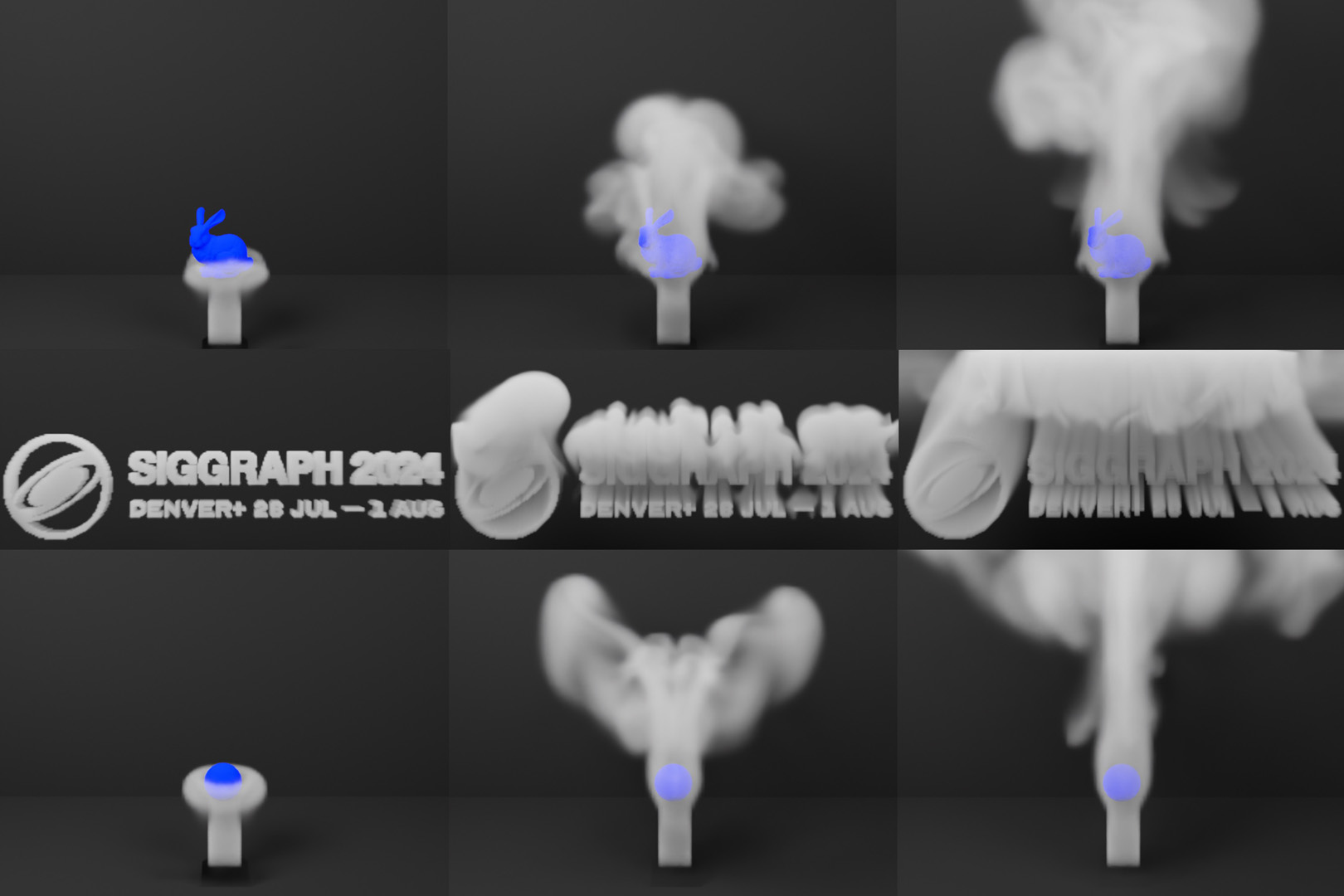
“Velocity-based Monte Carlo Fluids”
Conference:
Type(s):
Title:
- Velocity-based Monte Carlo Fluids
Presenter(s)/Author(s):
Abstract:
We present a velocity-based Monte Carlo fluid solver with operator splitting and walk-on-boundary boundary handling, which overcomes the limitations of its existing vorticity-based counterpart. Our method can readily incorporate various techniques drawn from conventional non-Monte Carlo methods, such as buoyancy effects, divergence control capabilities, and numerical dissipation reduction methods.
