“Adaptive Grid Generation for Discretizing Implicit Complexes”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Adaptive Grid Generation for Discretizing Implicit Complexes
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
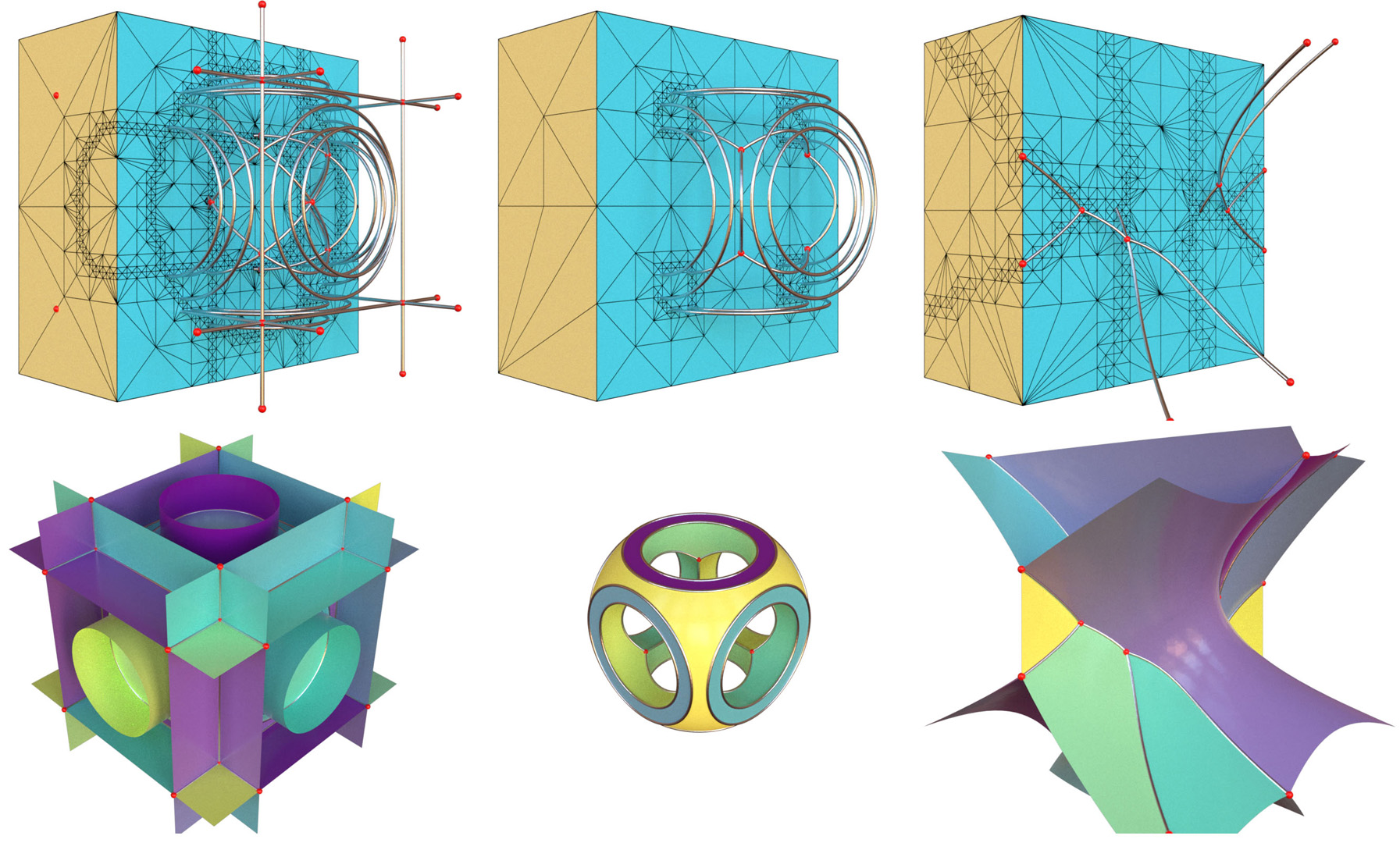
We present a method for generating a simplicial (e.g., triangular or tetrahedral) grid to enable adaptive discretization of implicit shapes defined by a vector function, including the arrangement of implicit surfaces, CSG shapes, material interfaces, and curve networks.
