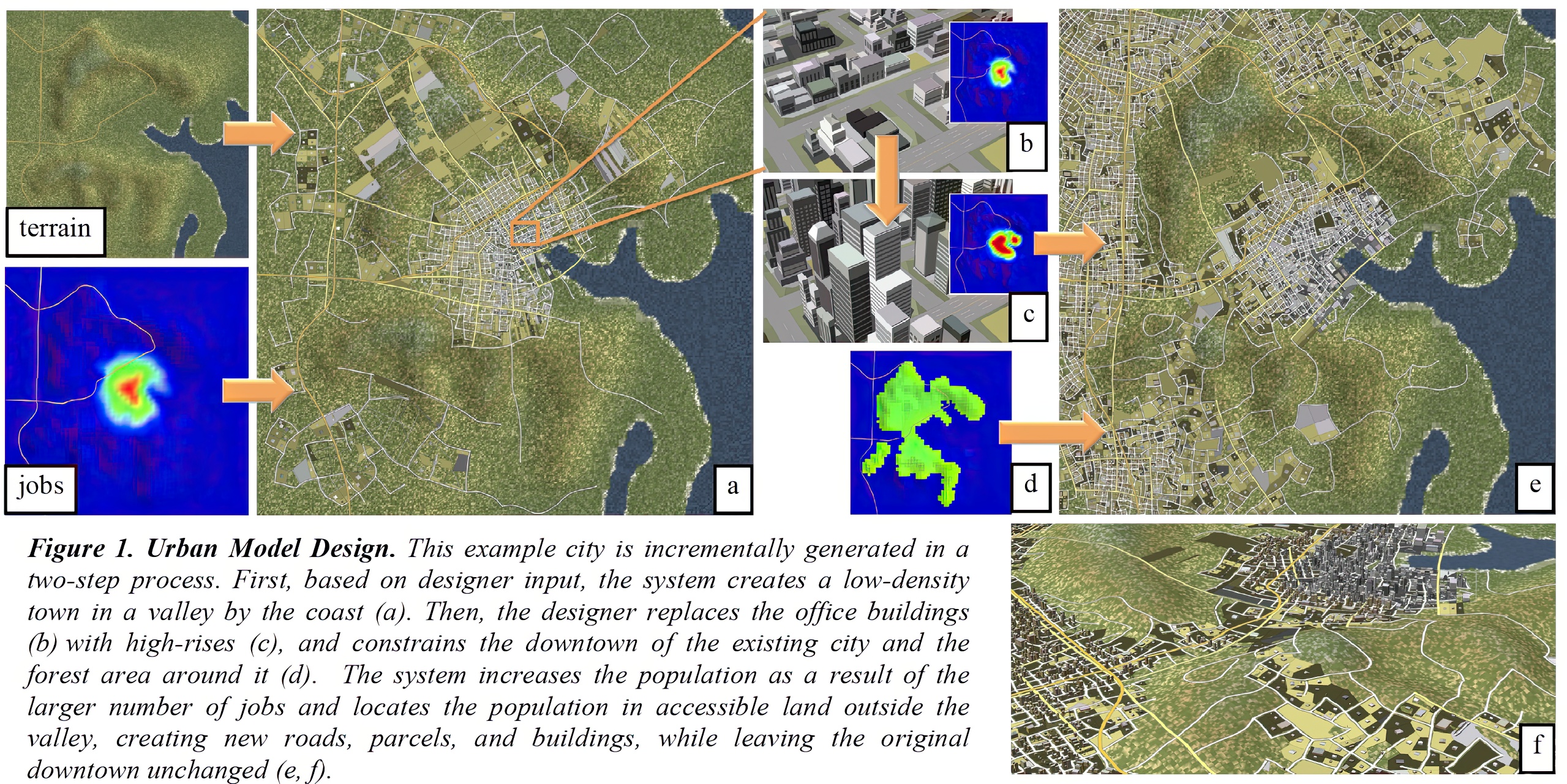
“Interactive design of urban spaces using geometrical and behavioral modeling”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Interactive design of urban spaces using geometrical and behavioral modeling
Session/Category Title:
- Urban modeling
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Moderator(s):
Abstract:
The main contribution of our work is in closing the loop between behavioral and geometrical modeling of cities. Editing of urban design variables is performed intuitively and visually using a graphical user interface. Any design variable can be constrained or changed. The design process uses an iterative dynamical system for reaching equilibrium: a state where the demands of behavioral modeling match those of geometrical modeling. 3D models are generated in a few seconds and conform to plausible urban behavior and urban geometry. Our framework includes an interactive agent-based behavioral modeling system as well as adaptive geometry generation algorithms. We demonstrate interactive and incremental design and editing for synthetic urban spaces spanning over 200 square kilometers.