References:
[1]
Christopher Batty, Florence Bertails, and Robert Bridson. 2007. A fast variational framework for accurate solid-fluid coupling. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, 3 (jul 2007), 100?es. https://doi.org/10.1145/1276377.1276502
[2]
Blender Foundation. 2023. Blender 4.0. Blender Institute, Amsterdam. http://www.blender.org
[3]
J.U. Brackbill and H.M. Ruppel. 1986. FLIP: A method for adaptively zoned, particle-in-cell calculations of fluid flows in two dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 65, 2 (1986), 314?343. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9991(86)90211-1
[4]
Robert Bridson. 2015. Fluid simulation for computer graphics. A K Peters/CRC Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315266008
[5]
Wesley Chang, Venkataram Sivaram, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, Toshiya Hachisuka, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Tzu-Mao Li. 2023. Parameter-Space ReSTIR for Differentiable and Inverse Rendering. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2023 Conference Proceedings (Los Angeles, CA, USA) (SIGGRAPH ?23). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 18, 10 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3588432.3591512
[6]
Todd F. Dupont and Yingjie Liu. 2007. Back and Forth Error Compensation and Correction Methods for Semi-Lagrangian Schemes with Application to Level Set Interface Computations. Math. Comp. 76, 258 (2007), 647?668. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40234399
[7]
S. Ermakov and A. Sipin. 2009. The ?walk in hemispheres? process and its applications to solving boundary value problems. Vestnik St. Petersburg University: Mathematics 42 (09 2009), 155?163. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063454109030029
[8]
Ronald Fedkiw, Jos Stam, and Henrik Wann Jensen. 2001. Visual Simulation of Smoke. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques(SIGGRAPH ?01). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 15?22. https://doi.org/10.1145/383259.383260
[9]
Bryan E. Feldman, James F. O?Brien, and Okan Arikan. 2003. Animating suspended particle explosions. ACM Trans. Graph. 22, 3 (jul 2003), 708?715. https://doi.org/10.1145/882262.882336
[10]
Bryan E. Feldman, James F. O?Brien, and Bryan M. Klingner. 2005. Animating gases with hybrid meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3 (jul 2005), 904?909. https://doi.org/10.1145/1073204.1073281
[11]
Fan Feng, Jinyuan Liu, Shiying Xiong, Shuqi Yang, Yaorui Zhang, and Bo Zhu. 2023. Impulse Fluid Simulation. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics 29, 6 (jun 2023), 3081?3092. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2022.3149466
[12]
Nick Foster and Dimitri Metaxas. 1996. Realistic Animation of Liquids. Graphical Models and Image Processing 58, 5 (1996), 471?483. https://doi.org/10.1006/gmip.1996.0039
[13]
Nick Foster and Dimitris Metaxas. 1997. Modeling the Motion of a Hot, Turbulent Gas. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques(SIGGRAPH ?97). ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., USA, 181?188. https://doi.org/10.1145/258734.258838
[14]
Charles P. Frahm. 1983. Some novel delta?function identities. American Journal of Physics 51, 9 (09 1983), 826?829. https://doi.org/10.1119/1.13127
[15]
Francis H Harlow. 1962. The particle-in-cell method for numerical solution of problems in fluid dynamics. Technical Report. Los Alamos National Lab. https://doi.org/10.2172/4769185
[16]
Francis H. Harlow and J. Eddie Welch. 1965. Numerical Calculation of Time?Dependent Viscous Incompressible Flow of Fluid with Free Surface. The Physics of Fluids 8, 12 (12 1965), 2182?2189. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1761178
[17]
V Hnizdo. 2011. Generalized second-order partial derivatives of 1/r. European Journal of Physics 32, 2 (jan 2011), 287. https://doi.org/10.1088/0143-0807/32/2/003
[18]
Chenfanfu Jiang, Craig Schroeder, Andrew Selle, Joseph Teran, and Alexey Stomakhin. 2015. The Affine Particle-in-Cell Method. ACM Trans. Graph. 34, 4, Article 51 (jul 2015), 10 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/2766996
[19]
James T. Kajiya. 1986. The Rendering Equation. SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 20, 4 (aug 1986), 143?150. https://doi.org/10.1145/15886.15902
[20]
Alexander Keller. 1997. Instant Radiosity. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques(SIGGRAPH ?97). ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., USA, 49?56. https://doi.org/10.1145/258734.258769
[21]
Patrick Mullen, Keenan Crane, Dmitry Pavlov, Yiying Tong, and Mathieu Desbrun. 2009. Energy-preserving integrators for fluid animation. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, Article 38 (jul 2009), 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/1531326.1531344
[22]
Mervin E. Muller. 1956. Some Continuous Monte Carlo Methods for the Dirichlet Problem. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics 27, 3 (1956), 569 ? 589. https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177728169
[23]
Mohammad Sina Nabizadeh, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Albert Chern. 2021. Kelvin Transformations for Simulations on Infinite Domains. ACM Trans. Graph. 40, 4, Article 97 (jul 2021), 15 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3450626.3459809
[24]
Mohammad Sina Nabizadeh, Stephanie Wang, Ravi Ramamoorthi, and Albert Chern. 2022. Covector Fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 41, 4, Article 113 (jul 2022), 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3528223.3530120
[25]
Rahul Narain, Jonas Zehnder, and Bernhard Thomaszewski. 2019. A Second-Order Advection-Reflection Solver. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact. Tech. 2, 2, Article 16 (jul 2019), 14 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3340257
[26]
Art B. Owen. 2013. Monte Carlo theory, methods and examples. https://artowen.su.domains/mc/.