References:
[1]
Eugene Allgower and Kurt Georg. 1980. Simplicial and Continuation Methods for Approximating Fixed Points and Solutions to Systems of Equations. SIAM Rev. 22, 1 (jan 1980), 28–85.
[2]
Eugene L. Allgower and Kurt Georg. 1989. Estimates for piecewise linear approximations of implicitly defined manifolds. Applied Mathematics Letters 2 (1989), 111–115. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:123564143
[3]
Eugene L. Allgower and Phillip H. Schmidt. 1985. An Algorithm for Piecewise-Linear Approximation of an Implicitly Defined Manifold. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 22, 2 (1985), 322–346. arXiv:https://doi.org/10.1137/0722020
[4]
Robert Anderson, Julian Andrej, Andrew Barker, Jamie Bramwell, Jean-Sylvain Camier, Jakub Cerveny, Veselin Dobrev, Yohann Dudouit, Aaron Fisher, Tzanio Kolev, et al. 2021. MFEM: A Modular Finite Element Methods Library. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 81 (2021), 42–74.
[5]
Douglas N. Arnold, Arup K. Mukherjee, and Luc Pouly. 2000. Locally Adapted Tetrahedral Meshes Using Bisection. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 22 (2000), 431–448. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:13167330
[6]
Sergei Azernikov and Anath Fischer. 2005. Anisotropic Meshing of Implicit Surfaces. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Shape Modeling and Applications 2005 (SMI ’05). IEEE Computer Society, USA, 94–103.
[7]
Brigham Bagley, Shankar Sastry, and Ross Whitaker. 2016. A Marching-tetrahedra Algorithm for Feature-preserving Meshing of Piecewise-smooth Implicit Surfaces. Procedia Engineering 163 (12 2016), 162–174.
[8]
Eberhard B?nsch. 1991. Local mesh refinement in 2 and 3 dimensions. IMPACT Comput. Sci. Eng. 3 (1991), 181–191. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:33479075
[9]
Guillem Belda Ferr?n, Eloi Ruiz Giron?s, and Francisco Javier Roca Navarro. 2022. Bisecting with Optimal Similarity Bound on 3D Unstructured Conformal Meshes. In Proceedings of the 2022 SIAM International Meshing Roundtable. Zenodo, USA, 86–87.
[10]
Martin Bertram, Gerd Reis, Rolf Hendrik van Lengen, Sascha K?hn, and Hans Hagen. 2005. Non-manifold mesh extraction from time-varying segmented volumes used for modeling a human heart. In EuroVis. Citeseer, 199–206.
[11]
J?rgen Bey. 1995. Tetrahedral grid refinement. Computing 55 (1995), 355–378. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:20829446
[12]
Jules Bloomenthal. 1988. Polygonization of implicit surfaces. Comput. Aided Geom. Des. 5 (1988), 341–355. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:16474404
[13]
Jean-Daniel Boissonnat, David Cohen-Steiner, and Gert Vegter. 2008. Isotopic implicit surface meshing. Discrete & Computational Geometry 39, 1–3 (2008), 138–157.
[14]
Jean-Daniel Boissonnat, Siargey Kachanovich, and Mathijs Wintraecken. 2023. Tracing Isomanifolds in R d in Time Polynomial in d using Coxeter-Freudenthal-Kuhn Triangulations. SIAM J. Comput. 52, 2 (2023), 452–486. arXiv:https://doi.org/10.1137/21M1412918
[15]
Jean-Daniel Boissonnat and Mathijs Wintraecken. 2022. The Topological Correctness of PL Approximations of Isomanifolds. Found. Comput. Math. 22, 4 (aug 2022), 967–1012.
[16]
Kathleen Sue Bonnell, Mark A Duchaineau, Daniel R Schikore, Bernd Hamann, and Kenneth I Joy. 2003. Material interface reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 9, 4 (2003), 500–511.
