“TwinCam: Omni-directional Stereoscopic Live Viewing Camera for Reducing Motion Blur during Head Rotation” by Tashiro, Fujie, Ikei, Amemiya, Hirota, et al. …
Conference:
- SIGGRAPH 2017
-
More from SIGGRAPH 2017:


Type(s):
Entry Number: 24
Title:
- TwinCam: Omni-directional Stereoscopic Live Viewing Camera for Reducing Motion Blur during Head Rotation
Presenter(s):
Description:
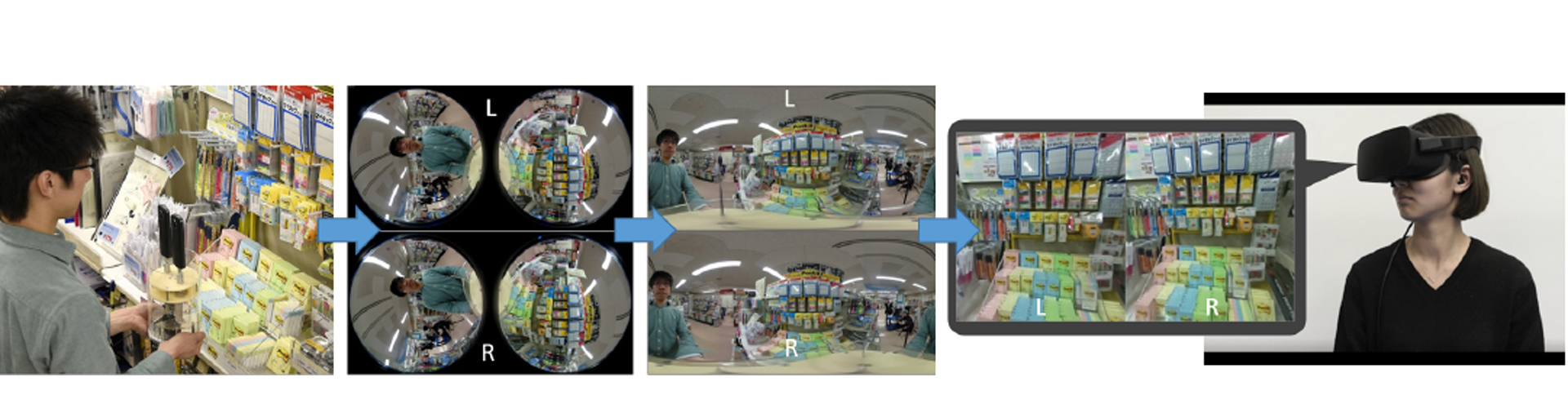
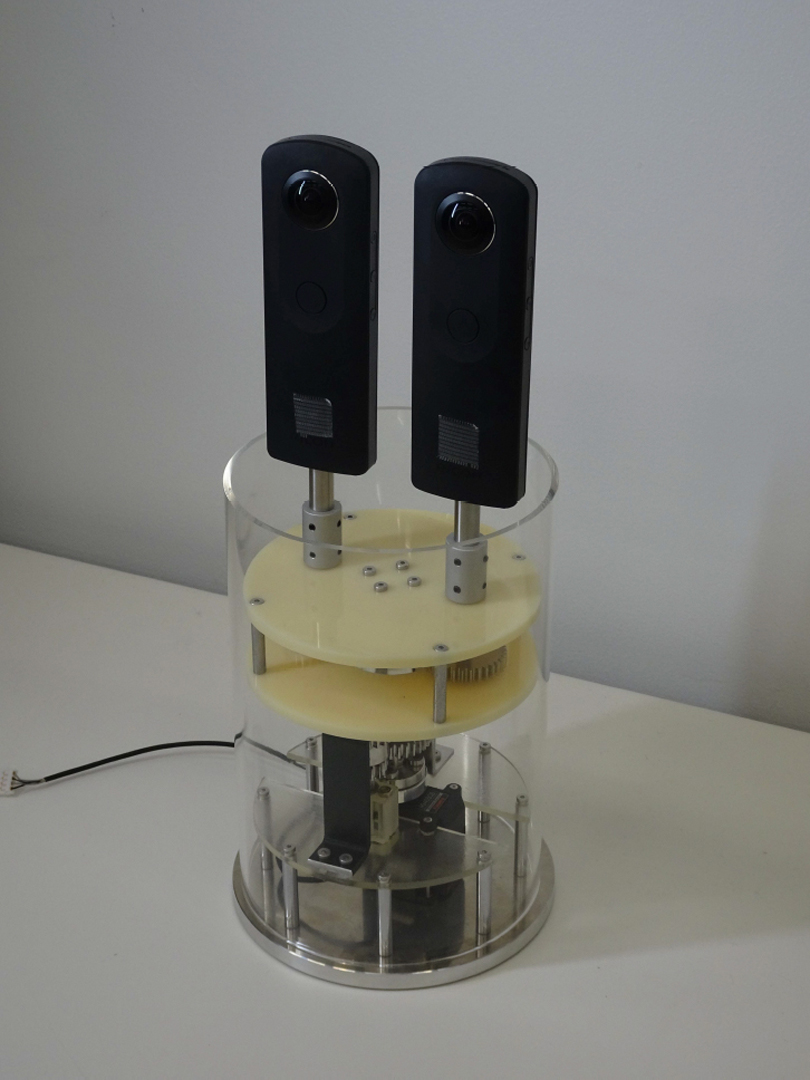
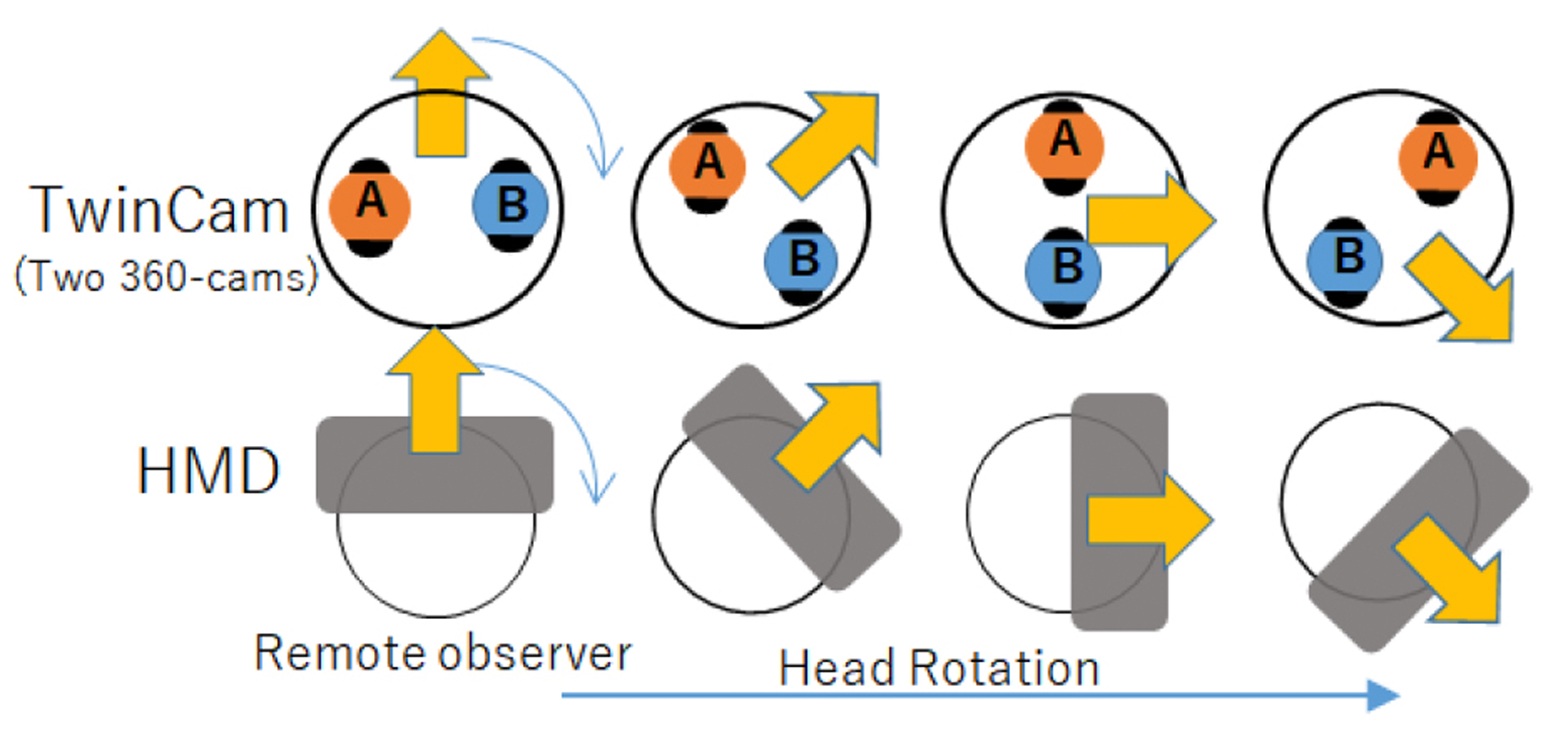
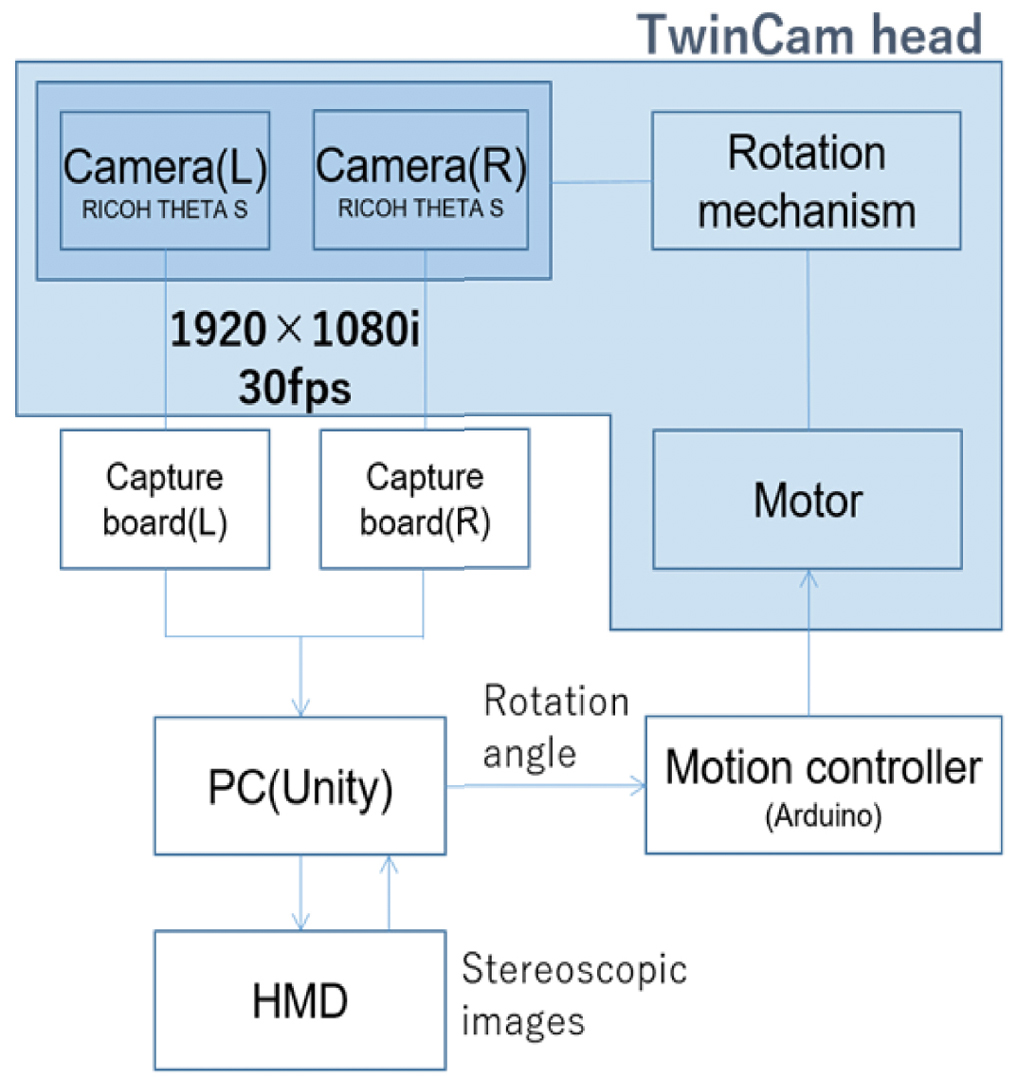
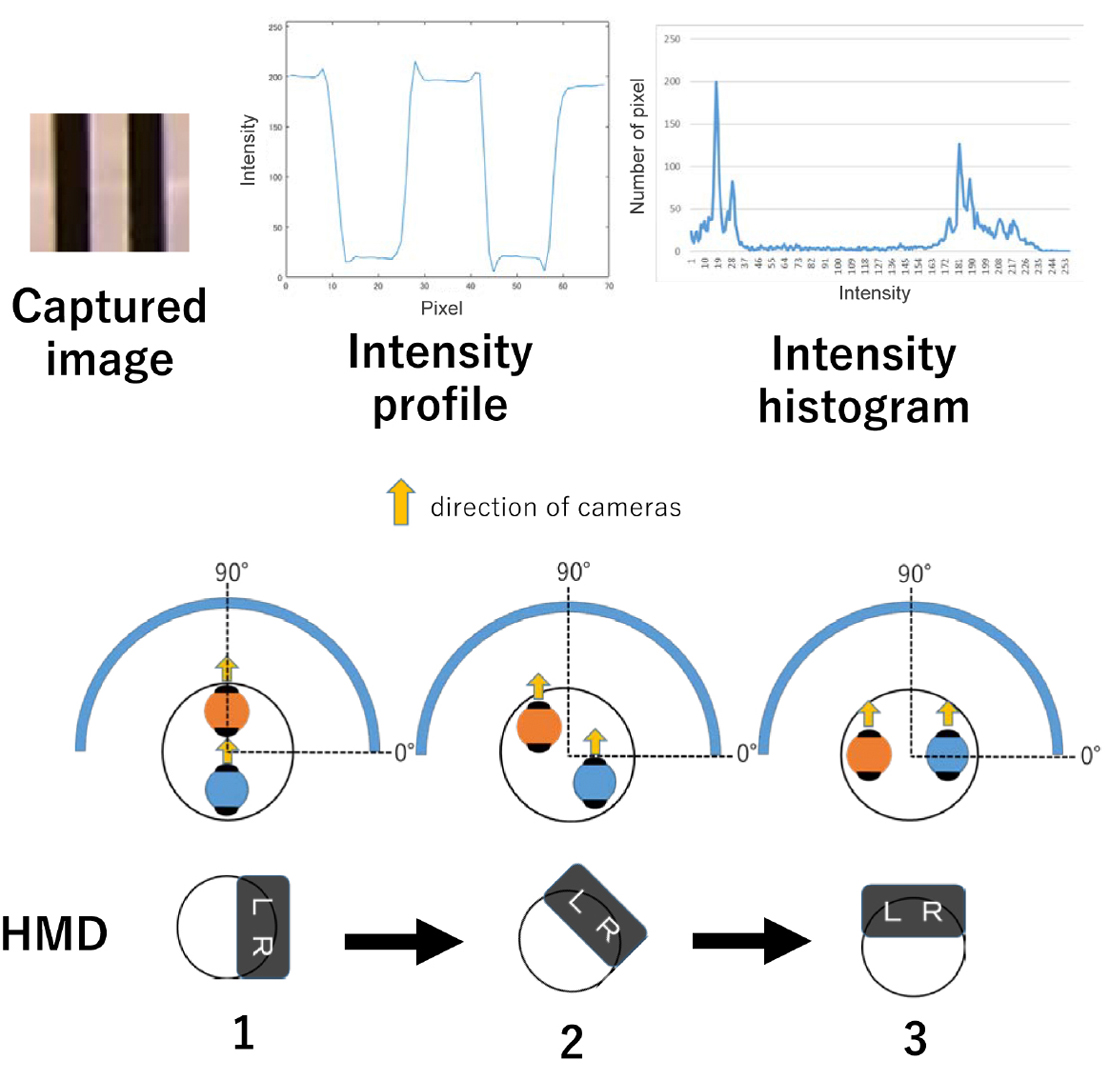
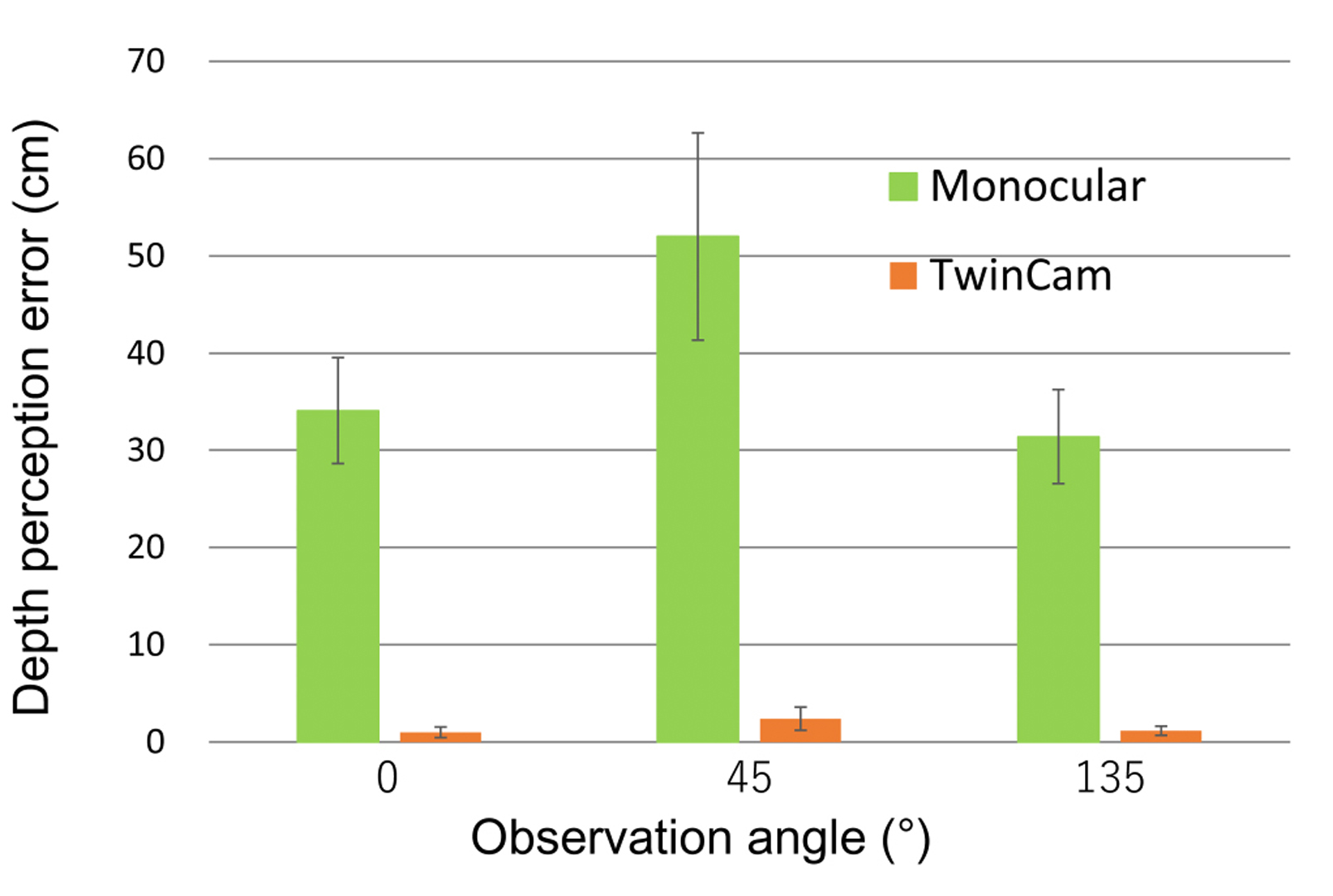
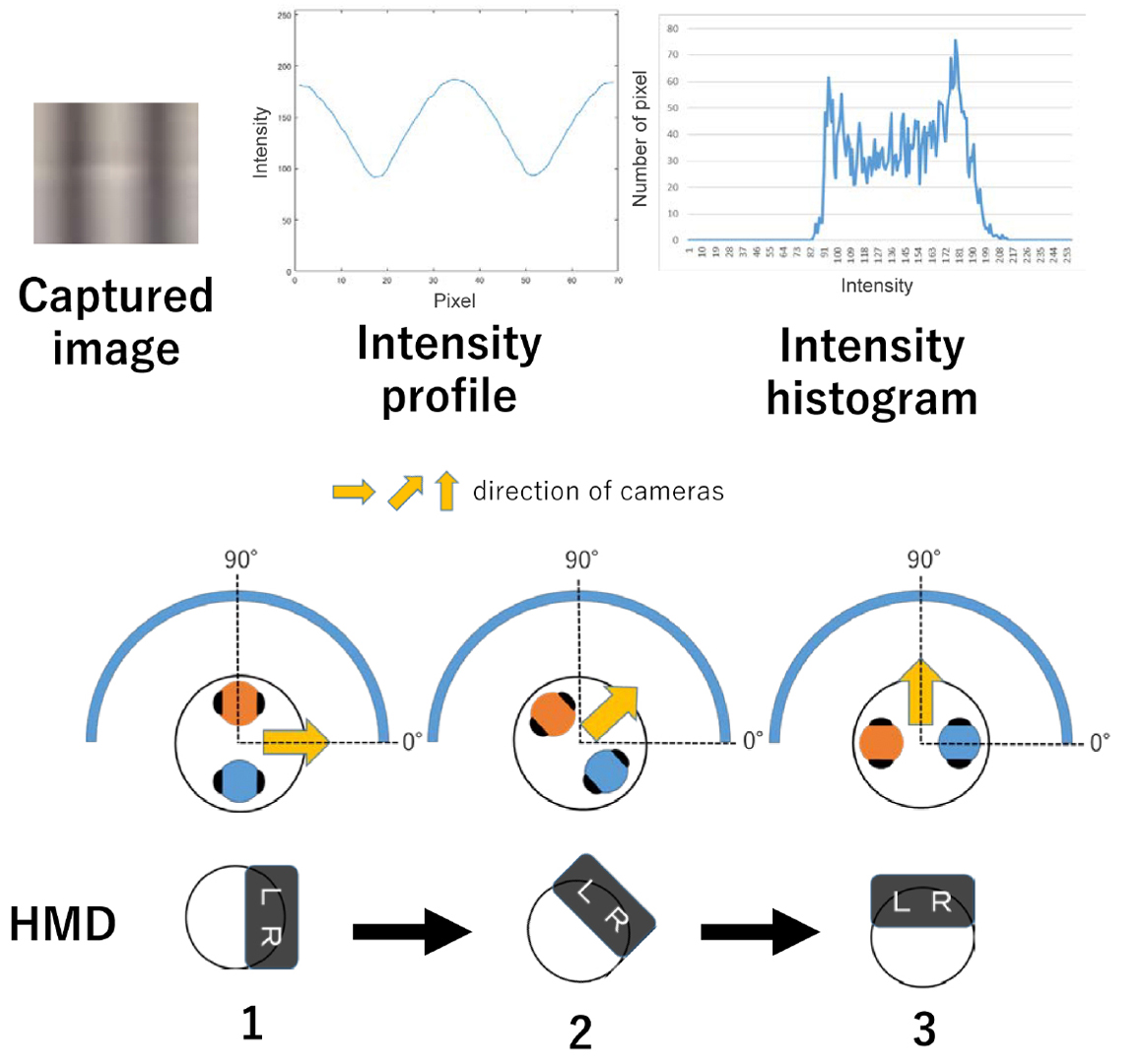
We developed an omni-directional stereoscopic live viewing camera (TwinCam) system to reduce the motion blur and latency during head rotation of a remote user wearing a head mounted display (HMD). The TwinCam system consists of two omni-directional live cameras (THETA S, Ricoh), rotation mechanisms with a motor, an image control PC, and an HMD. The camera base rotates synchronously with the azimuth angle of the HMD that the observer is wearing, while each camera lens is at a constant azimuth angle. This camera configuration greatly reduces image flow on the CMOS image sensor in the camera, and eventually, the motion blur on the HMD screens when the HMD rotates. The apparent image latency during the head rotation is minimized by the buffered image. A user study demonstrated that both reduced motion blur and compensated latency were effective in reducing the virtual reality (VR) sickness symptoms.
References:
Amit Agrawal, Yi Xu, and Ramesh Raskar. 2009. Invertible Motion Blur in Video. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3, Article 95 (July 2009), 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/1531326. 1531401
Robert S. Kennedy, Norman E. Lane, Kevin S. Berbaum, and Michael G. Lilienthal. 1993. Simulator Sickness Questionnaire: An Enhanced Method for Quantifying
Keyword(s):
- Stereoscopic live image
- motion blur
- latency
- telepresence
Additional Images:

Acknowledgements:
This work was supported by MIC SCOPE Project (#141203019) and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) 26240029, MEXT, Japan.