[27]
Sang Il Park and Myoung Jun Kim. 2005. Vortex Fluid for Gaseous Phenomena. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation (Los Angeles, California) (SCA ?05). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 261?270. https://doi.org/10.1145/1073368.1073406
[28]
Steven G. Parker, James Bigler, Andreas Dietrich, Heiko Friedrich, Jared Hoberock, David Luebke, David McAllister, Morgan McGuire, Keith Morley, Austin Robison, and Martin Stich. 2010. OptiX: A General Purpose Ray Tracing Engine. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 4, Article 66 (jul 2010), 13 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/1778765.1778803
[29]
Ziyin Qu, Xinxin Zhang, Ming Gao, Chenfanfu Jiang, and Baoquan Chen. 2019. Efficient and conservative fluids using bidirectional mapping. ACM Trans. Graph. 38, 4, Article 128 (jul 2019), 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3306346.3322945
[30]
Damien Rioux-Lavoie, Ryusuke Sugimoto, T?may ?zdemir, Naoharu H. Shimada, Christopher Batty, Derek Nowrouzezahrai, and Toshiya Hachisuka. 2022. A Monte Carlo Method for Fluid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 41, 6, Article 240 (nov 2022), 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3550454.3555450
[31]
Karl K. Sabelfeld. 1982. Vector algorithms in the Monte-Carlo method for solving systems of second-order elliptic equations and Lame?s equation. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR 262, 5 (1982), 1076?1080. https://www.mathnet.ru/eng/dan45069 (In Russian).
[32]
Karl K. Sabelfeld and Nikolai A. Simonov. 1994. Random Walks on Boundary for Solving PDEs. De Gruyter, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110942026
[33]
Rohan Sawhney and Keenan Crane. 2020. Monte Carlo Geometry Processing: A Grid-Free Approach to PDE-Based Methods on Volumetric Domains. ACM Trans. Graph. 39, 4, Article 123 (aug 2020), 18 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3386569.3392374
[34]
Rohan Sawhney, Bailey Miller, Ioannis Gkioulekas, and Keenan Crane. 2023. Walk on Stars: A Grid-Free Monte Carlo Method for PDEs with Neumann Boundary Conditions. ACM Trans. Graph. 42, 4 (aug 2023), 22 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3592398
[35]
Rohan Sawhney, Dario Seyb, Wojciech Jarosz, and Keenan Crane. 2022. Grid-Free Monte Carlo for PDEs with Spatially Varying Coefficients. ACM Trans. Graph. 41, 4, Article 53 (jul 2022), 17 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3528223.3530134
[36]
Andrew Selle, Ronald Fedkiw, ByungMoon Kim, Yingjie Liu, and Jarek Rossignac. 2008. An Unconditionally Stable MacCormack Method. Journal of Scientific Computing 35, 2 (2008), 350?371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-007-9166-4
[37]
Nikolai A Simonov. 2008. Walk-on-Spheres Algorithm for Solving Boundary-Value Problems with Continuity Flux Conditions. In Monte Carlo and Quasi-Monte Carlo Methods 2006. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 633?643. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74496-2_38
[38]
Jos Stam. 1999. Stable Fluids. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques(SIGGRAPH ?99). ACM Press/Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., USA, 121?128. https://doi.org/10.1145/311535.311548
[39]
Ryusuke Sugimoto, Terry Chen, Yiti Jiang, Christopher Batty, and Toshiya Hachisuka. 2023. A Practical Walk-on-Boundary Method for Boundary Value Problems. ACM Trans. Graph. 42, 4, Article 81 (jul 2023), 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3592109
[40]
Ingo Wald. 2023. OWL – The Optix 7 Wrapper Library. http://owl-project.github.io
[41]
Hang Yin, Mohammad Sina Nabizadeh, Baichuan Wu, Stephanie Wang, and Albert Chern. 2023. Fluid Cohomology. ACM Trans. Graph. 42, 4, Article 126 (jul 2023), 25 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3592402
[42]
Ekrem Fatih Y?lmazer, Delio Vicini, and Wenzel Jakob. 2022. Solving Inverse PDE Problems using Grid-Free Monte Carlo Estimators. arxiv:2208.02114 [cs.GR]
[43]
Jonas Zehnder, Rahul Narain, and Bernhard Thomaszewski. 2018. An Advection-Reflection Solver for Detail-Preserving Fluid Simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 37, 4, Article 85 (jul 2018), 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3197517.3201324
[44]
Yongning Zhu and Robert Bridson. 2005. Animating Sand as a Fluid. ACM Trans. Graph. 24, 3 (jul 2005), 965?972. https://doi.org/10.1145/1073204.1073298