[17]
Rita Borgo, Paolo Cignoni, and Roberto Scopigno. 2004. Simplicial-based Multiresolution Volume Datasets Management: An Overview. In Geometric Modeling for Scientific Visualization. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, 309–327. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:54075053
[18]
Jan Brandts, Sergey Korotov, Michal K???ek, et al. 2020. Simplicial partitions with applications to the finite element method. Springer.
[19]
Michael Burns, Janek Klawe, Szymon Rusinkiewicz, Adam Finkelstein, and Doug DeCarlo. 2005. Line drawings from volume data. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 24, 3 (2005), 512–518.
[20]
Amit Chattopadhyay, Simon Plantinga, and Gert Vegter. 2012. Certified Meshing of Radial Basis Function Based Isosurfaces. Vis. Comput. 28, 5 (may 2012), 445–462.
[21]
Bruno Rodrigues De Ara?jo, Daniel S Lopes, Pauline Jepp, Joaquim A Jorge, and Brian Wyvill. 2015. A survey on implicit surface polygonization. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 47, 4 (2015), 1–39.
[22]
L. de Figueiredo, A. Paiva, T. Lewiner, and H. Lopes. 2006. Robust adaptive meshes for implicit surfaces. In 2012 25th SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images. IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, CA, USA, 205–212.
[23]
J Ruiz de Miras and Francisco R Feito. 2002. Direct and robust voxelization and polygonization of free-form CSG solids. In Proceedings. First International Symposium on 3D Data Processing Visualization and Transmission. 352–355.
[24]
Tamal Krishna Dey and Andrew G. Slatton. 2013. Localized Delaunay Refinement for Piecewise-Smooth Complexes. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth Annual Symposium on Computational Geometry (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) (SoCG ’13). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 47–56.
[25]
S?ny Diatta, Guillaume Moroz, and Marc Pouget. 2019. Reliable Computation of the Singularities of the Projection in R3 of a Generic Surface of R4. In MACIS 2019 – Mathematical Aspects of Computer and Information Sciences. Gebze-Istanbul, Turkey. https://inria.hal.science/hal-02406758
[26]
Scott Dillard, John Bingert, Dan Thoma, and Bernd Hamann. 2007. Construction of Simplified Boundary Surfaces from Serial-sectioned Metal Micrographs. Visualization and Computer Graphics, IEEE Transactions on 13 (12 2007), 1528–1535.
[27]
Xingyi Du, Qingnan Zhou, Nathan A. Carr, and Tao Ju. 2022. Robust computation of implicit surface networks for piecewise linear functions. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 41 (2022), 1–16. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:249917144
[28]
Tom Duff. 1992. Interval arithmetic recursive subdivision for implicit functions and constructive solid geometry. ACM SIGGRAPH computer graphics 26, 2 (1992), 131–138.
[29]
Laurent Dupont, Michael Hemmer, Sylvain Petitjean, and Elmar Sch?mer. 2007. Complete, exact and efficient implementation for computing the adjacency graph of an arrangement of quadrics. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual European Conference on Algorithms (Eilat, Israel) (ESA’07). Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, 633–644.
[30]
Herbert Edelsbrunner and John Harer. 2002. Jacobi sets of multiple Morse functions. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, Minneapolis (2002), 37–57.
[31]
Gerald Farin. 1986. Triangular bernstein-b?zier patches. Computer Aided Geometric Design 3, 2 (1986), 83–127.
[32]
Michael S Floater. 2015. Generalized barycentric coordinates and applications. Acta Numerica 24 (2015), 161–214.
[33]
Flopine. 2020. ShATI – Cl?. https://www.shadertoy.com/view/wssBDf.
[34]
Paul Louis George, H. Borouchaki, F. Alauzet, P. Laug, A. Loseille, D. Marcum, and L. Mar?chal. 2017. Mesh Generation and Mesh Adaptivity: Theory and Techniques. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, USA, 1–51. arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/9781119176817.ecm2012
[35]
T. Gerstner. 2003. Top-down view-dependent terrain triangulation using the octagon metric. Technical Report. University of Bonn.