References:
1. AASHTO, 2004. AASHTO Green Book – A Policy on Geometric Design of Highways and Streets, 5th Edition, American Association of State and Highway Transportation Officials.Google Scholar
2. Aliaga, D. G., Vanegas, C. A., and Beneš, B. 2008. Interactive example-based urban layout synthesis. ACM Trans. on Graphics, 27(5), 160. Google ScholarDigital Library
3. Alkheder, S., Wang, J., and Shan, J. 2008. Fuzzy inference guided cellular automata urban-growth modeling using multitemporal satellite images. Int. J. of GIS 22, 11–12, 1271–1293. Google ScholarDigital Library
4. Chen, G., Esch, G., Wonka, P., Mueller, P., and Zhang, E. 2008. Interactive procedural street modeling. ACM Trans. on Graphics, 27(3), 103. Google ScholarDigital Library
5. Honda M., Mizuno K., Fukui Y., Nishihara S., 2004. Generating Autonomous Time-Varying Virtual Cities. International Conference on Cyberworlds, 45–52. Google ScholarDigital Library
6. Lechner, T., Watson, B. A., Wilensky, U., Tisue, S., Felsen, M., Moddrell, A., Ren, P., and Brozefsky, C., 2007. Procedural modeling of urban land use. NC State Univ., CS-TR-2007-33.Google Scholar
7. Leonard, K., Clarke, C., Gaydos, J. 1998. Loose-coupling a cellular automaton model and GIS: long-term urban growth prediction for San Francisco and Washington/Baltimore. International Journal of GIS, 12(7), 699–714.Google Scholar
8. Lipp, M., Wonka, P., and Wimmer, M. 2008. Interactive visual editing of grammars for procedural architecture. ACM Trans. on Graphics, 27(3), 102. Google ScholarDigital Library
9. McFadden D., 1973. Conditional logic analysis of qualitative choice behavior. Frontiers in Econometrics, New York, Academic Press.Google Scholar
10. Měch, R. and Prusinkiewicz, P. 1996. Visual models of plants interacting with their environment. In Proc of. SIGGRAPH 1996, 397–410. Google ScholarDigital Library
11. Merrell, P. and Manocha, D. 2008. Continuous model synthesis. ACM Trans. on Graphics, 27(5), 158. Google ScholarDigital Library
12. Montes de Oca, N., Levinson D., 2006. Network Expansion Decision-making in the Twin Cities. Journal of the Transportation Research Board: Transportation Research Record, Volume 1981, 1–11.Google ScholarCross Ref
13. Mueller, P., Wonka, P., Haegler, S., Ulmer, A., and Van Gool, L. 2006. Procedural modeling of buildings. ACM Trans. on Graphics, 25(3), 614–623. Google ScholarDigital Library
14. Mueller, P., Zeng, G., Wonka, P., and Van Gool, L. 2007. Image-based procedural modeling of facades. ACM Trans. on Graphics, 26(3), 85. Google ScholarDigital Library
15. Ortúzar S. J. D. and L. G. Willumsen, 2001. Modelling transport, Wiley, 3rd edition.Google Scholar
16. Parish, Y. I. and Mueller, P. 2001. Procedural modeling of cities. In Proc. of SIGGRAPH 2001, 301–308. Google ScholarDigital Library
17. Portugali J., 2000. Self-organization and the city. Springer.Google Scholar
18. Procedural Inc. 2009. www.procedural.com.Google Scholar
19. Putman, S., Hasnol Zam Zam, A., Choi K., McCarthy W., Yan Y., 2000. Integrated Transportation and Land Use Policy Analysis for Sacramento, California, Transp. Research Record, Volume 1722, 38–47.Google ScholarCross Ref
20. Reynolds, C. W. 1987. Flocks, herds, and schools: A distributed behavioral model. Computer Graphics (Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 87), 25–34. Google ScholarDigital Library
21. Sung, M., Gleicher, M., and Cheney, S., 2004. Scalable behaviors for crowd simulation. Computer Graphics Forum, 23(3), 519–528.Google ScholarCross Ref
22. Train, K. 2003. Discrete Choice Models with Simulation. Cambridge University Press.Google Scholar
23. Treuille A., Cooper S., Popović, Z., 2006. Continuum Crowds, ACM Trans. on Graphics, 25(3), 1160–1168. Google ScholarDigital Library
24. Tu, X., and Terzopouolos, D. 1994. Artificial fishes: Physics, locomotion, perception, behavior. In Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 1994, 43–50. Google ScholarDigital Library
25. Vanegas, C. A., Aliaga, D, Beneš, B, and Waddell, P., 2009 Visualization of Simulated Urban Spaces: Inferring Parameterized Generation of Streets, Parcels, and Aerial Imagery, IEEE Trans. Vis. and Comp. Graphics, 15(3), 424–435. Google ScholarDigital Library
26. Waddell, P., 2002. UrbanSim: Modeling Urban Development for Land Use, Transportation and Environmental Planning. Journal of the American Planning Association, 68(3), 297–314.Google ScholarCross Ref
27. Waddell, P., Ulfarsson, F., 2004. Introduction to Urban Simulation: Design and Development of Operational Models. Handbook in Transport, Volume 5: Transport Geography and Spatial Systems, Pergamon Press, 203–236.Google ScholarCross Ref
28. Weber, B., Muller, P, Wonka, P, and Gross, M, 2009, Interactive Geometric Simulation of 4D Cities, Computer Graphics Forum (Eurographics), 28(2), 481–492.Google ScholarCross Ref
29. Wonka, P., Wimmer, M., Sillion, F., and Ribarsky, W. 2003. Instant architecture. ACM Trans. on Graphics, 22(3), 669–677. Google ScholarDigital Library