[36]
Thomas Gerstner and Renato Pajarola. 2000. Topology preserving and controlled topology simplifying multiresolution isosurface extraction. In Proceedings of the Conference on Visualization ’00 (Salt Lake City, Utah, USA) (VIS ’00). IEEE Computer Society Press, Washington, DC, USA, 259–266.
[37]
Benjamin Gregorski, Mark Duchaineau, Peter Lindstrom, Valerio Pascucci, and Kenneth I. Joy. 2002. Interactive view-dependent rendering of large isosurfaces. In Proceedings of the Conference on Visualization ’02 (Boston, Massachusetts) (VIS ’02). IEEE Computer Society, USA, 475–484.
[38]
Roberto Grosso, Christoph L?rig, and Thomas Ertl. 1997. The multilevel finite element method for adaptive mesh optimization and visualization of volume data. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Visualization ’97 (Phoenix, Arizona, USA) (VIS ’97). IEEE Computer Society Press, Washington, DC, USA, 387–ff.
[39]
Jiateng Guo, Xulei Wang, Jiangmei Wang, Xinwei Dai, Lixin Wu, Chaoling Li, Fengdan Li, Shanjun Liu, and Mark Walter Jessell. 2021. Three-dimensional geological modeling and spatial analysis from geotechnical borehole data using an implicit surface and marching tetrahedra algorithm. Engineering Geology 284 (2021), 106047.
[40]
Mark Hall and Joe Warren. 1990. Adaptive polygonalization of implicitly defined surfaces. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications 10, 6 (1990), 33–42.
[41]
Younis Hijazi, Aaron Knoll, Mathias Schott, Andrew Kensler, and Charles Hansen. 2010. Csg operations of arbitrary primitives with interval arithmetic and real-time ray casting. In Dagstuhl Follow-Ups, Vol. 1. Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik.
[42]
Zhiyang Huang, Nathan Carr, and Tao Ju. 2019. Variational implicit point set surfaces. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 38, 4 (2019), 1–13.
[43]
Kin Chuen Hui and Z.H. Jiang. 1999. Tetrahedra Based Adaptive Polygonization of Implicit Surface Patches. Computer Graphics Forum 18, 1 (1999), 57–68. arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/1467-8659.00302
[44]
Zhongshi Jiang, Ziyi Zhang, Yixin Hu, Teseo Schneider, Denis Zorin, and Daniele Panozzo. 2021. Bijective and coarse high-order tetrahedral meshes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 40, 4 (2021), 1–16.
[45]
Tao Ju, Frank Losasso, Scott Schaefer, and Joe Warren. 2002. Dual contouring of hermite data. In Proceedings of the 29th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques. 339–346.
[46]
Payam Khanteimouri and Marcel Campen. 2023. 3D B?zier Guarding: Boundary-Conforming Curved Tetrahedral Meshing. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 42, 6 (2023), 1–19.
[47]
Byungmoon Kim. 2010. Multi-phase fluid simulations using regional level sets. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 29, 6 (2010), 1–8.
[48]
Dae-Hyun Kim, Ulf Doring, and Beat Bruderlin. 2000. Polygonization of Non-manifolds With the Aid of Interval Operators. ACM Eurographics Workshop on Implicit Surfaces (2000), 145–151. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:14381080
[49]
Maximilian Kohlbrenner, Singchun Lee, Marc Alexa, and Misha Kazhdan. 2023. Poisson Manifold Reconstruction — Beyond Co-dimension One. Computer Graphics Forum 42 (08 2023).
[50]
Igor Kossaczk?. 1994. A recursive approach to local mesh refinement in two and three dimensions. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 55 (1994), 275–288. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:123381194
[51]
Xinghua Liang and Yongjie Jessica Zhang. 2014. An octree-based dual contouring method for triangular and tetrahedral mesh generation with guaranteed angle range. Engineering with Computers 30 (2014), 211–222. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:14861190
[52]
Anwei Liu and Barry Joe. 1995. Quality Local Refinement of Tetrahedral Meshes Based on Bisection. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 16, 6 (1995), 1269–1291. arXiv:https://doi.org/10.1137/0916074
[53]
William E. Lorensen and Harvey E. Cline. 1987. Marching cubes: A high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. In SIGGRAPH, Maureen C. Stone (Ed.). ACM, 163–169.
[54]
Frank Losasso, Tamar Shinar, Andrew Selle, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2006. Multiple Interacting Liquids. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 3 (jul 2006), 812–819.
[55]
Joseph M. Maubach. 1995. Local Bisection Refinement for N-Simplicial Grids Generated by Reflection. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 16, 1 (1995), 210–227. arXiv:https://doi.org/10.1137/0916014
[56]
Nimrod Megiddo. 1984. Linear programming in linear time when the dimension is fixed. Journal of the ACM (JACM) 31, 1 (1984), 114–127.
[57]
Chohong Min. 2003. Simplicial isosurfacing in arbitrary dimension and codimension. J. Comput. Phys. 190, 1 (2003), 295–310.
[58]
William F Mitchell. 2016. 30 years of newest vertex bisection. In AIP Conference Proceedings, Vol. 1738. AIP Publishing.
[59]
Neil Molino, Robert Bridson, Joseph Teran, and Ronald Fedkiw. 2003. A Crystalline, Red Green Strategy for Meshing Highly Deformable Objects with Tetrahedra. 12th Int. Meshing Roundtable, 103–114.
[60]
Bernard Mourrain, Jean-Pierre T?court, and Monique Teillaud. 2005. On the computation of an arrangement of quadrics in 3d. Computational Geometry 30, 2 (2005), 145–164.
[61]
Gregory Nielson and R. Franke. 1997. Computing the separating surface for segmented data. 229–233.
[62]
Th Ottmann, Sven Schuierer, and Subbiah Soundaralakshmi. 1995. Enumerating extreme points in higher dimensions. In STACS 95, Ernst W. Mayr and Claude Puech (Eds.). Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, 562–570.
[63]
Steve Oudot, Laurent Rineau, and Mariette Yvinec. 2010. Meshing volumes with curved boundaries. Engineering with Computers 26, 3 (2010), 265–279.
[64]
Valerio Pascucci. 2004. Isosurface computation made simple: hardware acceleration, adaptive refinement and tetrahedral stripping. In Proceedings of the Sixth Joint Eurographics – IEEE TCVG Conference on Visualization (Konstanz, Germany) (VISSYM’04). Eurographics Association, Goslar, DEU, 293–300.
[65]
Alexander Pasko, Valery Adzhiev, Alexei Sourin, and Vladimir Savchenko. 1995. Function representation in geometric modeling: concepts, implementation and applications. The visual computer 11 (1995), 429–446.
[66]
Carl S. Petersen. 1984. Adaptive contouring of three-dimensional surfaces. Computer Aided Geometric Design 1, 1 (1984), 61–74.
[67]
Carl S. Petersen, Bruce R. Piper, and Andrew J. Worsey. 1987. Adaptive contouring of a trivariate interpolant. Geometric Modeling: Algorithms and New Trends (1987), 385–395.
[68]
Simon Plantinga and Gert Vegter. 2006. Isotopic meshing of implicit surfaces. The Visual Computer 23 (2006), 45–58. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:751474
[69]
Angel Plaza and Maria-Cecilia Rivara. 2003. Mesh Refinement Based on the 8-Tetrahedra Longest- Edge Partition. In Proceedings of the 12th International Meshing Roundtable. 67–78.
[70]
Sundaresan Raman and Rephael Wenger. 2008. Quality Isosurface Mesh Generation Using an Extended Marching Cubes Lookup Table. Computer Graphics Forum 27, 3 (2008), 791–798. arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/j.1467-8659.2008.01209.x
[71]
Aristides AG Requicha and Herbert B Voelcker. 1977. Constructive solid geometry. (1977).
[72]
Mar?a Cecilia Rivara. 1991. Local modification of meshes for adaptive and/or multigrid finite-element methods. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 36 (1991), 79–89. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:120011902
[73]
RI Saye. 2015. An algorithm to mesh interconnected surfaces via the Voronoi interface. Engineering with Computers 31, 1 (2015), 123–139.
[74]
Scott Schaefer and Joe Warren. 2004. Dual marching cubes: Primal contouring of dual grids. In 12th Pacific Conference on Computer Graphics and Applications, 2004. PG 2004. Proceedings. IEEE, 70–76.
[75]
Michael F. W. Schmidt. 1993. Cutting cubesvisualizing implicit surfaces by adaptive polygonization. The Visual Computer 10 (1993), 101–115. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:35201048
[76]
Elmar Sch?mer and Nicola Wolpert. 2006. An exact and efficient approach for computing a cell in an arrangement of quadrics. Computational Geometry 33, 1–2 (2006), 65–97.
[77]
M Haitham Shammaa, Yutaka Ohtake, and Hiromasa Suzuki. 2010. Segmentation of multi-material CT data of mechanical parts for extracting boundary surfaces. Computer-Aided Design 42, 2 (2010), 118–128.
[78]
Barton T. Stander and John C. Hart. 1997. Guaranteeing the topology of an implicit surface polygonization for interactive modeling. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH ’97). ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., USA, 279–286.
[79]
Robert F. Tobler, Thomas Galla, and Werner Purgathofer. 1995. ACSGM – An adaptive CSG meshing algorithm. Technical Report TR-186-2-95-13. Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms, Vienna University of Technology, Favoritenstrasse 9-11/E193-02, A-1040 Vienna, Austria. https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/1995/Tobler-1995-AAC/ human contact: technical-report@cg.tuwien.ac.at.
[80]
Gokul Varadhan, Shankar Krishnan, TVN Sriram, and Dinesh Manocha. 2004. Topology preserving surface extraction using adaptive subdivision. In Proceedings of the 2004 Eurographics/ACM SIGGRAPH symposium on Geometry processing. 235–244.
[81]
Chris Weigle and David C. Banks. 1996. Complex-valued contour meshing. In Proceedings of the 7th Conference on Visualization ’96 (San Francisco, California, USA) (VIS ’96). IEEE Computer Society Press, Washington, DC, USA, 173–ff.
[82]
Kenneth Weiss and Leila De Floriani. 2009. Supercubes: A high-level primitive for diamond hierarchies. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 15, 6 (2009), 1603–1610.
[83]
Kenneth Weiss and Leila De Floriani. 2011. Simplex and Diamond Hierarchies: Models and Applications. Computer Graphics Forum 30, 8 (2011), 2127–2155. arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/j.1467-8659.2011.01853.x
[84]
Hassler Whitney. 1957. Geometric Integration Theory. Princeton University Press.
[85]
Shangyou Zhang. 1995. Successive subdivisions of tetrahedra and multigrid methods on tetrahedral meshes. Houston J. Math 21, 3 (1995), 541–556.
[86]
Yongjie Zhang, Chandrajit Bajaj, and Bong-Soo Sohn. 2005. 3D finite element meshing from imaging data. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 194, 48 (2005), 5083–5106. Unstructured Mesh Generation.
[87]
Yongjie Zhang, Thomas JR Hughes, and Chandrajit L Bajaj. 2008. Automatic 3d mesh generation for a domain with multiple materials. In Proceedings of the 16th international meshing roundtable. Springer, 367–386.
[88]
Yongjie Jessica Zhang and Jin Qian. 2012. Resolving topology ambiguity for multiple-material domains. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 247 (2012), 166–178.
[89]
Tong Zhao, Pierre Alliez, Tamy Boubekeur, Laurent Bus?, and Jean-Marc Thiery. 2021. Progressive Discrete Domains for Implicit Surface Reconstruction. Computer Graphics Forum 40, 5 (2021), 143–156. arXiv:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/cgf.14363
[90]
Yong Zhou, Baoquan Chen, and Arie Kaufman. 1997. Multiresolution tetrahedral framework for visualizing regular volume data. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Visualization ’97 (Phoenix, Arizona, USA) (VIS ’97). IEEE Computer Society Press, Washington, DC, USA, 135–ff.